Cats are believed to have special vision. They are credited with a vision of the other world and many magical properties. To dispel all doubts, let us dwell on this issue in detail and examine how cats see our world, how they perceive humans and whether they distinguish colors.

Features of the structure of the eyes
Cat's vision differs from the human eye in the structure, the number of cones and tubules. In general, the structure of the eye in humans and cats has many common features. The top layer is the cornea - a light-refracting barrier. Under it is the choroid, which in front forms the iris and pupil. The iris is a muscle ring, and the pupil is a hole in it. Behind the iris is a mineral glassy lens. The inner shell is represented by a photosensitive retina, consisting of rod cells that perceive movement, as well as cones responsible for color perception. On the back side, nerve endings approach the inner lining of the eye. Inside the eye is a clear, thick, fluid.
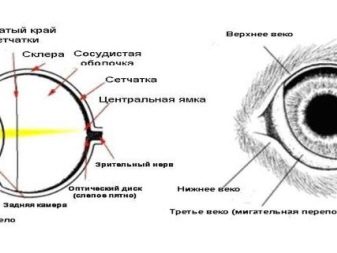

The type of vision in cats is binocular, due to which animals are able to assess the distance to the subject. They determine the location of a specific object by the difference in the location of the image on the retinas of the left and right eyes. However, the structure of cat eyes has the following features:
- the cornea in the cat's eye is larger and occupies almost the entire surface of the open part;
- the shape of the cat’s pupil is elongated; this feature explains the possibility of narrowing and limiting the amount of incoming light;
- between the retina and choroid there is a tapetum (a reflective membrane similar to fish scales), due to which part of the rays is reflected on the retina;
- the cat’s eye does not have a blind spot, at this point there is a special disk with cones;
- rods in the eye are much larger, which explains the ability of the animal to see in the dark.
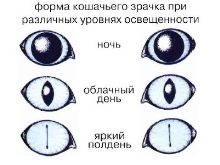

An interesting feature of the structure of the cat's eye is the multiplicity of light reflection. It is due to this that the eyes of cats glow in the dark, as well as in cases when, for example, lamplight is induced on animals. However, who would have thought that cats in daylight see worse. This fact is explained by high photosensitivity. To better see the object, the cat narrows the pupils, focusing on a specific subject, while the vertical pupil helps her protect her eyes from ultraviolet radiation.
Pictures taken with each eye merge into one, but the clarity of vision in the light is worse than in the dark.

Color perception
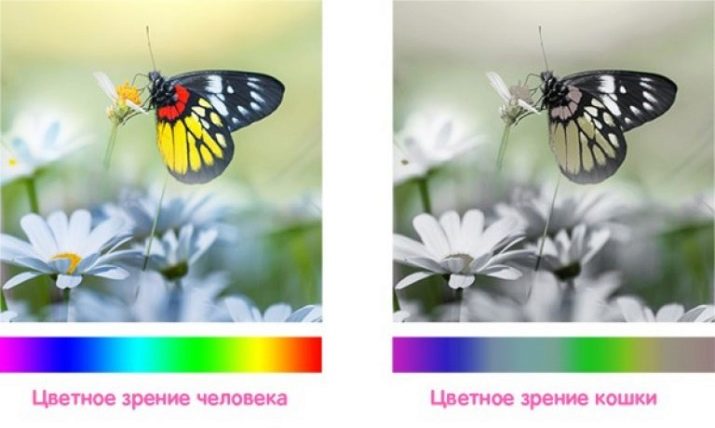
The widespread belief that cats see the world in black and white is not true. In fact, they are able to distinguish some shades, although the degree of their saturation is not the same as a person sees it. If we can distinguish a lot of color shades, then cats do not have so many. Moreover, almost all of them are less saturated and, most likely, even faded, shrouded in foggy haze.
They distinguish between shades of blue and green, they see gray and smoky tones. These colors are not accidental, due to photoreceptors in cats, night vision is better, therefore, the eyes of a cat do not perceive red, bright orange and yellow tones. Rather, due to the smaller number of cones, the paints will approach the tones characteristic of sharp night vision. For example, a cat will see yellow as greenish with yellow and gray shades, but the color will be warm.

