Suede is one of the most popular materials and is widely used in light industry and furniture production. Due to their high performance and attractive appearance, suede products do not lose their popularity over the years.
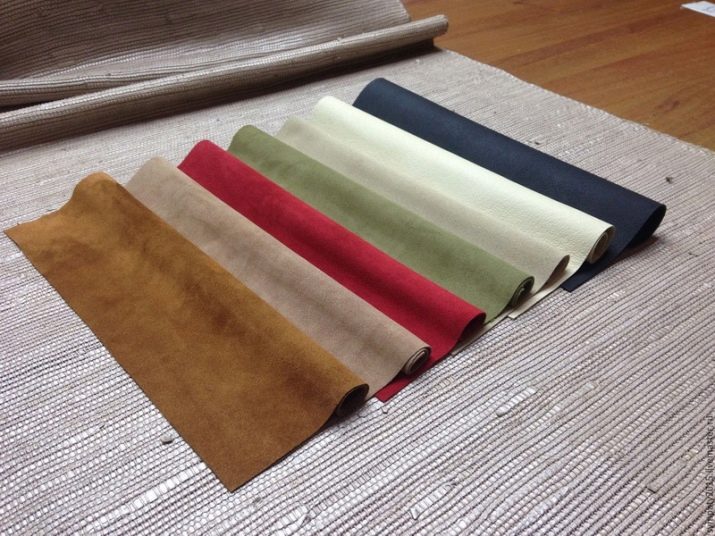

What it is?
Dressing the skins of domestic and wild animals since ancient times was considered one of the main crafts of the peoples of the North. Beginning in the Middle Ages, craftsmen infused reindeer skins with special compounds and animal fats, after which they sewed clothes and shoes from them. The technology for processing hides in a slightly modified form has survived to this day, and the material obtained as a result of dressing is called suede. Today, skins are impregnated with modern equipment using fish, seal and bone fats, as well as vegetable and ungulate oils. As a result of dressing, the skin acquires a thin and soft texture and becomes very strong and elastic. The material is characterized by a pleasant to the touch, fleecy surface on both sides, and is famous for its velvety and noble appearance.


Given the natural origin of raw materials, things made of natural suede are quite expensive. Therefore, thanks to modern technology, mankind has learned to produce material that perfectly imitates natural suede. Artificial canvases are visually practically indistinguishable from the prototype and are characterized by high wear resistance, resistance to stretching and abrasion, a soft and pleasant to the touch surface and are much cheaper than natural material.


Varieties
Today, there are two types of suede.




Natural
For the manufacture of suede, the skin of chamois, goats, antelopes and sheep is used, and the seal fat or whale with the addition of vegetable, hoofed or linseed oil is used as an impregnating composition. After applying the solutions to the surface, fats and oils react with the fibers of the skin, oxidize, and contribute to souring. To speed up the process of the appearance of hairiness, the raw materials are pre-soaked in a solution of formaldehyde, and after fat treatment they are placed in special machines called shock balers. In them, the material is subjected to continuous mechanical stress for 3-5 hours, after which it is stacked and warmed up. The process is repeated until the canvases acquire a yellow-brown hue.


Next, the material is thoroughly washed using a special solution, and then placed in a dryer. This is done in order to degrease the finished suede before sending it for painting. Freshly made natural suede is distinguished by a heterogeneous light brown color with the presence of light and dark spots, which is why it undergoes obligatory staining. At the end of the full treatment cycle, suede ceases to allow water to pass through and acquires high water-repellent properties.


The advantages of natural suede include high strength, presentable appearanceExcellent abrasion resistance and long service life of suede products. In addition, the material does not accumulate static electricity and does not leak water. Among the minuses, too high a cost and a moral and ethical aspect are noted, due to current trends in the use of environmentally friendly technologies and the rejection of the use of animal resources to meet human needs.


Artificial
There are two ways to make faux suede. The first is to apply a polymer coating to the knitted base, followed by laser grinding, which forms a pile. As a fabric base use cotton, wool and synthetic materials. The most optimal ratio of artificial and natural fibers in the fabric is considered to be 25% cotton and 75% polyester.


To connect the fleecy part with a fabric substrate, special PVA glue is used or a self-adhesive polymer is used. In some cases, lamination technology is used for bonding strength, after which it becomes impossible to separate the fleecy coating from the substrate. After the suede structure has been formed, the material is subjected to Teflon treatment, as a result of which the fabric acquires high dirt-repellent and moisture-proof properties. If, as an experiment, pour a little water on the fabric, then it will gather in large drops and, without being absorbed, will roll off the surface of the material.


