Bronze - the first alloy that people learned to make thousands of years ago. Since then, bronze products have been very popular. Today, modern craftsmen are trying to adapt foundry technologies to home conditions, for this it is necessary to know the chemical composition and physical properties of bronze, as well as the technical characteristics of the alloys obtained from it, including aluminum bronze.
This article talks about such an important indicator as melting temperature, as well as how to gradually carry out the process of melting and casting bronze.



Melting temperature
Exist table of melting temperatures of different types of bronze. Before proceeding directly to melting, it is necessary to understand what the temperature depends on at which a particular metal begins to melt or completely goes into a liquid state. Bronze actually represents a number of different alloys, which include copper as the main component, and other elements as additional (alloying) elements.
Such alloying substances may be aluminum, beryllium, tin, silicon and so on. That's just on the chemical composition of bronze all depend physical properties metal, including the melting point. To melt a copper alloy, you need to know it chemical composition, the only way to correctly determine the melting temperature in degrees Celsius. Let's get acquainted with the melting points.

Pure metal
Although it is extremely disadvantageous to produce pure copper, since its technical properties are in many ways inferior to the special grades that are made from this metal in the metallurgical industry, nevertheless the melting point of copper is necessary.
Why? The fact is that those brands of copper that are used in the national economy have in their composition a negligible amount of alloying substances, which are considered as impurities. Thus, due to the insignificance of their quantity, the melting point of copper grades is close to the melting point of pure copper and is approximately 1084.5 degrees Celsius.
As already mentioned, the melting temperature depends on the composition of the substance, for this reason, the melting temperature of bronze varies between 900-1140 degrees Celsius.


Mixtures
Bronze tin reduces the melting point of such alloys, it does not exceed 900-950 degrees Celsius.
Tinless, including aluminum bronzes have a wider range of temperatures that depend on the chemical composition of the copper alloy. Their melting point is 950-1080 degrees. It is also necessary to consider that bronze has high viscositytherefore, it is overheated after the final melting to ensure better melt flow. Let's look at the process of melting and casting bronze in stages.



Step-by-step instruction
In artisanal conditions, mainly small bronze items are made, for example, decor elements. More complex parts require high-precision casting, the technology of which is very difficult to implement without a specially adapted for these purposes premisesas well as special equipment. In some cases, you have to resort to fine-tuning the casting to the desired state using editing at homesuch as removing excess molten material by hand, grinding and polishing the product.
Before starting to melt the metal, it is necessary prepare the room and acquire the necessary tools and equipment. The main requirement for the room is the presence of good exhaust ventilation, as well as a floor made of non-combustible materials such as concrete, cement or brick. In the manufacture of small products, these requirements are quite simple to comply with, otherwise you will have to use a garage.
In order to make bronze smelting at home, you need to purchase a special muffle furnace with the ability to control the temperature, but you can get by with simple mining, the fuel for which will be charcoal.


Tool preparation
The novice caster should purchase or make the following tools on their own.
- A refractory crucible made of refractory material (such as cast iron or steel) is a special vessel with a spout where pieces of molten metal are placed.
- Devices for removing the crucible from the furnace, which minimize the risk of burns, are special hooks and tongs.
- Mold for pouring molten metal, which is made using the flask and model.
- The flask itself - two boxes that hold the mold with filler from the molding sand.
- A welder’s suit or just a very tight apron and mittens, the purpose of which is to protect a person from flying sparks and splashes of molten metal.