The color palette of the animal's vision includes purple. His pet sees not too distorted. It is noteworthy that cats perceive colors of cold temperature better. However, the spectrum of distinguishable tones directly depends on the degree of illumination, for example, in evening light, the shades may seem different, so the animal can confuse the same orange with red.
In general, cats do not have three, but two types of photoreceptor cones, which are responsible for color day vision. It is generally accepted that they are able to distinguish up to 25 shades of gray, but the situation with the color palette is worse than with the neutral one. This gradation is explained by the number of cones responsible for the perception of a particular color.
For any color that the animal sees, its own group of cells is responsible.

The percentage of each class of cones is different from the human. That is why the photosensitivity to the components of the solar spectrum is different. However, due to the presence of tapetum, activity in daylight or artificial lighting is hindered. Moreover, the tapetum itself does not emit light particles, it only reflects those that are.
In general, in addition to gray, the cat sees 6 primary colors (blue, white, yellowish, green, purple, black), and most clearly they perceive blue and purple. Red, brown, they merge into one color, which has a grayish admixture. They see it as if they had reduced the degree of brightness in a graphic editor by squeezing a color out of it in favor of neutral colors.

How do they see in the dark?
Often you can hear the phrase that cats perfectly see in complete darkness. This statement is incorrect: for the visual perception of surrounding objects at night, cat's eyes need at least a small amount of light. Their visual acuity is much better when compared with a person, but also a considerable part of the orientation in space is explained by the sensitivity of vibrissae, which provide information due to air vibrations. It is noteworthy that the cat feels the slightest vibration coming from the mouse paws. To understand which way the prey ran, she does not need to see several times better than a person. Just touch the ground with a vibrissa.
If we compare vision in the darkness of a person and a cat, then the gain will be 6: 1 in favor of the animal or even more due to the high concentration of photoreceptors. At dusk, the pupils of the animal expand, which allows you to catch the smallest particles of light. In relation to the body, the eyes of the animals are quite large, so cats are often called the most big-eyed pets. In the dark, the pupils seem to be bottomless, light is absorbed and reflected from the tapetum, after which it returns to the nerve endings.
At the same time, it seems to the person that the cat's eyes are glowing. In the dark, the pupils are dilated, which is necessary for greater absorption of light.


Ferris sector
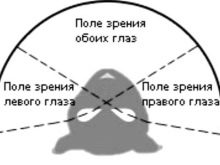
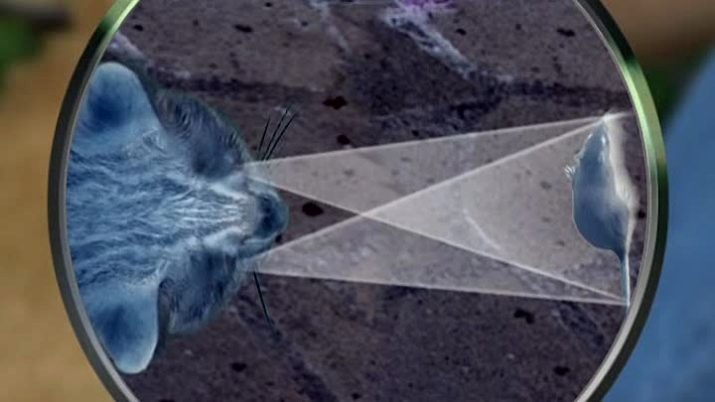
Due to the structure of the eyes, holding a cat is almost impossible. For a couple of seconds, she could bask in the sun, and after a moment she was able to jump up sharply and grab the prey. Agility is explained by the angle of view, which is much larger in comparison with a person. It is due to him that the animal can see what is happening around. The pupil shape in cats can change, depending on the strength of the light flux. Surprisingly, it can change the width.
The animal perceives the world with two eyes, in view of its special structure, a cat can easily move them relative to the visual axis. Each of her eyes sees 45% of the picture. The cornea is convex, so that coverage can reach 200 degrees versus 180 in the human eye. The outlines of the vertical pupils can change almost instantly, which occurs under the influence of external stimuli, so the pupil can be not only round, but even slit-like. The breadth of angular vision in cats is greater than in humans.
Making eye movements by changing the visual axis is a feature that explains the reason why a dormant animal can instantly grab a mouse running past. With about the same ease, cats follow flies and other flying insects.

