In the absence of long-term memory, information would not linger in the structure of the human brain and would disappear without a trace each time. In this case, the formation of the skills necessary for life is impossible.
What it is?
The definition of the term long-term memory (DVP) is recorded in many dictionaries. Neurophysiology focuses on the ability of all living organisms with a central nervous system to learn and remember material.
Knowledge is stored in memory for a long time without quantitative and qualitative losses due to neural connections due to complex biochemical processes in the body.
In psychology, this level of memory is considered the highest mental function, giving the opportunity to accumulate, hold, preserve and reproduce a huge amount of knowledge and skillsacquired over a long time.
The memory structure consists of sensory, short-term and long-term levels. These types are distinguished by the mechanisms by which the material is remembered by the volume and duration of information storage. The characteristic of the three-component model of coordinated working blocks is reduced to the initially involved sensory register with information storage for 1 second, sending material to a short-term storage for 20-30 seconds and placing knowledge for a long time in the archive.

Long-term memory is at the heart of 3 processes: coding, archiving and extraction of knowledge. The work of memory begins with memorization, then archiving and updating takes place, that is, the extraction of information from memory by reproduction.The volume of fiberboard and the duration of storage are unlimited. It all depends on the coding method, systematization of the material and the subject who perceives and remembers the information.
Two factors influence the placement of perceived material in the storage of brain structures: activity and meaningfulness. Activity consists in a strong connection of knowledge with certain emotions, the emergence of a conscious goal and the motivation to include remembering information in the process of activity.
The indicators of meaningfulness are the control in the process of memorization, analysis and structuring of the necessary knowledge, the search and selection of important thoughts, the establishment of logical connections between parts of the text, repeated repetition.

Long-term memory firmly retains the perceived material. She represents a kind of repository of knowledge in brain structures. It can be called a reliable archive in which all information is divided into many categories and laid out on shelves.
Warehouse with accumulated material has unlimited capacity.
The presence of memory indicates the personal integrity of a person. Loss of memory leads to the collapse of the personality. Violation arises from the inability to correctly encode and reproduce information.
In addition, memory may be impaired due to amnesia. In the first case, regular training helps. Forecasts in the second situation cannot be predicted. Amnesia can result in stress or trauma.
The causes of long-term memory impairment can be physiological characteristics: asthenia, damage to the central nervous system and brain, condition after a stroke, impaired intelligence, alcohol or drug intoxication. The cause of mental disorders is psychological trauma, depression, neurosis, overwork, chronically poor mood, strong emotional and mental stress.
Domestic causes are usually associated with poor nutrition, lack of sleep, excessive intellectual and physical stress, lack of regimen and improper planning of the day.

The following symptoms indicate a violation of DVP:
- difficulties with the conscious memorization of poems, dates, exam material;
- confusion, violation of causal relationships;
- decreased performance and mental abilities;
- inability to concentrate and concentrate, inattention;
- memory losses;
- social maladaptation;
- forgetfulness in everyday situations;
- distraction and confusion.

Long-term memory contributes to improving the quality of human life, achieving success in various fields.
A bit of history
The idea of distinguishing between short-term and long-term retention of information in memory appeared in the 19th century. The very mechanism of transferring information from a short-term storage to a long-term archive was described in the middle of the 20th century and is still the subject of controversy among researchers.
In 2011, an interesting discovery was made. Scientists at one of the medical centers in the United States were able to recreate the entire neural circuit, which is the basis of DVP. It turns out that when the incoming signal lasts for 10 minutes, strong compounds are formed that do not break up for a long time and can remain in the structures of the brain throughout a person’s life.

