"What a temperamental one!" - we are talking about an emotional and loud-voiced person expressing his thoughts accompanied by violent gestures. “Look, with character!” - relatives shake their heads over the child, flatly refusing to eat semolina or cut their hair.
What is temperament? And how does he differ from character? Or maybe it's the same thing? Let’s try to figure it out, reinforcing our reasoning with the thoughts of outstanding psychologists.
Definition
Before figuring out how one differs from the other, and what is primarily temperament or character, we will define both concepts.
It is customary to call temperament in psychological science the totality of a person's psychodynamic qualities that manifest themselves in the reactions of his psyche, as well as how intense they are, what their speed and pace are. By another definition, one can choose this: temperament is a person’s nature-determined tendency towards a certain type of behavior. It depends on this type whether the person is emotional, sensitive to the effects of the outside world, impulsive or restrained, sociable, introverted, is it easy for him to communicate with unfamiliar people, or it causes difficulties.

As for the psychodynamic features of human behavior, they are determined by higher nervous activity. Nervous processes have three main properties, identified by Academician I.P. Pavlov. To them he attributed strength, poise and mobility. It is their combinations that provide the basis for the four types of temperament.

It’s rare when you can meet pure choleric or melancholic, much more often in a person mixed properties of two types, but with one prevailing.
To identify the individual's belonging to one or another type, one should take into account the manifestations of such properties of temperament in him:
- Sensitivity - that is, an indicator of what should be the smallest impact on a person from outside so that he reacts to it;
- reactivity - the degree to which an involuntary reaction to any effect from the inside or outside is manifested - criticism (both constructive and not so), loud cry, offensive phrases;
- activity - an indicator of the degree to which a person is involved in the outside world and intensively acts in it, how persistent, focused and determined;
- what is more important for a person — external or internal factors or his aspirations and tasks, depends on the ratio of reactivity and activity in a person;
- the balance of plasticity and rigidity shows whether it is easy for a person to adapt to the external influence of circumstances or if he behaves inertly;
- depending on the pace of the reaction, one determines how quickly a person experiences mental reactions, as well as speech speed, an abundance of gestures, and a sharpness of mind;
- the scale of extraversion-introversion characterizes the factors on which a person’s reaction and actions depend - on an extrovert, they are directly related to external momentary impressions, and on an introvert, to images and thoughts that arise in his mind and have a connection with past and future events;
- emotional excitability shows what minimal effect on a person is necessary for an emotional reaction to occur, as well as the amount of time necessary for its occurrence.

Given all of the above properties, psychologists distinguish 4 main types of temperament.
Sanguine
An individual with this type of temperament has a high reactivity, however, it balances the activity. To what he is interested in, he reacts vigorously and soon, his facial expressions are quite intense, as well as gestures. It immediately shows him in what mood he is; he is not able to hide his reaction to a situation or person. He gives a strong reaction to all the events taking place with him - and no matter how significant it is. It is difficult for him to notice quiet sounds and weak light, in such conditions (in poor lighting) it is hard for him to work.
Sanguine people are very efficient and have a large supply of energy, which gives them the opportunity to do business without getting tired. Persons with this type of temperament know how to concentrate, easily switch from one task to another, have a flexible mind and resourcefulness. Sanguine people speak quickly and quickly think, highly flexible - thanks to this they do not focus on one emotion for a long time. A child with this type of temperament will find friends in the new class faster than anyone, it is easy for him to get to know and communicate. A person with a sanguine temperament has a high personal discipline, with age learns to control the manifestations of emotions. Most often, sanguine people are extroverts, as they respond to external events, and not to the processes taking place inside them.
It is not typical for such people to worry about what happened for a long time, to look for the causes of what happened and to do self-digging. Thanks to the plastic psyche, it is easier for a sanguine person to switch to new events and impressions than anyone else.

Choleric
With sanguine choleric people combines high reactivity, low sensitivity. However, the balance between activity and reactivity is broken, so choleric people are short-tempered, unbridled, lack of patience and restraint. Despite the fact that choleric is most often an extrovert, he is very persistent, not inclined to easily "switch" from target to target. Choleric people tend to get stuck on getting what they want due to low ductility and high inertness (compared to sanguines). It takes time to shift the choleric's attention to another task.