The second manufacturing method consists in fluffing microfiber with obtaining a soft and even fleecy surface. The process of pile formation is carried out on special brush equipment using the technique of splitting microfiber threads to the formation of small fibers. This suede is called woven and differs from the previous one in higher strength and resistance to deformation and stretching.

The advantages of artificial suede, which is sometimes called eco suede, include high strength, durability, uniform texture and color, unpretentious care and the ability to ventilate. In addition, the material is pleasant to the touch and not prone to the appearance of creases, the formation of cracks and abrasions. Among the minuses are the special soiling of white and gray products, the risk of tissue damage by the claws of pets and low resistance to washing non-woven suede. For glued products with a fabric base, dry cleaning or treatment with ammonia is recommended.



Differences from other materials
Before describing the differences between suede and textile fabrics and knitwear, it is necessary to understand the difference between artificial and natural materials. The main distinguishing feature of artificial suede is the absence of pile on the second side, which, upon closer examination, makes it easy to distinguish it from natural. In addition, a layer of leather will be clearly visible on a section of natural suede, while a fabric base is clearly visible in artificial. The smell of materials also differs, and if the natural fabric has a persistent smell of the skin, then it is absent in artificial fabrics. You can distinguish fabrics by their texture. So, natural suede has a special softness and some color inhomogeneity even after painting, and artificial fabrics are ideally uniform and more rough to the touch.


If it is not possible to inspect the reverse side of the material and doubts arise about its naturalness, then it is recommended to hold the product in your hands for some time: artificial suede will not change its temperature and remain cool, while natural suede will quickly heat up. In addition, if you drag your finger along the pile of natural material, then the villi will change their position and the track will become darker, while on the artificial canvas everything will remain unchanged. Another difference between natural and artificial material is the fact that when sewing clothes and shoes made from natural suede, the edges of the fabric are not processed, while artificial fabrics need an overlock. You can distinguish materials by reaction to water. Natural suede will instantly absorb moisture and darken, while water will slide off the artificial material without leaving a wet mark.


The main difference between suede and other types of synthetic and natural fabrics is versatility. The material is equally suitable for sewing clothes and shoes, which significantly expands the scope of its application and allows you to complement the ensembles with leather goods and spectacular accessories. Natural suede is often confused with nubuck. The main difference between these materials is the raw materials for their production. For nubuck, the skin of larger animals, such as cows, moose and deer, is used, and grinding technology using abrasive materials is used for mossing.
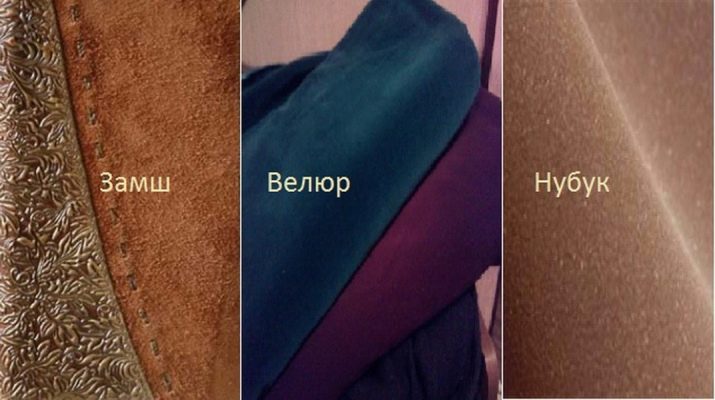

This process is called chrome treatment or tanning. In addition, suede pile is much thicker and higher than that of nubuck, and has a softer to the touch structure. Nubuck is often subjected to oiling, which increases the waterproof properties of the fabric, which, in turn, makes the material a little rough and rough. The functional characteristics of nubuck are significantly lower than the working properties of suede. So, shoes made of nubuck quickly get wet and get dirty. And if suede shoes can be wetted during cleaning, then only dry cleaning is allowed for nubuck.

