Before going to his tracks or route, the cyclist must check the pressure in the wheels of his bike. Riding on flat tires is not recommended: both the rubber and the rim on which it is worn can be damaged.
Why maintain the right pressure?
Maintaining Required pressure values in bicycle wheels solves the following tasks:
- it does not allow the wheel to break through at the slightest bump, on cracks across the road, in case of accidental collision with a drain sewer hatch, etc .;
- a pressure close to the average, but above the minimum, increases patency on dirt roads and tracks with a small gravel, sand and clay coating;
- higher than average pressure, but close to maximum, will increase the rollback on the highway and streets with asphalt pavement.
Neglecting these simple rules for pumping wheels is fraught not only with frequent breakdowns of rubber, but also with the appearance of “eights” on the wheel rims.


26 inch pressure for any wheels
Wheels with a diameter of 26 inches are placed on mountain, hybrid, road, "extreme" and teenage bicycles.
The pressure in the tires of mountain bikes is chosen empirically. For each cyclist, it is different. So, for cross-country models, a value of 3-4 atmospheres is chosen - it is ideal for asphalt streets and country roads.
Semislick tires are designed for maximum pumping - they are designed for highway and street riding, where there is asphalt. With weaker pumping (from minimum to average), the contact area of rubber with the road will increase, and it will become much more difficult to quickly accelerate.

For highways, follow these minimum values.
Wheel rim diameter | Number of atmospheres | Pounds per square inch |
12 | 2,4 | 35 |
14 | ||
16 | ||
18 | ||
20 | 2,5 | |
24 | 4,5 | 35–65 |
26 | ||
28 |
Extremely low values are indicated. High ones range from 5 to 9. Try not to exceed them - otherwise the rubber will burst at high speed or when running into the slightest bump. Pump a few tenths of the atmosphere lower than indicated in the table.


The pressure values also depend on how much a particular rider weighs, and on the route on which dirt or gravel, rocky roads come across. Tire width also makes adjustments. Choose the pressure for the future by driving along the most difficult roads under the control of a pump equipped with a pressure gauge.
Weight cyclist, kg | Pressure, atm |
50–60 | 2,4-2,9 |
60–70 | 2,9-3,2 |
70–85 | 3,2–3,7 |
85–100 | 3,7-4,0 |
100–120 | 4,0–4,1 |
If you currently do not have the opportunity to weigh yourself - you should download the average value taking into account the roads on which you most often ride. But on children's bicycles it is better to pump up maximum pressure: when a child learns to ride, less effort is required for him when riding, spent on acceleration.

More accurate values
The load on the rear wheel is on average 10-15 kg more - the seat is located closer to it. The weight of the cyclist is distributed between these wheels. For comparison, the weight of a biker with a value of 85 kg is taken.
Wheel load | 50 mm | 37 mm | 32 mm | 28 mm | 25 mm | 23 mm | 20 mm |
50 kg | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6,8 | 7,5 | 8 | 8,8 |
35 kg | 2,5 | 3,4 | 4,4 | 5,4 | 6,1 | 6,8 | 7,5 |
The smaller the width of the tire, the more pressure it needs to be inflated. That is why road bikes have a maximum pressure, and with a bike with the same wheel diameter, the pressure is minimal, reaching 2 atmospheres. Of decisive importance is the constancy of the body weight of the same biker, and the road contact spot on the road bike is the smallest.

So that the tire does not slip when the rider gets on the bike and starts off, and the optimum pressure is selected for the tire of a particular variety.
Without pressure gauge
Checking the pressure without a pressure gauge is easy, but this method is inaccurate. If you are unable to squeeze a little tire - the pressure in the wheel is average or above average. At low pressure, you can wash it with your fingers. A universal option is to pump the wheel to medium and high values and remember how much you managed to push it with your hand, and whether it worked at all. More precisely, they can pump up a compressor at a car service station. The main thing is that while driving, the rubber should almost not slip, because subsidence will accelerate its wear.

Weather correction
In winter, the pressure pumped up at home can drop - it is better to pump a little above the average or near maximum value. At zero degrees or in frost it will fall by 1 ... 1.5 atmospheres. On a hot day, on overheated asphalt, on the contrary, it can jump by the same amount, it is better not to get to a maximum of 1.
Cord quality
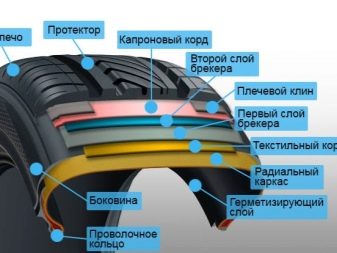
The weaving density of the cord — it consists of Kevlar or Aramid filaments — is indicated in the TPI value (number of filaments per inch). Low TPI value - from 30 to 65 - requires low pressure, from too high a tire will simply break. Higher tolerates the same pressure. If the tire has, for example, a three-layer cord with 100 TPI units in each, feel free to pump up pressure close to the maximum.
A tire with a low TPI may not be able to withstand your multi-kilometer marathons on the highway at high speed - at 30 ... 40 km / h a high pressure of 6 ... 11 atmospheres is required.

Conclusion
Whatever your weight, bike parameters and road quality - you will not immediately find the optimum pressure. It is reachable only after a few trips. And there is no need to change a dozen punched cameras and bursting tires to calculate it.
See below for how to pump up your bike properly.