Comparison with short-term memory
All memory components function in concert. Knowledge for long-term storage comes from the information capacity held by short-term memory (KVP). Two-stage memorization has a certain biological meaning. Random and unnecessary information is screened out and does not go to storage in fiberboard.
Non-essential information does not overload the brain. The perceived material is emotionally experienced, reconstructed and placed in the storage of brain structures for a long time.
When comparing two types of memory are observed differences in the duration of storage of the material, the strength of its retention and information capacity. Information is stored in the FEC for 20-30 seconds, after which some part of the material is lost forever, and the other part of the successfully encoded information is stored in the FEC archive, where it is stored from several minutes to many years. KVP encodes information visually or acoustically, DVP encodes information on a semantic level.
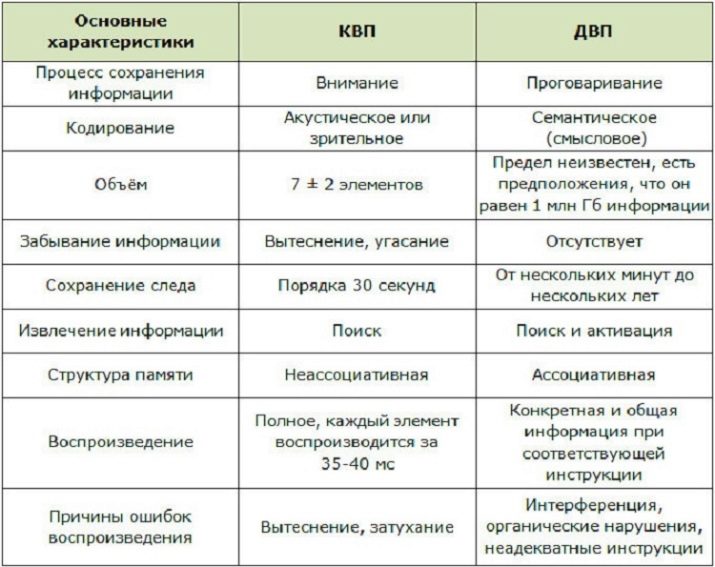
The mechanism for storing information in the case of CWP is attention, in the case of fiberboard - speaking. The structure of the KVP is characterized by the absence of associations, the fiberboard is characterized by associativity. Information playback errors in the first type of memory arise due to its crowding out and fast attenuation. The causes of erroneous reproduction with long-term memory can be organic disorders, inadequate instructions and interference.
Varieties
All types of fiberboard are closely related. An autobiographical view can preserve an event of one’s own life for a long time. In some cases, this species is correlated with episodic memory, when a separate fragment is fixed and sent to the brain archive for a long time. Reproductive view makes it possible to recall and reproduce a previously saved object.
Associative memory relies on functional relationships between remembered objects.
The totality of hereditary reactions that are transmitted from generation to generation through genes refers to biological, generic, gene memory. Genetic memory is designed to store information about ancestors at an unconscious level. It is believed that such information remains for life in a long-term storage of brain structures.
By the criterion of accessibility of memory, implicit and explicit memory is distinguished.
Implicit
Unconscious long-term memory level hidden and not aware of by man. The individual does not make volitional efforts and mental stress to remember. It would seem information forever forgotten is unexpectedly retrieved from the archive at the right time in life.
People typing regularly on a computer do not remember the key order until they start typing. The fingers themselves know where the keys are. And a person does not have conscious access to this knowledge.

The implicit memory trace has great power. People with amnesia due to concussion, traumatic brain injury, or emotional shock can forget their past lives. But motor and professional skills remainbecause the information has not been erased from the implicit part of the storage.
Explicit
This type of memory is associated with consciousness and the desire to purposefully keep and preserve the accumulated experience. So remember the rules, formulas, dates, learn foreign languages. The individual, if necessary, extracts knowledge from memory and voices.

