Jellyfish in the aquarium are rare. Basically, they can be seen in aquariums. At home, you need to spend a lot of work and money to contain fragile beauties. Those who succeed get a bewitching sight. Beautiful, virtually unearthly creatures, hang in the water. It is hard to look away from the amazing translucent figures.


Features
Most jellyfish live in sea waters, but there are also freshwater species, they are used for keeping in aquariums. These are invertebrate animals, they belong to the type of cnidarians (coddling). About 10 thousand species of such organisms live in the waters of the Earth. They have no brain, kidneys, stomach, intestines, organs of vision. Their digestive system is presented in the form of a pouch.
Jellyfish hunt and protect with the help of nematocysts (stinging cells).
They are not relatives of octopuses, squids and especially fish. Jellyfish are close to sea anemones, corals and plankton.
Beautiful and seemingly calm jellyfish are real predators. Stinging cells located at the ends of long tentacles emit poison, paralyze the victim. Daphnia, brine shrimp, copepods, plankton can become prey for jellyfish. These organisms must be added every day to the aquarium with jellyfish. One of the difficulties of keeping is the problematic provision of crustaceans.

The life path of jellyfish is cyclical, it is divided into several stages.
- Adult individuals periodically throw sperm and eggs into the water, which, when combined, are fertilized, and after a while turn into a larva (planula). Outwardly, it looks like a ciliates shoe. Planules are fixed to stones or algae.
- The second stage occurs when the larva develops into a polyp.This organism can grow into a large colony, which is not afraid of temperature changes and many other harmful factors. A polyp is able to take care of itself, forming a podocyte (protective capsule). In this state, the body can remain for quite some time until the environment becomes favorable for the appearance of small jellyfish.
- In the third stage, at a water temperature above 25 degrees, the process of formation of jellyfish begins from polyps. In some years, so many of them accumulate in the abnormal heat that they fall into rivers and flow upstream to places where they have never been seen before. At first, these are very small organisms, not more than 4 mm. Over time, babies grow up and become adults.
Growing jellyfish in a home aquarium, it is quite possible to trace all stages of their development. But the difficulty lies in providing the population with constant live food. A free-floating jellyfish is able to take care of itself by hunting small crustaceans. It is more difficult to organize a diet of a polyp, which is confined to one place. In order for him to receive proper nutrition, the concentration of copepods, artemia and daphnia in the aquarium should be quite high.
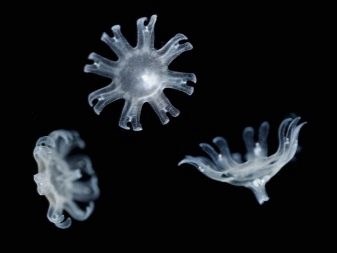

Varieties
Keeping live jellyfish at home is an expensive and troublesome task. Therefore, many decorate their aquariums with fakes. Imitating products are made from modern non-hazardous materials, their appearance is difficult to distinguish from living individuals.
Fans of live cnidaria can keep the following types of jellyfish in their tanks.
- Amakuza. The animal grows up to 10 cm, has long stinging tentacles, with the help of which it hunts plankton and small jellyfish.
- Aurelia. They are also called moon jellyfish. They live on different continents of the planet in fresh water bodies, weak backwaters, in tropical climates. Under natural conditions, individuals grow up to 30 cm. Aurelia is the most popular species among lovers of cnidarians. They do not require a lot of light, which helps inhibit the rapid growth of algae and effectively highlight jellyfish in a transparent water column.
- Cassiopeia Mangrove. If aurelia has a purple or lilac hue, then in Cassiopeia a transparent body casts a purple or greenish color. Sometimes jellyfish rise to the surface of ponds to keep warm. For this phenotype, the temperature in the aquarium is maintained within 23-26 degrees. These individuals are toxic, care should be taken with care.
- Papuan. This phenotype prefers water with a small concentration of salt. Their body forms a dome 50-60 cm in diameter. In an aquarium, they look impressive. They feed on plankton; zooxanthellae are also added as food.
- Ropilema. Large (up to a meter in diameter) jellyfish with a spectacular red tint. They feed on smaller, similar creatures, so they are kept in separate aquariums. At home, jellyfish do not reach meter sizes, but their volumes still remain impressive.
- Soverby. Dome-shaped jellyfish with a transparent body and a slightly milky tint. They are freshwater, eat crustaceans, live in warm, neutral water with a gentle course.
- Filoriza. A transparent jellyfish with white spots that mysteriously glow in the dark. Filoriza is very poisonous, only experienced aquarists can contain it. These individuals require large containers for their living, as they have to pass more than 1000 liters of water through themselves during the day.
- Equorea Crystal. Jellyfish are especially beautiful at night when they glow in the dark thickness of the water with green lights. But they can only live in aquariums, as they need a lot of water



Aquarium selection
People have long tried to grow jellyfish in their aquariums, but, unlike fish, they did not take root. Tender bodies were wounded on the angular walls of the aquarium, which led to the death of pets.In addition, to maintain them afloat, a weak movement of water layers is necessary. Keeping captive jellyfish made possible only with the invention of the carousel aquarium. Its device allows water flows to constantly move slowly, and this helps jellyfish to be in a "suspended" state.
To prevent pets from fighting against the straight walls of the aquariums, models for them are chosen with rounded shapes that allow animals to slide off a sloping surface.
A cylindrical aquarium is considered optimal. In it, with translational rotation, a light stream of water is created, directed tangentially to the walls of the tank. It is necessary to adjust the flow rate correctly. Too slow movement will cause the jellyfish to sink to the bottom, and fast movement will lead to their accumulation on the surface. In addition, from active pressure they will constantly move and get injured.
Aquarium jellyfish are very sensitive to water conditions. It is necessary to install external or bottom filters and keep the water in a constant fresh state. Incorrectly selected filters can lead to the suction of the pets themselves, so their choice should be taken very seriously. You can take advantage of biological treatment and run bacteria-cleaners into the aquarium, but they, in addition to garbage, will consume nutrients intended for pets, as well as emit air bubbles. For a gentle body of a jellyfish, aeration is very dangerous, since bubbles, accumulating under the dome, can damage it.
Lighting should be set for specific types of jellyfish: some like a lot of light, others like twilight.
It is necessary to focus on the preferences of the aquarium inhabitants to maintain the temperature regime: tropical jellyfish require warm water (over 25 degrees), and some species require a medium cooled to 10-17 degrees.
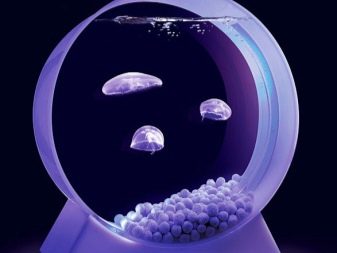

Conditions of detention
One pair of cnidaria needs a capacity of 40 liters. Water is used with medium hardness, with a neutral pH. For an effective supply of beautiful jellyfish and for their safety, the design of the aquarium should be minimized: only a few bushes of plants and soil from small pebbles with smooth edges or glass balls. Having prepared the aquarium, you should wait until the completion of the nitrogen cycle, and only then run the inhabitants.
Feeding jellyfish to inexperienced aquarists can be challenging. In the wild habitat, these animals consume a large amount of plankton, nauplius, artemia. Live food can be purchased at specialty stores for domestic animals, but many prefer to grow plankton on their own. Facilitates the feeding of jellyfish at home the presence of dry, balanced feed, which is used in combination with a live product.
The video will allow everyone to appreciate the size, shape and beauty of jellyfish.










