Overlock is very useful in sewing, when you have to overcast the edges of the fabric, especially thin and loose. This is a highly specialized and at the same time advanced in capabilities machine that can perform many types of overcasting, flat and role seams. The seams are performed with an overlock usually in 2, 3, 4 or 5 threads. In this article, we will consider the last option - a four-thread overlock.

Four thread overlock selection
Since different types of overlocks perform different types of stitches, a 4-thread overlock has its own scope. Compared with 3-thread, it has more advanced functionality and is included in the category of semi-professional overlocks. On a machine of this type, you can overcast the edges in 3 or 4 threads, and the seam width is adjustable - you can adjust a narrow or wide stitch. Also on most four-thread overlock models Several flatlocks of various widths are available.
The set of functions of this technique also includes a role seam (it is also called a hem). Note that all of these operations are basic, which any budget overlock should support, but they are performed with higher quality than a simple sewing machine. With the help of the latter, you will not be able to perform overlock seams, zigzag over the edges.
The quality of the overlock seams corresponds to the factory one, the machine's functions also include smooth edge trimming with the help of built-in knives.



The special functions of four-thread overlocks, for which they are usually bought, include working with loose fabrics, knitwear and elastic materials.This is already a more difficult level of sewing work, compared to sewing simple fabrics and turning their edges. The four-thread overlock also allows you to strengthen those parts of the product that will be subjected to more severe loads during use.
Thus, we recommend purchasing a four-thread overlock if your plans include working with the listed types of materials. Pay attention to the four-thread seams that a specific overlock model can perform, namely for what purposes they are performed and with what materials they are used. The main feature of the four-thread line is that in addition to the “base” of three threads, there is another, reinforcing line of the fourth. When you work with stretchable materials, this stitch plays an important role.


Models of four-thread overlocks can differ in the way of threading threads, material feed, in the number of settings and sewing speed. Most modern high-quality four-thread overlocks have differential feed. This ensures smooth fabric advancement without jerking or stretching. The threading in the loopers can be manual and automatic (the price of the machine depends on this), the same applies to adjusting the thread tension.

When selecting automatic or manual functions focus on your needs. If you have to perform a small number of sewing operations, and each of them does not involve complex settings, you can do with an overlock with manual dressing and adjustment. In other cases, you should consider purchasing an automated machine - for example, advanced four-thread overlocks are equipped with an automatic threading system in the lower looper.
The most expensive ones have a LCD display on which the basic settings are displayed.


How to thread the four-thread overlock?
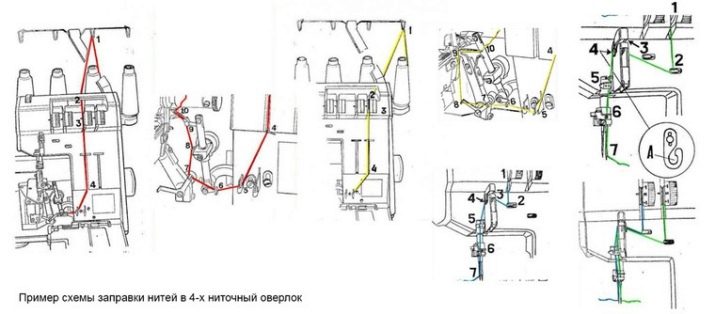
The process of threading the overlock is somewhat similar to refueling a sewing machine, but at the same time it has significant differences. Note that the instructions below correspond to the common overlock class 51.
To thread the four-thread overlock, thread them through the holes of the thread guides on the machine body, and then thread them into the thread tensioner plate, as shown in the threading chart in the instructions that came with your model. Then the thread is redirected to the needle and threaded through the overlock foot. To check if the thread is threaded correctly, It is recommended to make a test stitch before starting work.



Overlock loopers looped separately. The location of the thread mounts and tensioners in the loopers should also be checked according to the manual, these places may vary between different models. Modern overlockers for threading in loops often have a color coding system that greatly simplifies this process, or you can just use different color threads.
Four-thread models have several distinctive features that are essential when refueling: the thread from the left needle is threaded through the left tensioner, and from the right, respectively, through the right. But the thread tensioners in the loopers are located on the opposite principle.
In any case, a threading scheme should be applied to the body of any overlock, and you can properly prepare the machine for work by following this scheme.
Thread tension and stitch adjustment
After the threads are tucked into the overlock, you need to correctly adjust their tension, as well as the sizes of the stitches. Most models of overlocks have a disc with digital values of thread tension (if the type of adjustment is manual). Integer values allow you to approximately set the tension level, for more precise settings are half divisions. To understand, reduce or increase tension, you need to look at the line. If wrinkles form on the fabric along it, you need to loosen the thread, if the stitches in the line resemble a ladder - on the contrary, increase it.
Thread tension is associated with the regulation of stitch length and stitch width. For most four-stitch seams, the correct stitch setting assumes a 2.5-5 mm stitch length. With other sizes, you need to be careful that there is no contraction, and if necessary, compensate for this by tensioning the thread, as described above.


Work with seams
When dealing with various four-thread stitches, it is useful to know some basic tricks. For example, when fitting products and correcting some areas of clothing, you may need to open the seams. When changing old products, this generally takes a substantial part of the work. To open an overlock seam with scissors or a razor is one of the options, but not the most convenient. You will have to cut many threads, and then remove their trimmings. It is better to dissolve the seam first, and then opening and removing most of the threads can be done much faster and easier.
To quickly dissolve the threads of the overlock seam, take a closer look at it and find the top line - the one closest to the edge. You need to pick it up with tweezers or a needle and pull it out while opening the threads of the other end of the seam.
Then the operation will need to be repeated with the bottom line, and the entire seam will sprawl itself - it remains only to remove the threads.


conclusions
Thus, the four-thread overlock as a semi-professional overcasting machine is well suited for seaming the edges of products from most materials. It has many useful settings. Developers of modern models of such overlocks seek to bring the setup process to the most simplified standardized operations. In order not to waste unnecessary efforts when operating the overlock, It is recommended to purchase a machine with a convenient threading system (supporting color coding or with automatic looper dressing).

Also in practice, differential feed and sewing speed are important. High-speed models are those in which the last parameter is 1300-1500 stitches per minute. Finally, do not forget about such a simple but useful function as backlighting. It is much more convenient to work with models that are equipped with LEDs. Based on these criteria, you can choose the four-thread overlock that suits you.
In the next video you will find an overview of the four-thread Jack JK-798D-4 overlock.










