When a childhood friend meets, after many years the mental manipulation of images enables a person to reproduce some necessary details of information and find out in the changed appearance the features of a school friend. At this moment, visual-figurative thinking is triggered.
Features
In psychology, this type of thinking is referred to as a symbolic act of thought, in which a problem is modeled and solved using representations. This involves mental work with operating objects and visual images. This type of thought process helps the subject to recreate the variety of different characteristics of a particular phenomenon or object, to establish their unusual combination.
Visual-figurative thinking is inextricably linked with real actions and objects. In this, it differs from imagination, in which the image is recreated from memory. This type of thought process is subject to perception or perception.
It dominates in children aged 2 to 5 years. Kids think in visual images and do not own concepts.

We give an example. The child is shown two identical balls made of dough. He visually examines them, estimates the volume. Then, a cake is made from one ball. The volume did not increase, but the shape changed. Nevertheless, now the cake requires a lot of space on the table, which means, according to the baby, there is more dough in it than in a ball. In children, this type of mental activity is subject to perception, so it is difficult for them to abstract from what is immediately evident.
Older preschoolers and primary school children are also characterized by a visual-figurative thought process. When the teacher, when explaining the new material, reinforces the information by demonstrating the subject or its image, he uses the visual-figurative thinking of the students.
Mastery of manual skill is achieved using this type of thinking. In developed forms, such thinking is characteristic of people in creative professions. Writers, poets, designers, fashion designers, artists, sculptors, musicians, actors are able to vividly and vividly represent certain objects, phenomena or events.
The combination of some elements of the object, their movement, the ability to highlight the main signs in the mind create the basis for the formation of a visual-figurative thought process. For this purpose, special tasks have been developed.

Raman
This exercise allows the baby create a new object based on a set of specific images. The source material can be digital and alphabetic characters, mathematical signs, geometric shapes. For example, a child is offered to portray a cat or a dog from digital signs. Often the baby is given complete freedom of action and they look in which direction he is directing his imagination.
Finding and restoring the missing part also belongs to the combination group of exercises. The game “Chessboard” is also used. The essence of the game is to create a field of various elements, while you need to alternate the particles.
Gradually increase the size of the fields and the time to reproduce them.
Transformational
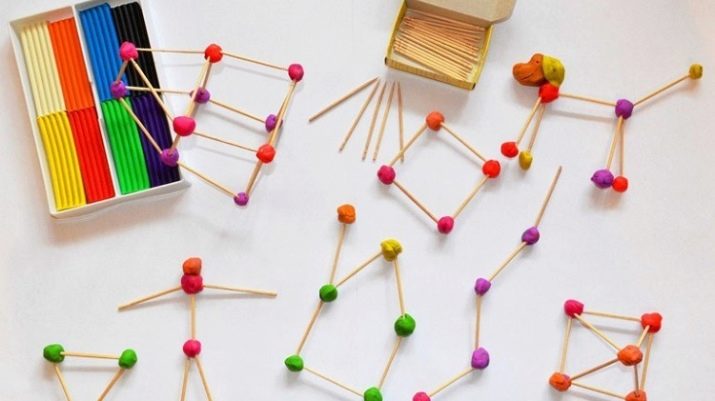
To perform this type of exercise they take a finished finished image and offer the child to change it, create something completely new. Usually matches or sticks are used, from which a certain figure is folded. The kid must shift a few matches so that a new item is obtained. Sometimes they suggest removing a few sticks to change the image.
An excellent job for speed is rendering. For example, all participants in the game are handed out leaflets with twenty depicted letters "M". Each graphic sign must be turned into a new subject, but in such a way that all 20 created images of the surrounding people can recognize. Then the originality and recognition of the depicted objects are discussed.

Why is it important?
This type of thinking is clearly manifested in preschool age. At this stage, there is an accumulation of various visual, tactile, sound displays, with which the baby is easier to interact with the outside world. In the thought process carried out with the help of images, imagination, spatial perception, the logical construction of structural chains, and assessment of the situation are actively used. A child develops the ability to represent an object without having it in sight.
Psychologists recommend that much attention be paid to the development of a visual-figurative thought act, because this process helps the child to master three-dimensional display, spatial thinking.
The use of images forms the aesthetic component of the personality, develops creative mental activity, accelerates the solution of logical and mathematical problems.

