The current business reality is that only 15% of medium and large-sized entrepreneurs seeking to strengthen their market position achieve the goal. It is for this reason that the relevance of business etiquette increases by several times, since non-compliance with its standards, among other reasons, often leads to the breakdown of useful business relations.

General principles of business correspondence ethics
In a broad interpretation of ethics, they mean a set of general principles aimed at regulating social relations. Accordingly, the ethics of business relations considers issues related to the accepted order and style of interaction in the business sphere.
Detailing the ethical aspects of business relations is business etiquette, including, for example, the negotiation procedure, rules of corporate conduct, business traditions and rituals, elements of subordination, manners and styles of communication and writing, as well as issues of correctness in dealing with partners and business colleagues.
The significance of ethics and etiquette, as its integral part, lies in the fact that the regulatory framework that has arisen as a result of long-term practice greatly simplifies communication, creating a clear and accessible context in the business sector that allows one to correctly achieve goals and save time significantly.
In other words, we are talking about a special algorithm for solving business problems that makes it possible to set and successfully achieve the desired business goals rationally and without conflict. The level of ownership of this algorithm allows you to draw direct conclusions about the degree of professionalism of a business partner or opponent in a business dispute.


In this context, it is important to adhere to the following general principles:
- punctuality everywhere and in everything;
- compliance with information security;
- sound altruism;
- a favorable image appropriate to the business environment;
- Correct oral and written language;
- following the rules of business speech culture.

Types of business correspondence are diverse and, with a certain degree of conventionality, they can be divided into two main varieties:
- interstate - between state organizations, foreign missions and officials (various notes, memoranda and other forms) - elements of diplomatic relations;
- commercial - letters of semi-official status used in the field of business relations between institutions and organizations.

Principles of writing a letter
The style of writing a service letter, despite linguistic and some traditional differences, has a certain general basis and a group of establishments developed by established practice. For example, a number of protocol requirements, determined by the position of the sender and the addressee, are based on the initial settings for mutual respect and correctness. Therefore, regardless of the type of document, structurally, it must necessarily contain the following elements:
- appeal (official status of the addressee);
- compliment (polite ending of the letter);
- signature;
- date (day, month, year and place of writing the message);
- sender's address (surname, official status, address are placed at the top or bottom of the 1st page of the letter).


In addition, there are a number of provisions directly related to letters:
- business letters are set out on letterheads or sheets of paper exclusively on their front side;
- pagination is made in Arabic numerals;
- messages are executed in hard copy;
- erases and corrections are not allowed in the body of the document;
- the document is folded inward;
- the waiting time for a response to a letter is no more than ten days.

A business message should have an express purposeful focus and contain one question, and the whole meaning of the text should be completely and completely subordinate to its content, whether it is a proposal for a transaction, a commercial request, or simply relevant information.
Logic and conciseness, the absence of any “lyrical” digressions are the main characteristics of efficiency.

Typology of Business Letters
The classification of business messages is diverse and depends on their functionally targeted orientation. For example, letters are:
- informing;
- reminiscent of;
- invitations
- information reviews;
- orders;
- accompanying;
- other types.


In commercial correspondence, the most typical are:
- inquiries;
- offers;
- orders;
- complaints;
- letters of guarantee.

As one of the forms of business communication, in the strict sense of the word, letters are divided into 2 types - business and private-official.
By business include correspondence, which runs among organizations and institutions. A private-official letter is a message that is sent to an institution by a private person, or, conversely, by an institution - to a private person.

Correspondence Requirements
There are a number of business correspondence rules.
- The letter should stimulate the emergence of business interest in the recipient, clearly and on the basis of convincing evidence to show the benefits of partnerships and the inappropriateness of breaking partnerships. The text should be incentive, motivating for cooperation.
- The manifestation of excessive personal emotions in a business letter is not the best way to prove your case and solve a problem.
- In order to avoid overloading and clogging of the text of the letter, one should avoid any figurative comparisons, metaphors, allegories and hyperbolas.
- For a clear and concise presentation of the topic, it is better to use simple sentences, avoiding particulars and excessive detail. The main idea of the message should be supported by exclusively relevant arguments, which are usually placed in the attachments to the letter (diagrams, graphs, digital data).
- The text should highlight paragraphs, each of which, representing an independent thought, begins with a new line.
One paragraph should occupy no more than 4 lines, because when reading longer paragraphs, the text seems to merge, and the main idea of the message is lost. A paragraph is considered normal, including 2-3 sentences.