Once you are convinced of the presence of all of the above, you can proceed directly to the melting of bronze.
- Preheat ovenby setting the temperature with the knob. The temperature depends on the chemical composition of bronze, as we discussed above. For example, for aluminum bronze, this temperature will be 1040-1084 degrees Celsius.
- Next is a must warm up the form, this is done so that the molten metal does not freeze when it enters a cold container.The form is placed in the oven when it warms up to a temperature of 600 degrees, after which the thermostat is set to 900 degrees. When the temperature inside the oven rises to 900 degrees, the mold is left to warm up for 3-4 hours, after which it is carefully removed using special devices and cooled to 500 degrees Celsius.
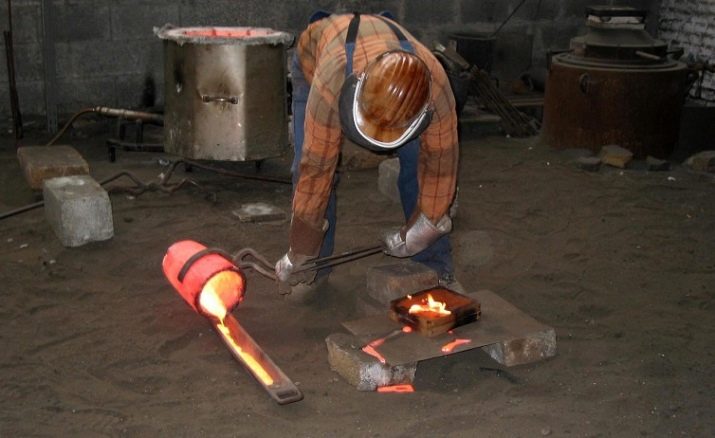
- Put a crucible with pieces of bronze, intended for melting, inside heated to the desired melting temperature of the furnace and brought to complete melting of the metal. After that, the crucible is left to overheat for another 5 minutes in order to achieve better metal flow and better casting quality.
- Pull a crucible from a furnace or a hearth using hooks and tongs and begin to fill in the mold.

Let's look at how to make it right form for obtaining high quality products. In foundries, this mold is made using flask where they pour a mixture of clay, sand and coal powder. The flask consists of two halves, each of which is a box where the molding mixture will be filled.
- First, take the first box and begin to fill it with the mixture, pouring it to half, put the model inside the box.
- Then continue to pour bulk material until they fill the box to the very top. During operation, it is required to constantly level and tamp the molding mixture.
- Set on top of the second box and continue to pour a mixture of clay, sand and coal powder.
- In the second box, it is necessary to provide sprues - holes for pouring molten bronze into the mold.
- When both drawers are filled to the top, they are separated using a sharp object. One half of the model is in one drawer, the other in the other.
- They carefully take out the model, reconnect both drawers - the resulting emptiness is the form for filling.


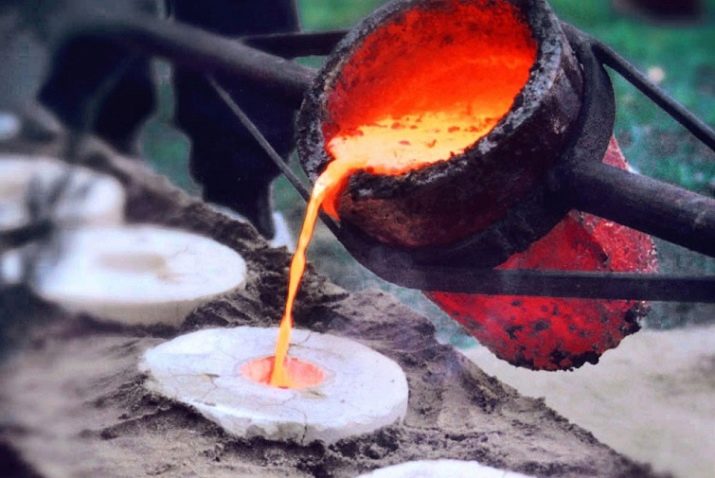
Casting mold
The molten metal is poured from the crucible into a thin stream moldmaking sure that the trickle flows continuously. If the molded part is notable for the complexity of the outline need to use a special centrifuge, which with the help of centrifugal force will help the melt to distribute correctly inside the mold, completely filling it.

How to improve product quality?
In fact, truly a quality thing cannot be obtained at home without refinement.
You can also improve the quality and appearance by making mold using fusible material. To do this, they preliminarily make a plaster cast from the model according to which our part will be manufactured, this cast should consist of two parts that fasten to each other. Paraffin or wax melted in boiling water is poured into the formed cavity, and after its solidification, the gypsum shell is removed.

Next, the resulting fusible model is placed in a special casting mass, forming holes for draining paraffin and gulf of molten bronze. After that, the foundry mass is placed in boiling water, the paraffin melts, and it is easily poured out of the mold.
The resulting mold has a greater smoothness, it produces better products than from a mold made in the usual way.


The following video shows the process of smelting bronze at home.