Application options
The scope of natural and artificial suede is quite wide. The material is actively used for sewing clothes and shoes, upholstering furniture, as well as for the manufacture of gloves, bags and jewelry.
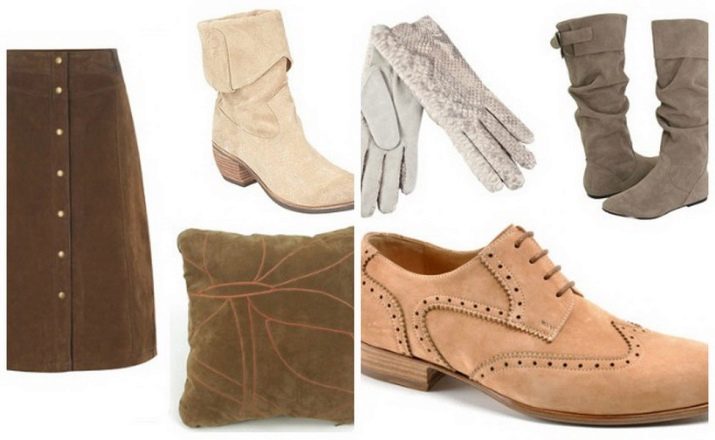

clothing
Suede is used for sewing sheepskin coats, jackets, jackets, skirts and coats. For tailoring outerwear, the ideal option is jacket suede with a cotton or knitted base. Often, to increase the decorative qualities of the fabric, the pile is given a certain orientation. Suede clothing fits nicely to the body, sits well on the figure and looks very dignified. When buying suede, it is better to choose products in bright colors. This is due to the fact that on blue or black clothes, small fibers, hairs and threads will be much more noticeable than on a beige, sand or pink model.
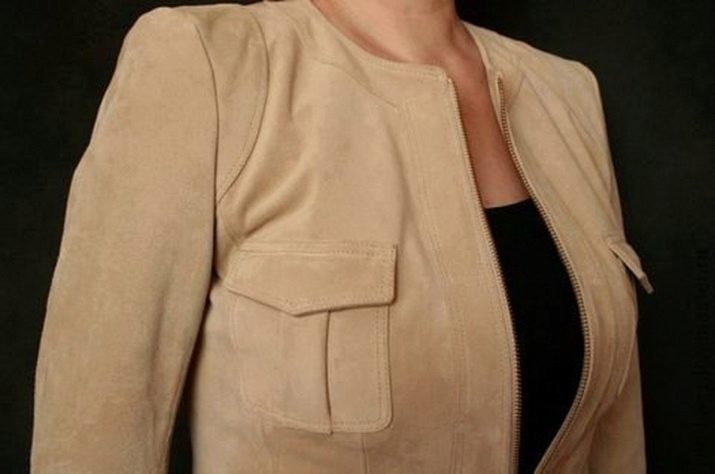






With independent sewing, it is better to choose artificial fabric with a knitted base. Such a suede, unlike a material with a cotton base, is easier to sew and drape, making it well suited for sewing blouses and skirts. But for the manufacture of suits and jackets, on the contrary, it is better to purchase just the cotton version. In addition, it must be borne in mind that when sketching parts made of thick suede, holes from needles and pins remain on the material, and therefore sewing needles should be chosen as thin and sharp as possible.


Footwear
Suede shoes have not gone out of fashion for many years. Due to its versatility and presentable appearance, shoes made of such material go well with almost any wardrobe. In suede boots or boots, the legs always remain dry and do not freeze. The fabric successfully combines the ability to ventilate and repel moisture, which is why it is often used for sewing sports shoes. For the production of such models, the skin of large animals is used, which has increased strength and wear resistance.




Accessories & Jewelry
Suede leather goods are always at the peak of popularity. The material is ideal for sewing bags, gloves, straps and purses, in addition to which you can always get an elegant jewelry in the form of a bracelet or pendant.




Upholstery
To fit sofas and armchairs in furniture production, they often use artificial suede made of microfiber. This is due to the high performance of the material, such as abrasion resistance, the ability to preserve the original color and ease of cleaning. In addition, the material is not prone to rolling and is available in a wide color palette.


Cleaning material
Thin perforated suede is widely used as a cleaning and polishing material and is used to care for the surface of optical lenses, LCD monitors and plasma TVs. Suede rags have a long service life and do not lose their working qualities for a long time. In addition, the fabric absorbs water perfectly, leaves no whitish stains and dries quickly. This allows you to use the material for washing car windows, headlights, interior and body.