Size matters
Regarding the size of the objects that the cat sees, there are conflicting opinions. Someone is sure that the cat does not see large objects located nearby. It is emphasized that if the object is motionless, vision is even worse. However, one can argue here: a cat without fear jumps on boxes, cabinets and even a person, cleverly climbing on it. If she could only see silhouettes and outlines, she could hardly move with great ease and grace.
Most likely, breeders who adore cats have often noticed that pussies are more responsive to movement. Having planted the animal in front of him, the man blinked, and the cat immediately caught this movement, despite the fact that the human eyes were very close to the eyes of the pet. One could say that the animal reacts to the air flow more than to the eyes. However, if you do not blink, but look with your eyes left and right, there are no air currents, but the cat at that moment marks the movement; what is happening is literally in front of his eyes. At the same time, he does not move back, does not squint, does not try to focus, which means that he has no problems with vision. He instantly notices movement: what are the burning hunting eyes talking about.

One can argue with the opinion that animals do not perceive different objects poorly on the screen of a monitor or smartphone. If you monitor the pets for a long time considering what is happening on the record, then he proves: they can recognize on the screens of their owners and with curiosity follow the movements of other animals. There is a known case when a cat who misses the deceased owner, for a long time watched the recording on the smartphone, where he was captured. Her eyes focused precisely on him, she rubbed her face against the screen and purred.
As for the sense organs, then, of course, they add to the accuracy of world perception, and therefore help to determine the size. At the same time, mustaches give clear information about the location, degree of remoteness and size of different objects. Together with them, vision is a survival mechanism that enhances hunting instincts.
The cat perfectly sees objects that are far from it, but as they are removed, their outlines gradually blur.

Perception of the world
Most likely, cat breeders were faced with the fact that their pets had to literally dunk in food that was in front of the animals in the animals. And the point here is not in bad sense of smell, but in the peculiarities of vision. Cats may not see clearly objects that are in front of their noses. Individuals are farsighted, clearly distinguishing between objects that are located from them in the range from 70 cm to 6 m. This distance allows you to calculate the length, height and strength of the jump. However, if you follow the behavior of some individuals, you can find that they with pleasure and high accuracy fall into their “prey” with their paw, playing with the tablet. Considering that it is nearby, the size of the object is small, and bright light comes from the screen, this may indicate that not all individuals are farsighted.
Games for cats allow you to conduct a lot of experiments showing that pets react to different moving objects in different ways.

The opinion of how a cat sees a person is also contradictory. It is generally accepted that the animal does not see the owner clearly, but it does not focus its eyes, does not look at it or other objects, as visually impaired people do, it does not pull back like farsighted ones. The animal moves quite confidently, it is not unusual for it to be awkward when the owner or any large objects are nearby. The cat very accurately calculates the accuracy of the jump, being on the windowsill. He can easily jump into the window, without hitting the flower pots located nearby. It is unlikely that he would succeed if he only saw the fuzzy outlines of objects and relied solely on his vibrissa. Of course, the ability to rotate the eyes helps in quick orientation, but focusing is also important.
As for attributing to cats magical properties or the so-called sixth sense in relation to humans and the world around them, it is explained by the presence of vibrissae located on the cheeks, above the eyes, and also on the paws. It is they who give the animal information about the danger, but not the effect of otherworldly forces or a special magical look.
Neither the large size of the eyes, nor their structure in any way affect the cat’s ability to look into other worlds. Cats do not see the other world, neither dead people, nor ghosts. They see us a little worse, but in general their daytime vision is not so bad.

See how cats see the world in the next video.


































