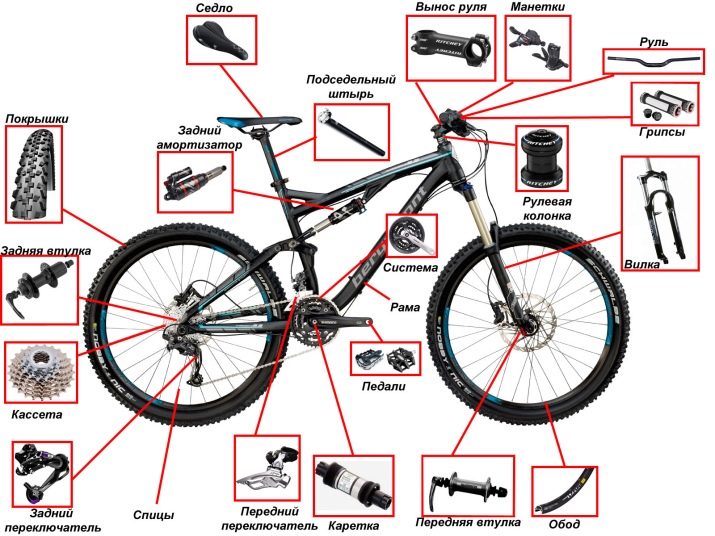
About how the bicycle is arranged, many know from childhood, but in general terms. For example, this: it consists of what we see, that is, of wheels, a frame, wings, pedals, a chain and a steering wheel. In our article, we will dwell in more detail on the anatomy of bikes, find out the name of its main parts and their purpose, and also give recommendations on choosing the basic structural elements of a two-wheeled vehicle.
Types of bicycle frames
A description of the structure of bicycles is best started with a review of the frames, since it is this element that is fundamental in the structure of a two-wheeled vehicle. Depending on the design, it can be open or closed. A distinctive feature of closed frames is the straight upper pipe, in the open version it is located at the bottom and has a slightly curved shape - this frame is designed specifically for female users.
The vast majority of modern velor is made of aluminum, but you can find products from other materials. Each of them has its pros and cons.
So, steel structures are functional, reliable and practical only if they are made of chromium-molybdenum alloys. All other types of steel, unfortunately, leave much to be desired: they are voluminous, heavy and do not differ in durability.


Aluminum bribes with its low weight therefore, frames of this metal are universally used for the production of racing bikes. At the same time, aluminum is more susceptible to destruction, and most often this happens unexpectedly.


But titanium frames are not afraid of either cold or heat. They are not afraid of aggressive acid-base solutions, which is why their use differs in duration.
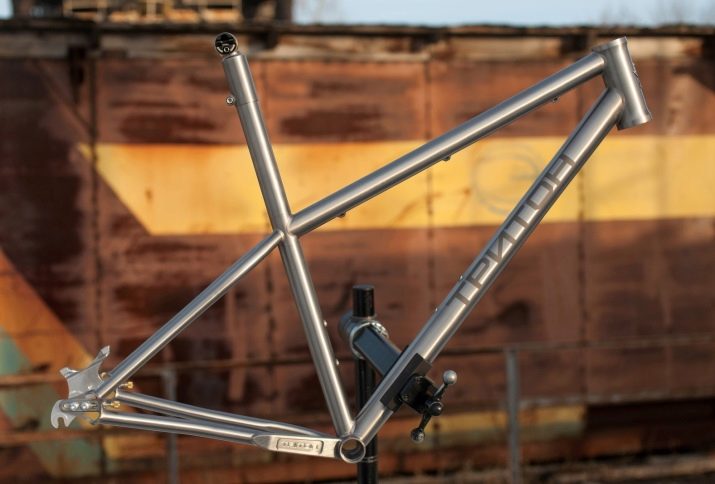