Orthopedics
Due to the ability of the material to breathe, suede is widely used in the manufacture of orthopedic insoles and specialized shoes. For these purposes, a special type of technical suede is used, the working qualities of which are clearly defined in the standards of GOST 3717-84. As raw materials, sheep, goat and deer skins are usually used, characterized by a short pile and a dark brown non-marking color.
Technical goals
In the manufacture of natural suede, pork split is often used. Unlike cattle skins, it gives low-quality suede, which is used for sewing work gloves, aprons, covers for various equipment and technical equipment.


How to care?
Any suede is quite demanding in care, so when buying products from it, some points must be taken into account. So, suede clothes made of microfiber and natural linen can be easily washed and even soaked for a while in a warm soapy solution, however, the water temperature should not exceed 40 degrees. After washing, the product is recommended to be slightly wet with an absorbent cloth and hung on a coat hanger. Squeezing suede is strictly prohibited. During the drying process, it is necessary to blot the fabric from time to time with a towel, otherwise numerous smudges may appear on the surface, which can be difficult to remove without repeated washing. You do not need to stroke a suede stretch skirt or coat. The material is not prone to creases and bruises and perfectly restores its original shape.

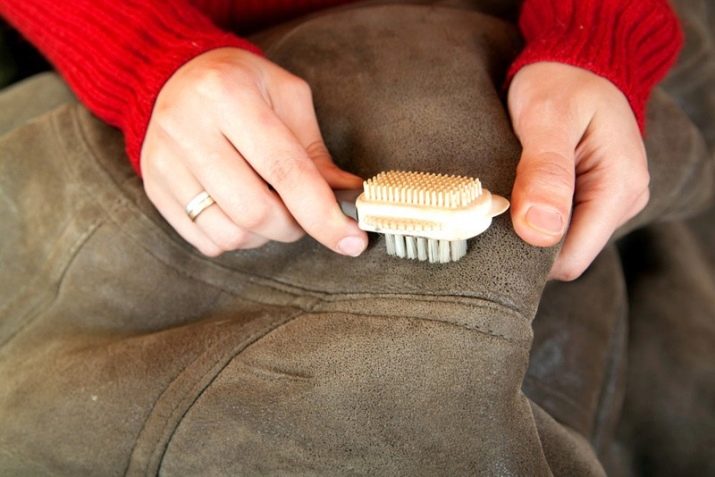
In addition to washing, it is necessary to carry out regular dry cleaning of things. To do this, you can use a rubber brush, moving it in one direction of the pile. In no case should freshly planted dirty stains be attempted to wipe off. In such cases, you need to wait for the stain to dry completely, then shake off the dried dirt with an elastic brush and clean it with a silicone sponge. To remove greasy food stains, the contaminated place is poured with talcum powder and left for three hours. Then gently shake off the powder with a brush and brush the product with a rubber brush. For lack of talcum powder, starch diluted with ammonia to a pulp consistency can be used. In case of incomplete stain removal, mix water with ammonia in a ratio of 4: 1 and blot the stain.

Covered after a long storage, the pile must be held over the steam and combed with a hard toothbrush. If the spots are fresh enough and have not yet had time to eat into the material, then you can try to remove them with a cotton swab dipped in soapy water. To prepare the solution instead of soap, it is better to use a shampoo taken at the rate of 20 g per liter of water. After treating the stain with such a composition, it is necessary to collect the foam and quickly blot the area to be cleaned with a dry towel. Such cleaning should be carried out very quickly - so that the material does not have time to get wet.
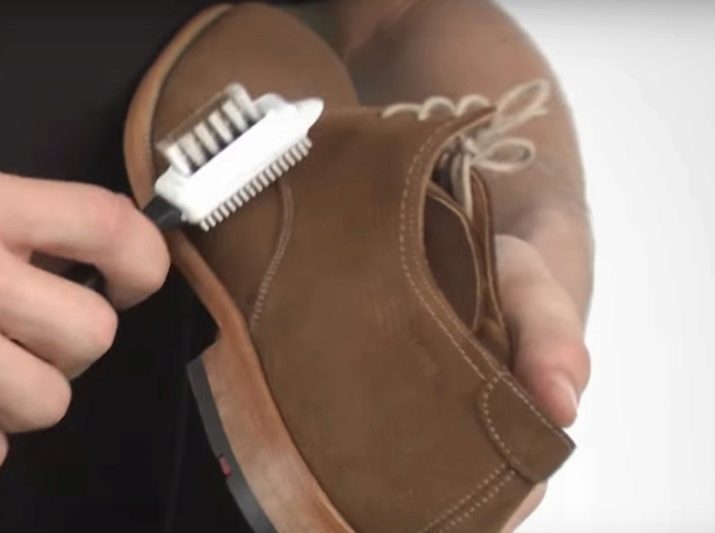