How to form?
The active formation of such thinking begins at the age of three. Certain images gradually develop, information accumulated in early childhood by feeling and examining things accumulates. Then the children's imagination rapidly develops, and the baby is able to think up or imagine a phenomenon, an object, an integral situation. It is necessary to teach the child to mentally see objects in different spatial positions, to change their location in the mind.
Psychologists use various techniques to diagnose the necessary degree of development of a visual-figurative thought process.
- There is a way to work with ridiculous images. The kid is offered a picture with a character who finds himself in an unusual situation when the hero has to perform an action unusual for him. For example, instead of a chick, a frog sits in a nest, and a bird brings her a bone for food. The child explains why the image does not correspond to reality. He must determine what happens in nature and offer his own version of the development of events. If a child copes with 7 out of 10 tasks perfectly, then his visual-figurative thinking is at a high level of development.
- The design method involves painting the image. The speed and accuracy of the reaction are evaluated. The kid is given pictures with familiar animals, toys, geometric shapes drawn. He should complete the drawing in one and a half minutes. The speed of the task is important.
- The “Collect Picture” technique involves restoring an entire image from familiar fragments. Evaluation criteria are determined by the speed of execution. With good imaginative thinking in a child, several minutes should be spent on assembling the picture. During this time, the baby connects imagination, memory and applies the method of exclusion.
- There is also a technique based on the search for an excess image. The kid is given several signs of pictures similar in some groups. He must find a print that does not match the basic composition of the grouped images.




Development methods
A three year old child needs collapsible toys. First, he is shown the correct disassembly and assembly of the pyramid, then the baby must repeat the action. Over time, the study of the properties of the subject is added. The kid learns to determine the shapes, sizes of objects, to distinguish shades. It is important to interest the child, draw him to draw with pencils, felt-tip pens, crayons, paints. Before drawing or building a tower, the child should talk about his next steps.
Children 5-6 years old perfectly develop a figurative thought process with games with designers. They master the construction of visual spatial models that reflect the connections and relationships of real things. The development of a figurative thought process forms flexibility, mobility and the ability to operate with visual images.
For older preschoolers, the development of the thought process with the help of images stimulates the use of the following methods and techniques:
- observation of natural phenomena with a subsequent description and image of the information seen or heard;
- assembly of puzzles;
- solving puzzles, puzzles, riddles;
- Sketches from memory;
- the image on the sheet of concepts that do not have visual signs: fun, joy, sound, friendship, melody, thought;
- modeling from clay, clay;
- visiting museums, exhibitions, excursions;
- creation of different applications.

The development of preschoolers provides for the following main stages of education:
- demonstration;
- explanation;
- teamwork;
- independent actions on the model and creativity, not limited to a certain framework.
The formation of the children's thought process with images is facilitated by exercises where it is proposed to describe a rainbow, sunset, dewdrop, massage brush or any other phenomena and objects. Widely used exercises with varying sticks or matches, turning over some symbolic signs, for example, the letter "E" to get another letter: "W".
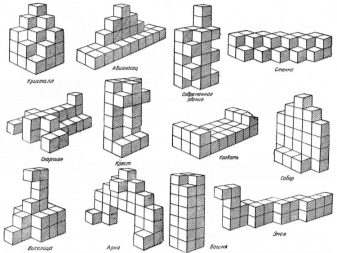
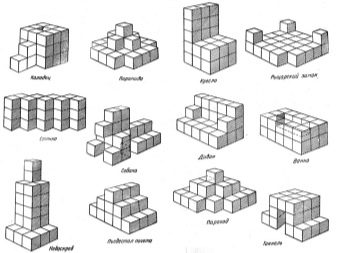
Cubic Quests very effective in terms of the development of visual-figurative thinking. The exercise is mastered in stages. First, 7 elements are constructed from 27 ordinary cubes.
- At the first stage, children are invited to carefully examine them and find similarities with some objects or forms. The more associations found, the better.
- The second stage involves the neat connection of the two elements.
- At the third stage, the baby is advised, after carefully examining the figures, to first dismember them, and then again fold the details into exactly the same object as they were.
- The fourth stage involves assembling the figure according to the model. First, a bed, sofa, snake, boat or other object is made of cubes. The kid carefully examines it, analyzes it. Then the sample is closed, and the child from memory must build the same object. In conclusion, it is compared with a sample.