Magnesium is another light metal, but it is susceptible to corrosion.Therefore, it is very important for the user to ensure that chips and scratches do not appear on the bicycle frame.
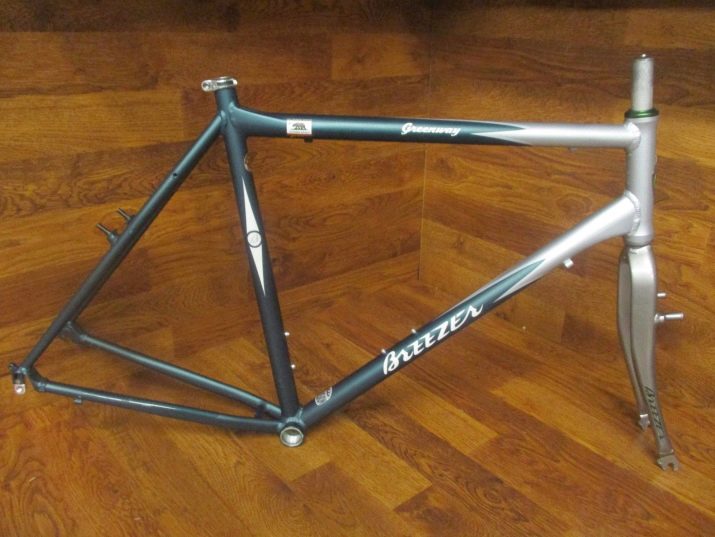

The most durable and lightweight carbon frames. But a sharp point strike can cause them quite serious damage - such bicycles should be handled as carefully as possible. Carbon production is based on the use of high technology and is expensive, therefore, there are not many companies offering carbon fiber-framed bikes in this segment.


Depending on the features of the shock absorption mechanism of the rear wheel, the bicycle frame can be active or passive. Passive is understood as the complete absence of separate hinges designed for use under increased load. Passive cushioning is the result of the natural flexibility of the material from which the bicycle frame is made. These bikes are called hardtails.
A design with active shock absorption assumes the presence of moving parts (hinges or a hinge system), usually called pendants.
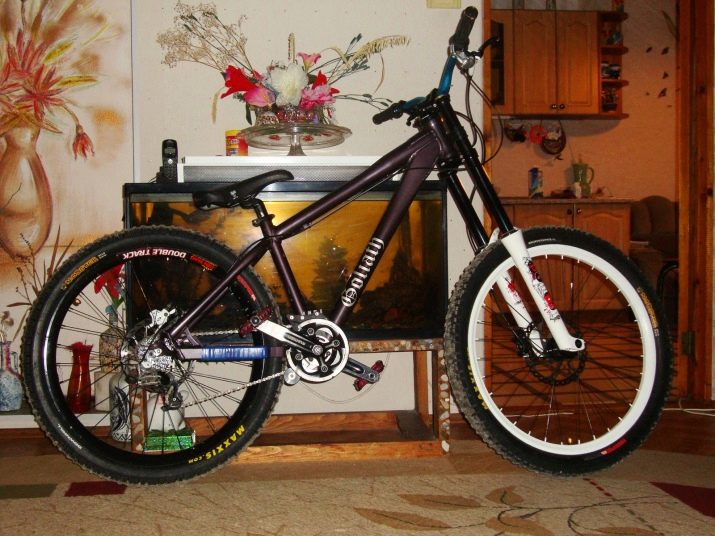

Active frame bicycles are divided into single-lever and multi-lever. A single-link suspension is characterized in that the movement of the wheel in this case is made around one point, which remains static regardless of the characteristics of the suspension travel. In a multi-link suspension, in contrast, the wheel spins around a point that can change its position.
Operation of this or that transport equipment directly depends on the planned type of driving. For example, when creating a frame for cross-country, manufacturers tried to make it extremely ergonomic and lightweight, which provides riders with the opportunity to take a comfortable position for free pedaling without unnecessary physical energy when moving excess weight.
It is for this reason that the driving frames in this style are most often made under hardtails in order to obtain savings on the mass of the shock absorber and all elements in order to strengthen the bike frame.