Phlegmatic
Phlegmatic people are highly active, but reactivity is low. In addition, these people are extremely stingy with the manifestation of emotions - it is hard to wait from them as a flood of laughter, and a manifestation of sadness. Most often, representatives of the phlegmatic type of temperament look unperturbed. During a general panic, it is phlegmatic people who remain calm, which often helps others to calm down. Facial expressions and gestures are also stingy, interesting stories from such personalities can not be expected.
Phlegmatic people find it difficult to switch their attention, especially if you need to do it quicklyin addition, a sharp change of scenery also unsettle them. However, what phlegmatic people can’t refuse is a huge supply of energy and high working capacity. Understanding the task, these "workhorses" can literally turn mountains. In addition, the difference between phlegmatic people is in the ability to thoroughly study the questions posed, to get to the point, which makes them excellent narrow specialists. The patience of individuals with this type of temperament is truly gigantic; it is very difficult to get them crazy. Phlegmatic people are polite and restrained, calm and do not lose their temper, even in the most uncomfortable situations. Most of these people are introverts, it does not matter for them what is happening around them, the processes that are going on inside them are much more important. Most often, people think phlegmatic people are strange because of their restraint and equanimity, but those friends who have known them for a long time, “time-tested” love and value phlegmatic people precisely because of their unwaveringness and stability.

Melancholic
People with this type of temperament are highly sensitive, while being low reactive and very inert. Such an explosive mixture makes melancholic people very touchy and sensitive. People of such a warehouse have a quiet and unexpressive voice, facial expressions and gestures. Constant doubts about one's own strengths lead to the fact that the melancholic gives in to difficulties that arise on the way. Melancholy people have low working capacity, easily tired, their attention is difficult to focus on one task. External processes affect melancholic people, but only in terms of reflecting on their internal experiences, which is why most representatives of this type of temperament are introverts.

The way a person works productively is connected precisely with the type of his temperament. And the choice of a profession or occupation should be made, given this factor. For example, in works requiring thoughtfulness, an analytical mindset, calmness, measuredness, some “stubbornness”, corrosiveness, there is no specialist better than a phlegmatic person. But as for activities that require constant communication with people or work in multitasking mode, a sanguine will be indispensable here. Choleric people are great for the role of leader, they are good at “lighting up” subordinates with ideas. However, over the chief choleric should be someone who will restrain his exuberant nature, not allowing him to turn into a tyrant. A melancholic works well only in an atmosphere of complete psychological comfort, it is very easy to hurt him, so the boss should be especially attentive and sensitive with him.

By the way a person reacts to events taking place with him, one can judge his temperament. Someone stoically endures all the hardships of everyday life, and someone disheartened even the weather outside the window. Someone, having discovered that he had put on a sweater inside out, will laugh at himself, while someone will be embarrassed. It’s very difficult for some people to get out of the rut with the usual little things like a broken zipper on the jacket or turning off the light without warning. And someone is prone to flashing like a match from everything that does not go according to his plan. So the main types of temperament are manifested.

Psychologists have proved that a person is born with a "ready" temperament, and with the course of life he remains unchanged.Why this happens is not yet clear.
It is wrong to call the type of temperament determining in relation to other psychological differences of a person. The personality is multifaceted, and the type of temperament is just one of its components. Today, the theory of temperaments is supplemented by such definitions as inhibition of the nervous system and its excitement. Psychology with biochemistry and genetics also find out how the type of temperament is determined by hormones (serotonin, melatonin, dopamine), as well as other biochemical mediators.
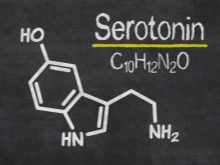
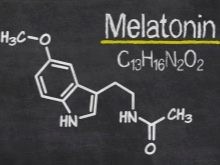
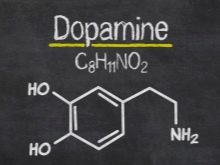
It should be noted that the state of the psyche caused by various circumstances of life is really interconnected with the type of temperament. But the way these states will be manifested outside is the result of education. Of course, it is more difficult for a choleric to control flashes of emotions, to show patience and restraint, and for a melancholic to politely communicate with colleagues, without panic, however, if you have desire and desire, this is possible.