- The business written message should not use descriptive adjectives, unnecessary clarifications and details. At the end of writing, it is advisable to check the document and eliminate phrases that do not carry relevant semantic content.
- Literacy is a basic element of text. The presence of spelling and other errors in the message is unacceptable.
- Indication of the subject of the letter is required. The topic in the documents should be reflected briefly and succinctly, this saves time when reading and positively characterizes the sender. If the letter is sent by e-mail and contains particularly important information, it should be equipped with a special “flag” available in the electronic service.
- Good readability of the text is provided by Arial or Times New Roman fonts with an average font size. If there is a special need, it is possible to highlight key ideas in italics or bold.


- In the text, it is useful to use subtitles (3-4), which provide an easier understanding of the text.
- Enumerations, lists and lists are better to draw up using special markers.
- Corporate identity template (scheme) is an excellent indicator of efficiency and objectivity in business communication. It is especially appropriate in the corporate aspect, because it allows you to stand out in a favorable light and to comply with the established officiality.
In an email, it’s best to optimize the template for different screen resolutions.


Business Message Structure
The structure of the business message is typical. Traditionally, it contains:
- introduction;
- the main part;
- conclusion.

The introduction summarizes the purpose of the letter. The main part describes the essence of the issue. In conclusion, it is desirable to summarize the content of the main part, for example, in the form of conclusions. "Postscripts" and various kinds of footnotes are undesirable.
In conclusion, phrases that are similar in form to manipulations are inappropriate, such as: “I hope for a mutually beneficial partnership” and so on. It’s better to say goodbye in a business letter with simple phrases - “Regards,” “Best Regards,” and so on.
At the bottom of the message are indicated: F. I. O., official status, company name, signature is put. Contact numbers are also indicated.
Tables and graphs are attached as a separate file (package), indicating this at the end of the letter. If there is a group of attachments, then their inventory is given with the names.
You can use the abbreviation and special abbreviations only if you are sure that the recipient will understand them.

To give the text greater logical rigor and consistency in business vocabulary, the following speech turns are used as binders:
- for this reason;
- based on the foregoing;
- by virtue of this;
- in accordance with the data;
- Based on this;
- Considering;
- and others.
It is useful to address the addressee by name during the entire message. If the message is addressed to a stranger, then at its beginning indicate the source of the recipient's address.

Features and nuances of business correspondence in electronic format
In virtual space, business interaction, representing communication in miniature, is specific, and no less requires compliance with the relevant standards of etiquette. Competent work with a letter, in accordance with practice, involves the following notes regarding volume, language, structure and format.
- The theme formula must absolutely exactly correspond to the subject stated in the text. This allows you to quickly adjust the reader to the desired business spirit.
- The optimal volume of a document sent by e-mail fits into a “one screen”, with a maximum amount of text - one sheet in A4 format.
- The optimal size of investments is no more than 3 Mb.
- It is recommended that the sent files be “packed” into standard Zip or Rar encoding archives. Others are often blocked during shipment.
- Hyperlinks must be standard (blue, underlined below).
- The answer to the addressee should be placed above, at the beginning of the letter, and not below. This eliminates the need for the correspondence partner to redundantly and forcefully scroll through the previous text.
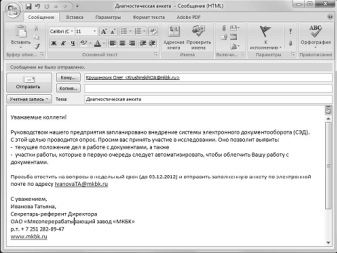

- It is necessary to use the writing language that is most understandable to the partner. The question of the advisability of using professionalism, internal vocabulary, slang expressions and abbreviations (especially in external correspondence) in a message is decided separately, depending on the context and qualities of the correspondence partners.
- It is important to inform the partner about the receipt of his message - this is a sign of good taste and part of business etiquette, showing respect for him.
- The answer should be as prompt as possible. If for some reason it is not possible to quickly respond, the partner should be notified of the receipt of his letter and indicate the time of response. An ethical and comfortable pause before giving an answer is 48 hours after receiving the message. After this time, the person usually believes that the message is lost or ignored. An excessive pause in correspondence is often associated with the risk of losing a partner and is interpreted in business as a violation of ethical standards.
- At the end of the message should be placed contact details that are indicated in all letters, without exception, regardless of the order of distribution.
- During shipment, it is important to pay particular attention to privacy issues.

For more information on business correspondence etiquette, see the next video.