Wheel arrangement
Bicycle wheels are lightweight, but fairly durable designs. They distribute the energy of movement, so with the help of their rotation they allow you to hold the bicycle frame exactly in an upright position. For the most part, bicycles have rear-wheel drive when the rear wheel provides movement and the front wheel is driven.
Any bicycle wheel includes several structural parts.
- Sleeve. This is the central part, including the axle, bearings and rim. The sleeve is responsible for the occurrence and maintenance of sufficient torque for the bike to move. The internal layout of the rear hubs is slightly more complicated than that of the wheels located in front, since they take part in the forced unwinding of the entire wheel.
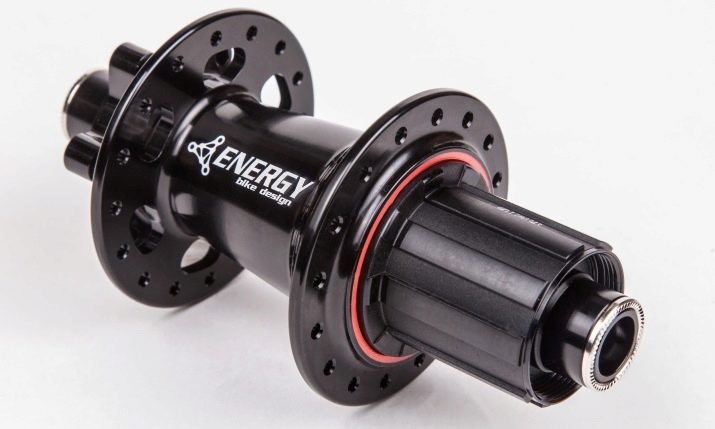

- Rim. The metal ring into which the knitting needles are inserted. This element determines the necessary resistance of the wheel to any dynamic loads and mechanical damage. The rim is usually made of alloys and coated with a coating of chromium.
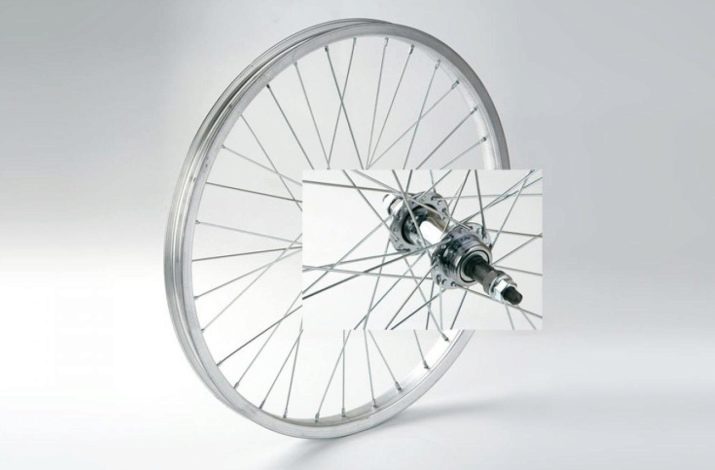

- Bicycle tires. They include a camera as well as tires. The chamber is made of hollow rubber, and is pumped with air until the necessary pressure is created. It interacts with the external environment through a nipple through which air enters the tires through a pump or compressor.
To effectively protect the integrity of the camera from pointed needles, a special rubberized flipper is attached to the inner surface of the rim.


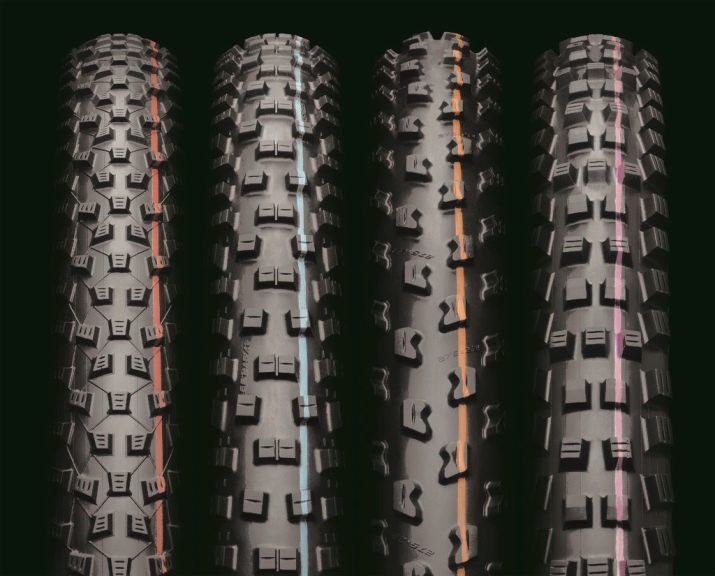
The outer surface of the tire is called the tire, and its components are the sides, sidewalls, as well as the tread. Depending on the operational capabilities of the bike, there are several types of tires:
- slicks and half slicks - such options are optimal for flat tracks, so they are most often installed on roadways;
- road - these include tires with a medium-sized pattern; similar models are mounted on mountain bikes;
- hybrid - such tires are effective both in off-road conditions and on a flat track, although they are inferior in patency to more aggressive options.