Drying suede products is recommended away from heating appliances and direct sunlight. Brown things are well cleaned with coffee grounds, and light and white with skim milk and soda, diluted in a ratio of 0.5 tbsp. l soda for half a glass of milk. Updating the color of clothes is done with spray paint for suede. The use of stain removers and acetone-containing compounds is strictly prohibited. Simple stains can be removed with a regular soft eraser.
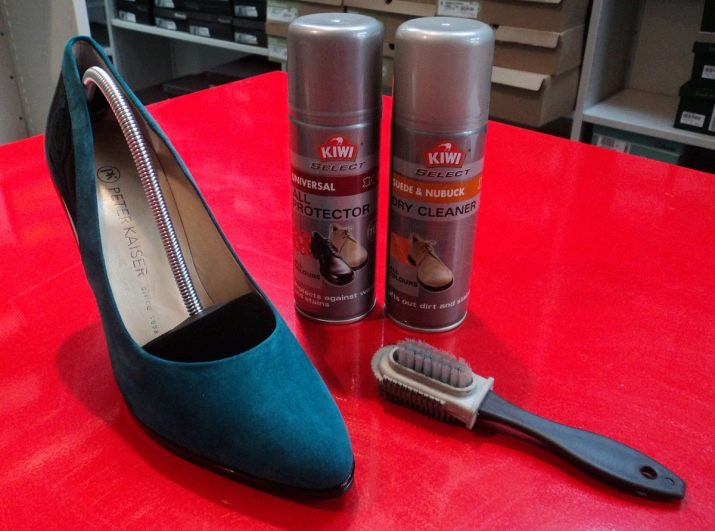

When taking care of shoes and bags, it is necessary to use a sponge dampened in soapy water, while avoiding strong wetting of the product. After processing, the thing is dried. and then combed with a hard brush. In winter, saline stains from reagents can be removed with 5% acetic solution. To do this, moisten a soft cloth in the solution and try to gently wash off the stains, paying more attention to the borders of the stain. However, many troubles can be avoided by treating new suede shoes with fluorocarbon or silicone water- and dirt-repellent impregnation.

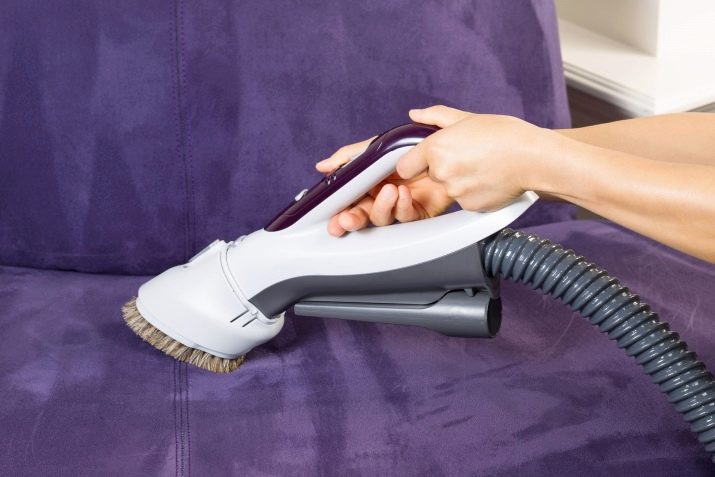
Furniture care consists in the regular washing of removable covers. As a rule, microfiber is used for their manufacture, so they are washed well. If the upholstery is not removed, then stains and other contaminants are cleaned using any of the methods described above. The only prerequisite for cleaning non-removable upholstery is to get it wet as little as possible, which is caused by the risk of moisture penetrating inside and the associated difficulties. When buying furniture with suede upholstery, you need to take into account that the height and density of the pile quite strongly affects the abrasion resistance and the complexity of care. Thus, products with a short pile have higher performance characteristics and are most preferred as upholstery for regular use. If a suede sofa is already quite a few years old and it has started to grease, then a special brush with a combined design with the presence of metal and rubber elements or an ordinary eraser will help to rectify the situation. As for daily care, such furniture should be regularly vacuumed, cleaned with dry salt and periodically combed with a soft brush.

Competent and timely care of suede products will allow things to retain their original appearance for a long time and not lose their functional and decorative properties for a long time.
See how to take care of suede in the next video.





