A responsible aquarist, noticing a slight greening of the water, will not wait until the greens cover the entire space of the tank, but will try to solve the problem as soon as possible. But for starters, it is important to find out what caused this phenomenon and eliminate the root of the problem, after which regular preventive measures should be taken.


Why is green water dangerous?
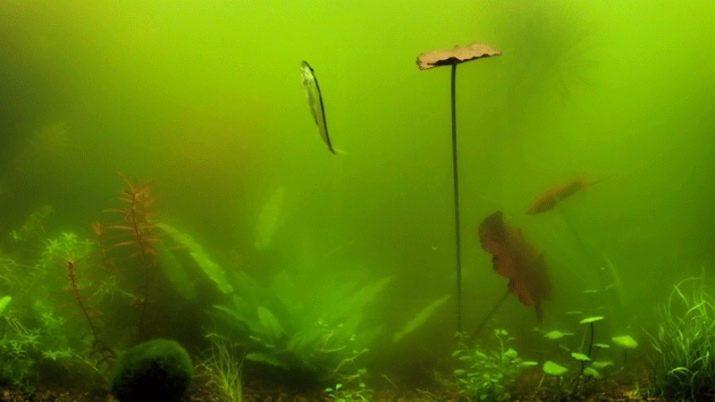
Every aquarist is probably familiar with the greening of water. The phenomenon is an uncontrolled development of phytoplankton. An artificial reservoir acquires a green color under the influence of an abundance of pigmented cells. Sometimes the color of the water may become tan or reddish. Phytoplankton can be compared with ordinary algae, which, unlike known plants, does not grow on the walls of the aquarium, but multiplies in the water column.
It is not worth it to be very scared. These microscopic organisms in small quantities will not harm the aquarium inhabitants, but they can upset the bio-balance by taking useful elements from aquarium plants. During the growth process, phytoplankton changes water indicators and worsens the development of green spaces; as a result, this process leads to a significant reduction in oxygen in the water, and this can already negatively affect the condition of animals and fish.
The danger of green water lies in the fact that as the phytoplankton multiplies, the pond becomes increasingly cloudy, and soon through the green dregs it becomes impossible to see the aquarium world. The owner may not notice the poor condition of the fish in time and miss their disease.
Finally, greening in the aquarium significantly spoils the appearance of the artificial reservoir, making it groomed, abandoned.

Main reasons
There are several reasons for this problem. Most often, the following factors lead to greening.
- Excess organic components. During decay, the waste products of aquarium inhabitants, dead leaves and parts of exfoliated shells release nitrogenous compounds into the water that feed phytoplankton. The more decaying fragments, the faster the unicellular algae spreads, and the faster the water turns green. To find out that an abundance of organic matter has led to a negative process, you can find out by a large number of fish excrement and the remains of molting of armored animals. By the way, this process not only provokes the development of microorganisms, but also becomes a source of poisoning of the reservoir, which reduces the quality of the water.
- Excess light. One of the most common reasons. Usually the water turns green in the aquarium, which is located under the ultraviolet rays. That is why aquarists prohibit placing a container on a south or southeast window. Powerful lighting equipment that lasts longer than 12 hours a day leads to the development of microalgae.
- Filter malfunction. Weak filtration systems can also cause greening of water. A poorly functioning filter, designed for a smaller volume than is actually used, is not able to completely eliminate pollution. Uncleaned debris becomes a tasty food for unicellular algae. A filter that is rarely cleaned leads to the same process.
- The abundance of vegetation. Until lighting is turned on, plants are engaged in the production of carbon dioxide in the dark. This element is extremely important for the development of phytoplankton. In this regard, a large number of green spaces leads to the multiplication of microorganisms.
- Fever. The optimal temperature limits for aquarium animals and plants are 22-26 degrees. With an increase in indicators, unicellular algae spread very quickly throughout the water column. You can recognize the cause by looking at the aquarium thermometer.
- Bad cleaning. This causes not only the reproduction of algae, but also fish diseases. Cleaning should be of high quality and regular. The smaller the capacity of the aquarium, the more often it needs to be cleaned. So, a 15-liter aquarium must be cleaned weekly, and a 100-liter artificial pond requires cleaning once a month. The process consists in cleaning the walls of green plaque, thinning and cutting of overgrown plants, cleaning siphons of soil, and cleaning the filter.
- Incorrect replacement. A beginner aquarist is not immediately drawn into the process of caring for the aquarium and at first may change part of the water too rarely or often. In both cases, the reproduction of unicellular algae is possible. It is important to take responsibility for replacing water.
- Poor fish food. Poor powder feed, half-eaten by fish, settles to the bottom, where it begins to decompose. This process becomes a factor in the spread of a colony of microscopic algae.



How to deal with it?
When the flowering of aquarium water has become serious, it is required to resettle all residents. The fish can be temporarily placed in another tank with the same water values. A container is enough for plants where methylene blue is added. If the water is just starting to turn green, then you can not plant the aquarium inhabitants. Fighting green algae can take some time. You can do this in many ways.
Natural cleansing
The plaque formed on the walls of the aquarium can be destroyed by living "orderlies", for example, catfish. Snails, pecilia, and lightning can take part in the purification.Frequent inhabitants of aquariums are planktonic crustaceans, which also cleanse the reservoir of microorganisms by passing and filtering water through itself. If the choice of an aquarist fell on crustaceans, populate them in large numbers, as these creatures always become a treat for predatory fish.
Living "filters" are able to remove greens from the scenery, the walls of the aquarium, soil. This method will become even more effective if, during the cleaning period, reduce the portion of food for fish, reduce the duration of daylight hours and turn on aeration systems at high power.