To make the bike noticeable in the dark, a luminous plate of a bright orange color - a reflector is fastened on the needles. According to traffic rules, reflectors must be present on all types of bikes.
Tire characteristics largely determine the overall impression of the ride, so their choice should be given special attention. First you need to evaluate the size of the element, as a rule, it is indicated by two pairs of numbers: the first one determines the diameter of the wheel, and the second indicates the width of the tire itself. To give an example: a tire marked 26x2.1 is used for standard wheels measuring 26 inches with a width of 2.1 inches. Wherein the wider the tire, the more firmly it will hold the bike on bends, although it will lose significantly on the roll.


Keep in mind: the less pronounced the tread pattern, the harder the tire is designed for. Thus, the most "toothy" pattern will be acceptable for use on clay, off-road and dirt, but for denser and harder coatings, you can opt for rubber with a flatter pattern and softened compound.


A compound is a mixture of several types of rubber, which provides the necessary wear resistance, strength and grip characteristics of tires.

Management and depreciation systems
One of the basic elements of the device is cushioning mechanism, which determines the mitigation of shock loads on the frame and other bicycle structures due to damping of vibrations. The depreciation system includes several components at once.
Traditionally, the front glass of the bicycle frame is mounted inside the fork through the steering shaft, and a wheel is mounted in its ears. In order to ensure unimpeded rotation in the corners, a steering column is mounted in the glass.
Why do we need a steering wheel, we think there is no need to explain, but its technical and operational parameters - the width, amount of rise, apsvipu and beksvipu - you need to pay special attention. The last two provide the necessary bend of the steering wheel back and up.
We draw special attention to the fact that a wider steering wheel allows the user to give maximum control over his vehicle and thereby contribute to increasing control efficiency, but at the same time they slow down this control a little.


Rising the steering wheel ensures the correct position of the rider: the lower it is, the more aggressive the rider is forced to take. Apsvip and backsvip parameters are individual, often they help the simplest metal structure to transform into a physiologically comfortable element in the entire bike scheme. When buying a suitable steering wheel, it is best to go to a sports store and hold the offered products in your hands, which will allow you to get an idea of exactly which operational parameters will be optimal for you.
Bends are inserted along the edges of the steering wheel - special plugs that help reduce injuries. Do not underestimate the risk that the ends of the steering wheel carry - situations where users damage their stomach or legs, happen very often.

To prevent hands from slipping during the ride, the design provides rubberized handles (they are called grips).
In modern models, lock-on grips are installed, which differ in the presence of locking rings at the ends. This solution greatly facilitates their installation and does not allow slips to slip. Simpler models hold only due to friction.


