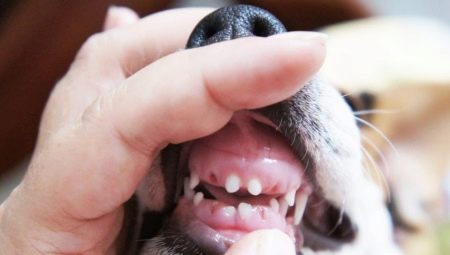
With the help of teeth, a dog can get its own food and chew it, grind it, find out relations with its fellow tribesmen and protect itself if necessary. With the teeth, the female has the ability to move her puppies from one place to another, and even cleaning the hair from blood-sucking insects is impossible without the participation of the front incisors of the dentition.
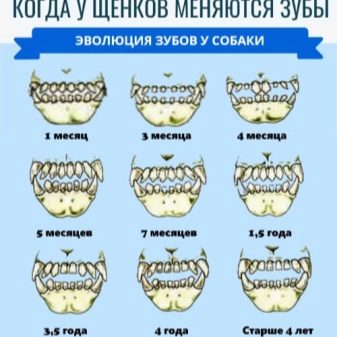
Puppies do not have teeth immediately after their birth, and at first milk teeth grow in babies, and then they are replaced by permanent ones, in the amount of 42 pieces. This whole process takes place in the first year of a dog’s life and ends at the age of 9 months. Teeth change in animals on their own, but at the same time they sometimes need dental care. A person intervenes in the natural course of events only if there is any anomaly in the development of the dentition or for the treatment of diseased teeth of his pet.


Time and order of loss
The pattern of appearance of the first dental units in dogs of most breeds is the same. Veterinarians note that small breeds of decorative dogs lag behind the formation of the dentition by about 1-2 months, while the average species or large breed of dogs are ahead of them in development

Physiologically by nature, it is laid so that a dog grows 32 milk dental units. They appear not all at once, but sequentially, each in its own time.
- Fangs. They appear first in puppies, and this happens by the end of 2 or 3 weeks of life. Fangs appear first on the upper jaw - on the right and left, and then on the lower. In total, 4 milk canines grow in babies.
- Incisors. In puppies, 6 incisors are cut on the upper and lower jaws. Above the incisors appear at the end of the 3rd week of the puppy's life, and from below they begin to grow at 4 weeks. Incisors are divided into hooks, middle and margin.
- Premolars. A dog grows 6 such dental units above and below, on each jaw. The growth of premolars occurs almost simultaneously with incisors - at 3-4 weeks of the dog’s life, and first these teeth erupt in the upper jaw, and a week later the premolars already appear below.
- Permanent teeth. The function of molars in puppies is performed by premolars, which in structural form are not similar to what the permanent molars of an adult dog look like.
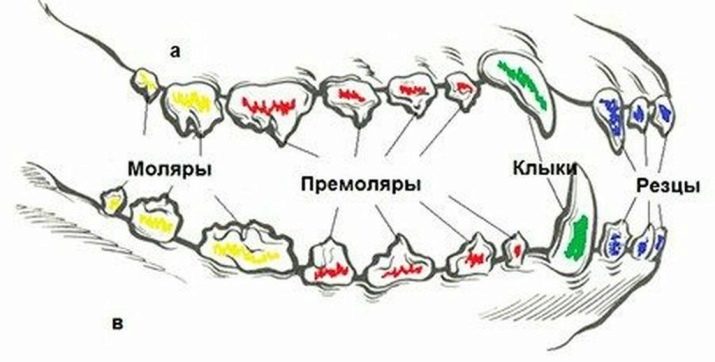
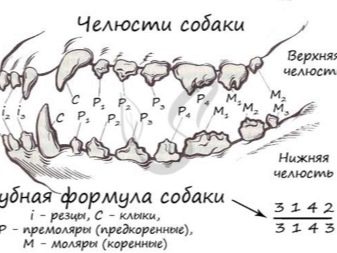
By the presence of erupted teeth, you can easily determine the age of the dog in the first year of life in weeks. The puppy's dental formula has a peculiarity - on the upper and lower jaw the number of teeth is the same:
- 6 incisors;
- 2 fangs;
- 8 premolars.
In babies, the first teeth are very thin and sharp, similar to needles. However, such a dentition is short-lived, since the dentin constituting the dental tissue has a softer structure, in contrast to the permanent teeth. The milk row is very quickly worn away and its change begins.