Mechanical way
To get rid of greens mechanically, heed the advice of experienced aquarists.
- Put a high-quality filter in the tank, the power of which corresponds to the volume of the tank. Regularly clean all hoses, tubes and jaws that make up the device. If it is an external unit, then it can be cleaned less frequently. The internal filter needs to be cleaned weekly.
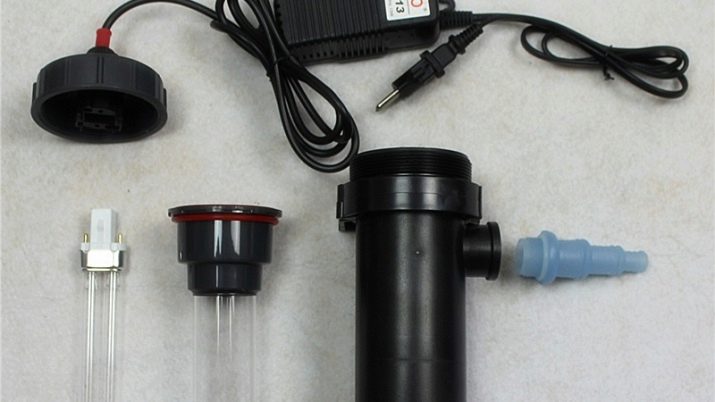
- To reduce the spread of unicellular algae, put a special ultraviolet sterilizer, and also equip the aquarium with a diatom filter, which will more effectively clean the artificial pond from harmful microorganisms.
Do not forget to periodically scrape green deposits from surfaces.

Chemicals
Experienced fish lovers prefer to combine the mechanical method and the use of chemicals. The introduction of chemistry helps to suppress the development of phytoplankton. The most popular remedies are as follows.
- Hyacinth. According to the instructions, the drug is added to water in a ratio of 1 ml per 10 liters of water. As soon as microorganisms die under the influence of the agent, they are eliminated by the filtration system.
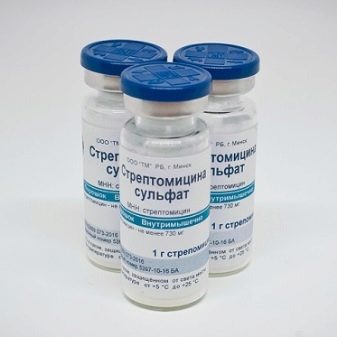
- Streptomycin. It is an antibiotic. Allows you to eliminate any kind of unicellular algae. It is diluted in an amount of 3 mg per 1 liter of water.
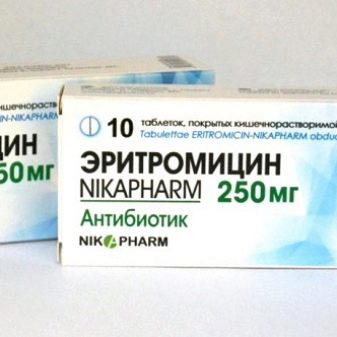
- Erythromycin. Also belongs to the class of antibiotics. To combat phytoplankton, you need to make 250 mg of the drug per 100 liters of water.
According to the reviews of aquarists, these products are safe for aquarium residents and do not require re-treatment.
Folk methods
Some aquarists turn to folk recipes for help. For example, a 3% solution of boric acid can overcome greens. The drug is added to the aquarium in a ratio of 1-2 ml per 1 liter of water.
Preventive measures
As a rule, a problem is easier to prevent than to overcome it. Therefore, in order to avoid the spread of phytoplankton, it is important to take preventive measures. To prevent water from blooming, maintain a normal microclimate in the artificial pond. This can be achieved by the following actions.
- Keep the tank away from direct sunlight.
- Before starting up the aquarium, place the soil slightly obliquely so that a low hill forms at the front wall.
- The optimal power of lighting devices is 0.5 W per 1 liter of water. Sometimes shade the aquarium so that the algae does not grow abundantly.
- Install a lid on the aquarium to prevent particles of dust and debris from entering. Check the aeration and filtration systems.
- Change the water once every two weeks. It is important to remove 30% of the total volume and change to fresh water that has settled during the day. In this case, the new water should be at the same temperature. Drain and flood by means of a siphon - then the turbidity will not rise in the aquarium.
- Buy high-quality food for fish and bring it in portions in such a quantity that the fish have time to eat it in 5 minutes. It is important to remove all uneaten residues on time.
- Do not overpopulate the aquarium with fish and plants. Flora releases too much carbon dioxide into the water, and from a large number of aquarium inhabitants there is a lot of waste. All these factors lead to the formation of phytoplankton.
- Constantly monitor the condition of the aquarium.
Inspect the plants and scenery for the presence of green plaque, observe the activity of fish, monitor the maintenance of the microclimate, and control the temperature regime.


About why the water turns green in the aquarium and how to deal with it, see the next video.