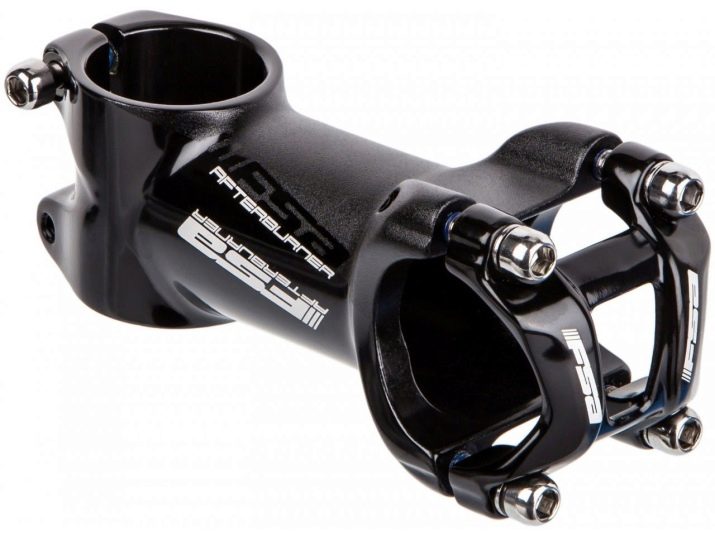
The extension is a part that provides the necessary removal of the steering wheel from the frame. It is fixed to the adjustment pipe.On different bike models, adjustable or rigid outriggers can be placed. On simple bikes they are not.

The saddle is mounted in the central part of the frame, it can vary in height, so users can always choose a comfortable fit. The width of the saddle varies depending on the characteristics of the bike. Let's say on road bikes they are a little wider than on mountain bikes (MTB).


Transmission and brake design
This is something without which no two-wheeled transport will simply go. The transmission is a very complex unit, which consists of a wide variety of mechanisms, namely:
- carriages;
- asterisks
- pedals;
- connecting rod mechanism;
- bike chain;
- tricks;
- various speed switches.


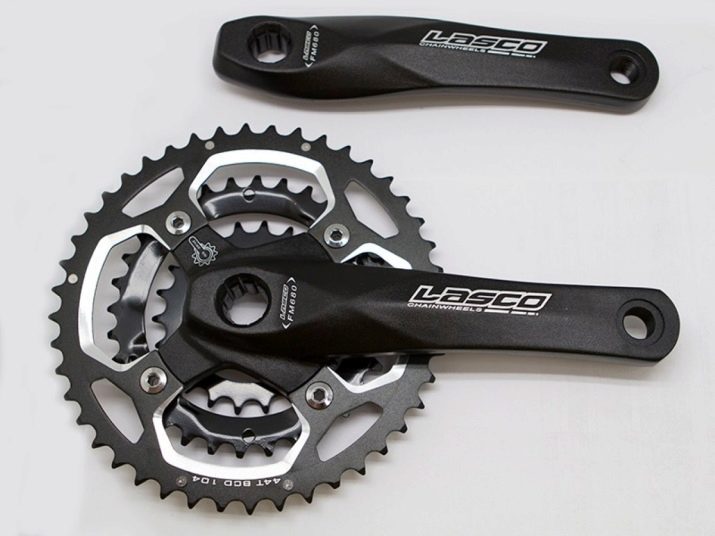
The carriage assembly is located at the bottom of the bicycle frame. It connects the connecting rods to the front sprockets. The carriage causes an unobstructed course due to the fixed bearings and the through axis attached to them.
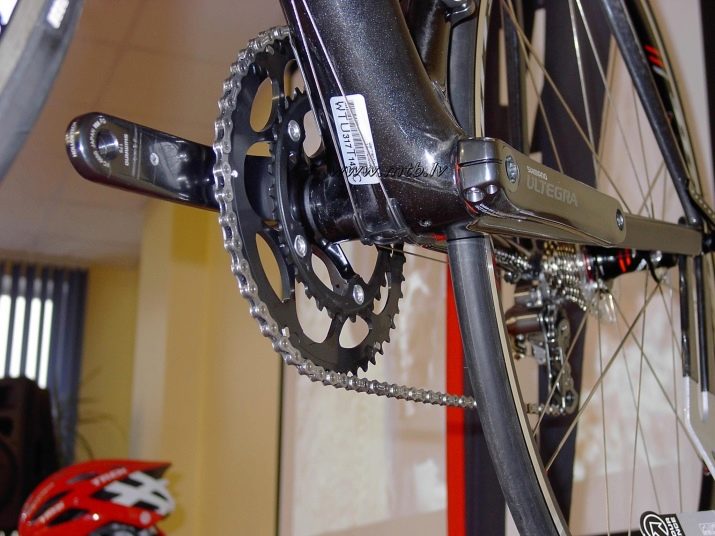

The connecting rods are the most important elements for the interaction of the carriage with the pedals. They can have several mounting methods: either square or slotted.