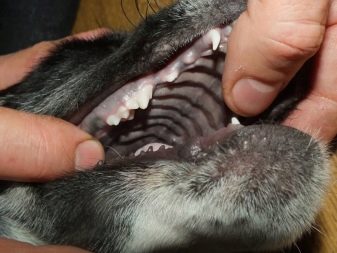
The puppy’s baby teeth fall out in the following sequence.
- The first incisors in the dog change, and this happens at the age of 3-4 months. At first the hooks fall out, after them the middle incisors, and the edges change last.
- Permanent molars appear behind the premolar region on the jaw arch at 4-5 months.
- At the age of 6 to 8 months, milk premolars begin to be replaced by permanent forms.
- At the age of 6-7 months, along with the change of premolars, a change of fangs occurs.
- In the period from 7 to 9, and sometimes up to 10 months, permanent indigenous premolars grow in the dog.
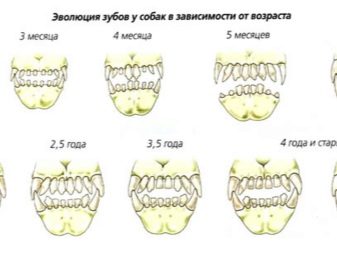
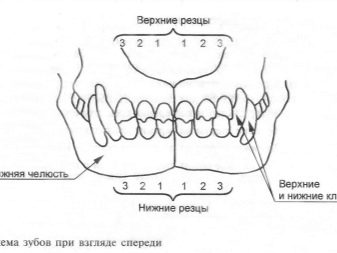
In total, an adult dog in the oral cavity should grow 42 permanent dental units with which the animal will live his whole life.
Dentition of the upper jaw:
- 6 incisors;
- 2 fangs;
- 8 premolars;
- 4 molars.
Dental formula of the lower jaw:
- 6 incisors;
- 2 fangs;
- 8 premolars;
- 6 molars.
The loss of milk teeth in a dog is due to the fact that, starting their growth, permanent dental forms, increasing in size, push and displace their milk predecessors. The first inconsistent tooth units have no roots and are relatively easily detached from the dog's jaw.

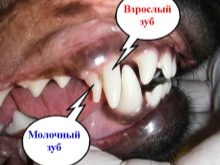
How do new teeth erupt?
When a puppy's teeth grow, then this process occurs so that he feels a certain pain discomfort and his general well-being may deteriorate. The baby often has an elevated body temperature, but this does not last long and most often occurs when he is sleeping. It’s easy to understand that a small pet has begun a period of changing the dentition - externally, the dog may become lethargic or, conversely, irritable and restless.
At such a time, the puppy’s behavior also changes - you will notice that your dog will have an irresistible urge to nibble, and this happens because his gums constantly itch. So that the puppy does not spoil your things and furniture, you need to provide him with toys. After milk units are replaced by a permanent dental formula, the symptoms associated with this process disappear.



A teething tooth that is about to fall out appears half detached from the gums and is often angled relative to other teeth. Sometimes the prolapse process is delayed and interferes with the growth of a new tooth, then you can see that the old and new, already erupted tooth are together. This neighborhood is abnormal and requires dental care, as permanent teeth in this case, the dog will grow with displacement, changing the shape of the bite.
It is important for the dog owner to track this moment in time and contact the veterinarian, since otherwise the dog is doomed to live with an irregular dentition.This will entail a violation of the process of chewing food, which means that over time the digestion process will also be disturbed.

At a time when the puppy's milk row is erupting or replacing, it is important for the owner not only to carefully monitor his pet, but also to contribute in every way to these processes. Veterinarians recommend swaying a tooth slightly with your finger, but in no case do not apply great effort and pull it out.
In such a period of life, the baby should be given bite not only toys, but also solid granules of dry food, bones and cartilage, solid vegetablesfor example, such as slices of fresh carrots - all this will help loosen the milk tooth and facilitate its loss.
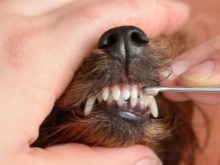


In dogs of large and medium-sized breeds, the dentition changes relatively quickly and without pathologies, since the anatomical structure of their oral cavity provides enough space for the growth of dental units of various sizes. Decorative miniature dog breeds most often face a delay in the loss of the milk row, as well as with abnormal growth and development of permanent teeth.
This is explained by the fact that the oral cavity in such animals is not only small, but due to the characteristics of the breed is anatomically deformed, for example, like a French bulldog or Pekingese. There is very little room for growth of teeth on the jaw arch, and if the tooth grows large in size, this inevitably leads to malocclusion. It is very difficult to conduct an examination of the oral cavity for preventive purposes in such dogs, therefore often the process of changing the dentition is left to chance.