There are 2 types of explicit memory: episodic and semantic.
- Episodic type associated with the memories of a particular individual, his personal life experience acquired in the distant or recent past.
- Semantic (historical) memory connected with the accumulated experience of all mankind. Any theoretical knowledge, rules, mathematical formulas, historical dates and events are directly related to this type of memory.
Diagnostics
There are various test methods for identifying how developed an MDF is in an individual.
The first technique is based on memorizing words that are not logically interconnected. Each word must be numbered. Subjects receive 2 lists with 10 words. Children from 6 to 12 years old need only 1 list. Words can be written on a blackboard or printed on separate pieces of paper. You can read them aloud, without allowing subjects to write them down.
For adults, the list is read 2-3 times, for children 4-5 times.

Sample word lists.
List No. 1:
- wizard;
- screen;
- boat;
- recipe;
- ball;
- wallet;
- dinner;
- gold;
- circus;
- conscience.
List No. 2:
- lily;
- ballet;
- Isle;
- poetry;
- square;
- psychic;
- air;
- freedom;
- sadness
- chocolate.
After attentive listening or reading it is necessary to write down words on paper from memory, preferably in the same order. Then the subjects are distracted by another activity. After 30 minutes, the words are again listened or read, then reproduced.
The next day and after a week, the procedure is repeated with a single reading or listening to the lists. The results of 4 procedures are obtained by the formula: C = B: A x 100, where C is the coefficient of long-term memory, B is the number of correctly reproduced words, A is the total number of words.

Indicators in the range of 75-100 indicate a high level of fiberboard, 50-75 - an average level, 30-50 - a low level, 1-29 - a very low level.
The second technique is designed to remember the semantic text. The essence of the technique is similar to the previous technique, but the text is not read aloud. Examples of texts are distributed to each subject. The main ideas highlighted in the text should subsequently be reproduced.
This technique is used to diagnose long-term memory in adolescents from 13 years old and adults. The test results are obtained by the same formula, the only difference is that here B is the number of correctly reproduced thoughts, A is the total number of selections in the text.

Sample text.
How many people, so many characters. It turns out that rain can also show its burrows and temperament. What is RAIN? These are ATMOSPHERIC SEDIMENTS, ARISING IN THE CLOUDS AND DROPING ON THE EARTH AS A LIQUID DROP WITH A MEDIUM DIAMETER FROM 0.5 TO 7 MM.
The best in the world is SUMMER WARM RAIN. It resembles a carefree childhood, when the whole village BABY RUNS Barefoot in the wet grass. Sometimes a shower is suddenly falling upon us. Often it reaches 100 mm / h and is accompanied by a storm. About such rain, we say: “FLATS AS FROM A BUCKET”. Due to heavy rainfall, our clothing sticks to the body. Where to hide from him?
IN COLD AUTUMN DAYS LONG LONG RAIN. We look out the window and dream of an early end to this COUNTERNOUNCY WEATHER. But it happens that a FINE RAIN RAIN sprinkles with a few drops of a person and stops, as if pondering what to do next. Maybe he is afraid of something or is shy? Such a rain REMINDS A WONDERFUL SENSE OF THE FIRST LOVE. But here the LAST DROP fell, LIKE A Tear.
How to develop?
Develop memory is necessary throughout life. This is necessary in order to avoid Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Peak and memory failures in old age. Cognitive function of the brain is plastic, so it lends itself well to development and training.
The bulk of the material should be divided into parts, blocks and structure it.

You can improve memory using various techniques:
- Aivazovsky’s method involves detailing each image;
- Cicero's method makes it possible to sort all the information in the archive of the brain;
- memorizing lyrics, songs, poems;
- associative memory games;
- solving Scandinavian and Japanese crosswords;
- unraveling logical computer puzzles;
- verbal-logical methods, alphanumeric code, various associative connections, methods of "places" and "hangers" in mnemonics;
- training attention and thinking through specific exercises.

To preserve excellent memory, experts recommend lead an active and healthy lifestyle, eat right, provide yourself with a good sleep, spend more time in the fresh air, play sports, avoid excessive loads and stressful situations, observe the daily routine and develop intelligence by reading books, playing chess and other ways.

You can learn more about the development of memory from the video below.