The pedals functionally represent the necessary support for the legs, through them the physical effort passes to the connecting rods. They can be performed in several ways.
- Classic (they are also called platforms). Such pedals are installed on the base level bikes. In this case, the user can ride in absolutely any shoe - here the clutch with the pedal is carried out through friction.
- Contact. Such pedals have special inserts that can be intended exclusively for specialized shoes.
- Extreme Mounted on sports bikes, they are distinguished by the presence of clamps, a rather wide surface, and also an impressive thickness.



The rear sprockets of the speed bike are fixed to the rear wheel hub. Traditionally, each front sprocket has a couple of rear ones. When driving, small sprockets provide increased transmission, while larger ones provide lower transmission.
The connecting part between them is a chain. Its movement is made through the switches, which, in turn, are controlled through the shifters on the steering gear.


The most important structural element of any two-wheeled vehicle are brakes. In the absence or malfunction of the brake system, it is strictly forbidden to bring vehicles to the streets.
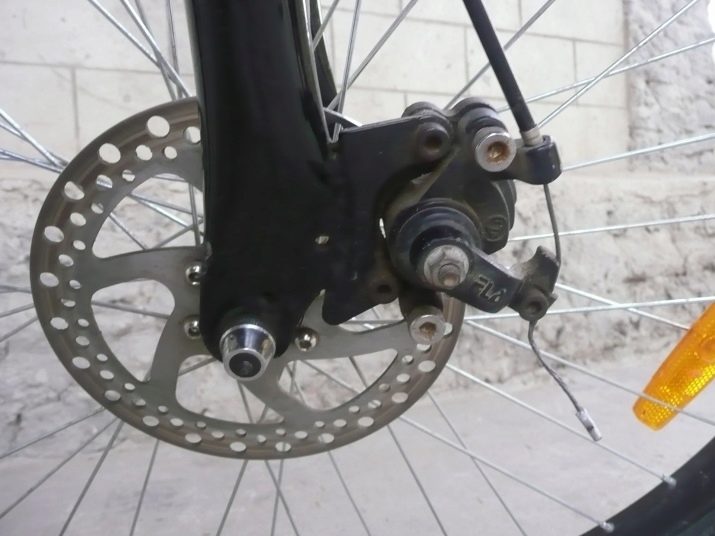

Modern brake mechanisms for bikes have several classes.
- Bypass. They represent small clamping devices with blocks. Usually they have only one mount.
- Disk. In this design, the pads are fixed to the disc by pressing the handle.
- Drum. This version of the brake system is now considered obsolete. In such bicycles, the drum attaches to the rear hub and creates an interaction between the pads by pedaling. In order to prevent the mechanism from turning in vain, a stopper is installed in it. The braking performance of such a system is lower than that of the first two, however, it is optimal for budget bikes.



Component Overview
When buying a bike, users often do not pay the necessary attention to spare parts, since the layout of the bike in most cases is provided by the manufacturer.
However, you will certainly come across a choice of spare parts in the following situations:
- if you decide to assemble the bike from scratch yourself;
- if you need to replace worn out parts that have failed;
- if you decide to upgrade, replacing low-quality components with more functional ones.
When choosing any parts It is very important to ensure their maximum compliance: you must know exactly their size and mounting option, as well as other technical features.
To make the right choice, you can simply take a worn part with you or rewrite all of its parameters.Before buying, it will be useful to clarify which varieties of a particular part can be used for each particular bike.

When choosing components, it is best to opt for products of well-known brands, the quality of which is time-tested. The vast majority of riders buy brand spare parts for their two-wheeled vehicles Shimano or Sram. In the bicycle parts segment, these two brands are considered monopolists.


Good quality possess components of firms Sunday, as well as Fit and United - They are most often chosen by lovers of extreme skiing. For high-speed bikes, you can recommend accessories from Cinelli.


Choosing a well-known brand, you will pay more, but the cost will more than pay off with the practicality and durability of the part.
See below for more information on bicycle design.