What to do if not dropped out?
During the eruption of dairy and permanent dental units, the puppy needs regular observation and examination of its oral cavity. There are times when a teething tooth leads to gum inflammation. Then the festering wound must be cured, since the purulent process can go to a healthy tooth. If there is no tooth in the dentition, this will lead to the displacement of all dental units located on the jaw. therefore all wounds and inflammation on the gums should first be washed with hydrogen peroxide, and then irrigated with warm infusion prepared from medicinal chamomile.
If the time has come, but the milk tooth has not fallen out, it must be pulled out, and the doctor can do this in the veterinary clinic. Sometimes it happens that in dogs grow both teeth next to each other - milk and permanent. Due to the weak and soft dentin, the milk tooth begins to rot very quickly. And since a permanent tooth grows next to it, it is also involved in the process of decay, as a result of which the dog may lose a permanent dental unit.
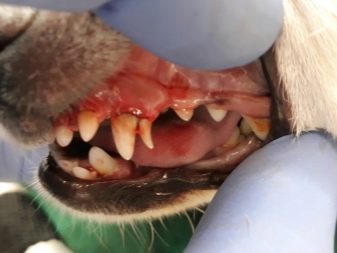
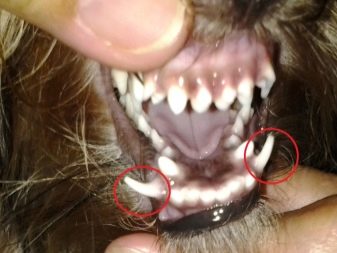
Another common problem with tooth growth is the so-called a hood that comes from gum tissue. A tooth covered with such a hood cannot break out on its own, and it either begins to rot inside the gum or grows in the wrong position, interfering with neighboring teeth.
Only a veterinarian can help the dog in this case, which with a surgical instrument will open a passage in the gum for tooth growth. This procedure must be done on time, without waiting for the onset of inflammation in the gum and decay of the dental tissue.

Dental Care Features
The owner of the puppy needs to conduct regular inspection of the oral cavity of his pet and you need to do this 1 time per day. Some dog breeders mistakenly believe that it is not necessary to pay attention to the growth of the milk row, since it will still change. Veterinarians have a different opinion and believe that on how favorably the period of growth of the milk dentition has passed and its timely replacement depends on what the dog will have permanent teeth.
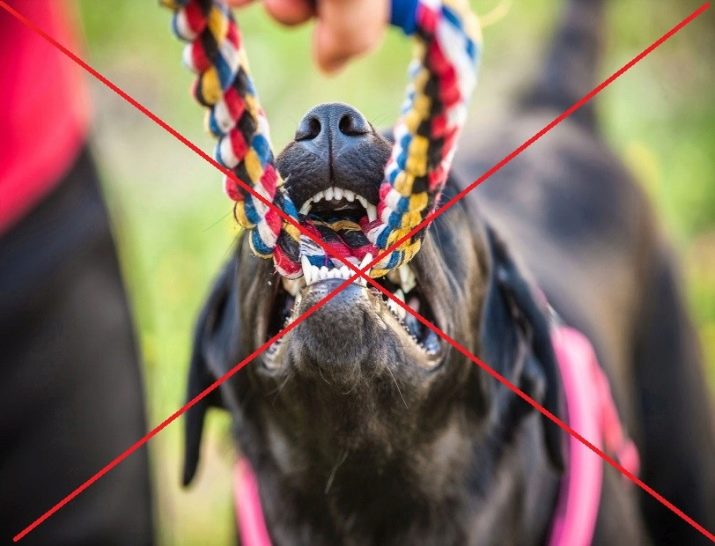
During the period of change and growth of the dentition, one cannot play games with the dog where she will have to forcefully pull her teeth - this can lead to serious injuries to the gums and dental units.

After the appearance of permanent teeth, they need to be carefully taken care of - the dog's oral cavity is treated with special toothpaste and a brush with a soft short hair. It is advisable for the pet to carry out this hygiene procedure every day on a regular basis.
In order for the dog’s dentition and bite to be formed correctly, she needs to be given sufficient load on the masticatory muscles. The dog must have a large number of toys of varying degrees of hardness, and also need to be given such food where she could use teeth - pieces of meat, cartilage, granules of dry food, bones.
Dogs that eat soft types of food, such as paste, porridge, meat soufflé, are much more likely to suffer from caries and malocclusion. Moderately-solid food helps to mechanically cleanse the surface of the teeth and strengthens the dog’s gums.
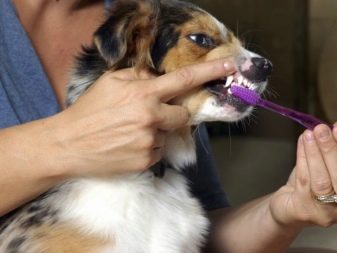

During the period of growth of the dentition, the dog needs to provide a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals - only in this case the tooth enamel will be formed strong and healthy. Preparations with calcium, fluorine and magnesium are introduced into the dog's diet in those volumes that correspond to its body weight. To choose the right dosage of the vitamin-mineral complex, it is best to seek the advice of a veterinarian.
Permanent teeth for the pet must be protected - for this Do not play games with him that could ruin or break the dog’s teeth. For example, it is not recommended to twist the stick that the dog holds in its mouth, do not pull the rope or rag with force, the tooth can become tangled in its fibers, and you accidentally pull it out. The health and longevity of a dog is largely dependent on the good condition of its teeth, therefore the owner is required to help his four-legged friend cope with this task.
For tips on changing teeth in dogs, see the video below.