Main differences
How a person behaves depends on what type of temperament he belongs to. It is on the “field” of temperament that the character of a person is formed, and his abilities also develop. That is, if we consider the ratio of concepts, then temperament is a kind of “base”, and character is a “superstructure”. If a person is well aware of not only his merits, but he also understands the shortcomings, it will be easy for him to turn in his favor, applying mental compensation.
The experience gained by a person in life plays a role. For example, a choleric who “loses” the same situation several times in a row with the same manner of his behavior (quick-tempered and unrestrained), respectively, can draw conclusions and lose, suppress in himself these properties, becoming inert and uninitiated. Nevertheless, serious life tests, as a rule, “tear off the masks”, and a person shows exactly those qualities that he tried to suppress, behaves in the way it is laid down in him. Choleric is prone to nervous breakdowns, fits of rage, a melancholic can also easily get a psychological trauma, but it will manifest itself in a different way. Phlegmatic, on the contrary, will fall into a stupor, losing the ability to more or less quickly respond to what is happening.

Quite a long time ago, academician I.P. Pavlov proved that, although personality traits are directly interconnected with its neurophysiological organization, they are not determined by it. His experiments showed that nervous activity can be changed. The formation of a human character and style of behavior depends not only on innate qualities, but also on everything that influences, has influenced, or will continue to influence a person throughout his life.

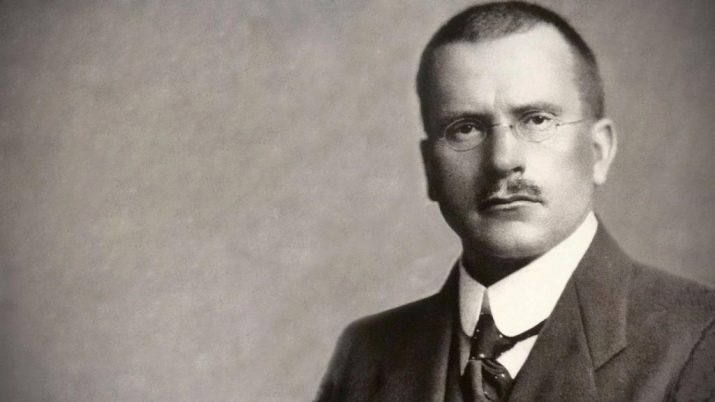
Modern psychologists attribute temperament to personality traits, despite the fact that it is due to nature. The division of people into extroverts and introverts is more often used, this scale was introduced by Carl Jung, an outstanding scientist-psychologist. G. Eisenkom, who developed a personality testing system. It has been established that in people with predominant introversion, the cerebral cortex is more highly active. Extroverts have other strengths - they are sociable, attentive to what is happening outside, active and assertive.

Interconnection
Now consider what the relationship between temperament and character, how much it is mutual, what is the difference between these concepts. The first is not decisive for the second, but, of course, both are closely interconnected.
- The manifestation of dynamic character traits depends on the type of temperament. For example, a sociable sanguine is completely different from a sociable choleric.
- The type of temperament affects how character traits develop. Moreover, development can occur both due to the properties of temperament, and contrary to them.
- Bringing up the necessary character traits in a child, one should take into account his type of temperament and, depending on him, choose a method of exposure.
- Having developed certain character traits, one can control the manifestations of those properties of temperament that can harm in a particular situation.

A combination of personality traits (in each case, individual), expressing how a person relates to reality and how this manifests itself in his behavior, is usually called character in psychology.

There is a connection of character with the type of temperament and the level of human abilities, and this connection is reciprocal. Each of these three components affects the rest. Depends on the type of temperament, how a person displays his character traits, and on the strength of character depends on whether the individual will "give free rein" to his destructive properties of temperament. A person’s abilities are also associated with temperament (strength of efficiency, methodicality, attentiveness, flexibility and sharpness of mind), and with character (ability to work in a team, organization, creativity, ability to take initiative).

An interesting video about temperament and character is waiting for you below.










