Almost every one of us is afraid of something. Some people cannot stand the darkness, others are afraid of heights or depths. But this fear does not always turn into a phobia. Normal healthy fear is dictated by the ancient instinct of self-preservation, survival, and there is nothing abnormal in it. Phobias, on the other hand, can change a person’s life, limit it, so they definitely need treatment.

Definition
Phobias are an inexplicable fear of something. This fear in most cases has no sound basis, but it has pronounced signs. From horror, a person loses control of himself, his heart rate quickens, his breathing depth changes, muscle cramps, nausea and vomiting, loss of consciousness, dizziness can be observed. A lot of phobias are accompanied panic attacks.
If, after an attack, a person is asked what exactly he is afraid of, then in most cases the answer will be that there is nothing to be afraid of. Fobes perfectly give an account to themselves of the groundlessness of fear, but they can not do anything about themselves in a moment of fright and panic. Therefore, they find no other way out how to start avoiding frightening traumatic situations, bypassing them, build your life in such a way as not to see, not to listen, not to perceive dangerous circumstances, to stay away from them as far as possible.
So people with fear of a confined space refuse to travel in the elevator and always walk, and sociophobes, afraid of public condemnation and society as a whole, close within their four walls and lead a hermit lifestyle,Aerophobes can travel at any distance only by land transport, without risking flying on planes, and no-ones who are afraid of the dark can only sleep when the lights are on.

Phobia is called any irrational fear of a person who, to one degree or another, forces him to change his life. Phobias are not considered a mental illness in the full sense of the word. They relate to anxiety disorders of personality. But this does not mean that phobias do not need treatment. Avoiding disturbing situations can greatly facilitate the existence of a phoba, but cannot eradicate his problem. And every time a person finds himself in certain situations or circumstances, he will experience panic horror, the attacks of which are noticeable even on a physical level.
Phobias gradually make a person a hostage, force him to make not the decisions that he would like to make, force him to abandon his dream job, sometimes from creating a family, from communicating with his own kind, from traveling.
The quality of life is steadily declining.
It is considered that almost 70% of the world's inhabitants suffer from various phobias, but only 8-11% of the population has fears in a pathological form. Asians, Africans and Hispanics, according to scientists, are less prone to phobic disorders than Europeans and Westerners. Women and children suffer from phobias more often than men.

The sooner the problem is noticed, the greater the chance of its complete cure. But true phobes rarely come to psychiatrists and psychotherapists for help at the initial stage of their disorder. And in most cases, a doctor is contacted even when the phobia begins to coexist with other mental disorders, such as clinical depression, obsessive-compulsive disorders, and sometimes schizophrenia and various mania.
A phobic mental disorder in itself increases the likelihood of developing other mental problems.
Varieties
The exact number of phobias that people are exposed to is not known to science. But the lists currently existing include about 300 types of fears from the classical ones - fears of darkness, heights, depths, cramped spaces, death, to very original ones - fears of mother-in-law, fears of the pope and cumpunophobia (panic button fear).
The lists of phobic disorders are regularly updated with new ones that correspond to the spirit of the times, for example, imohyphobia - this is a panic fear of incorrect use of emoticons in correspondence on the Internet, fear that the selected "faces" and "buns" will be misunderstood.

Conventionally, people's fears can be divided health concerns, food, spatial, natural and social. There is also a separate group of phobias - mystical.
The first group is the largest. Basically, it refers to all phobias in which a person experiences panic horror from the prospect of getting any particular disease or group of diseases. Such fears may be caused by the fact that the disease was in one of the relatives, in the patient himself, or in the abundance of frightening information about the disease, which for a particularly impressionable and disturbing person may cease to be just information and become a danger signal.
Here are just a few phobias of the first group:
- acliophobia - pathological fear suddenly deafen;
- acnephobia - irrational fear of acne;
- anginophobia - fear of sudden suffocation;
- apoplexyphobia - fear of cerebral hemorrhage, stroke;
- misophobia - fear of dirt, microbial infection, infectious diseases, manifested by a pathological attitude to the purity of your body and surrounding space;
- hydrobromophobia - fear that others will feel an unpleasant smell of sweat, body odor, manifested in the excessive use of deodorants, frequent washing;
- venereophobia - pathological fear of sexually transmitted diseases, which can even lead to a complete rejection of sexual relations, kisses, hugs;
- hemophobia - fear of blood type;
- carcinophobia (carcinophobia) - pathological fear of getting cancer;
- Maniophobia - a strong fear of possible mental illnesses, which, as it seems to the patient, can develop at any time;
- peladophobia - fear of baldness, in which a person is painful for bald people, tries to avoid contact with them, meetings, and is also overly concerned about the health of his hair;
- jatrophobia - pathological fear of doctors and nurses, often accompanied by a complete refusal of treatment, examinations, visits to medical specialists.


Food phobias come from certain beliefs of a person about food and sometimes cross all reasonable boundaries. These include fears such as:
- sitophobia - pathological fear is in general;
- phagophobia - fear of swallowing so as not to choke;
- hemophobia - fear of chemical additives in foods;
- toxicophobia - fear of being poisoned.

Most often, people have phobias associated with natural phenomena and animals. Quite widespread fears such as:
- arachnophobia - pathological fear of spiders;
- felinophobia - fear of cats and kittens;
- musophobia - panic from the sight of mice, rats;
- kinophobia - fear of dogs of any breed and size;
- herpetophobia - fear of snakes and reptiles.

There are people who are panicky afraid of thunder. They suffer brontophobia. And those who do not go to the forest, pathologically afraid of getting lost in it, are called hilophobic. If a type of fire causes a person to have a panic attack, then his problem is called pyrophobia, and walks with a dosimeter in your hands because of fears that the level of radiation will suddenly rise are caused by radiophobia. People who are afraid of the sea are called thalassophobia and those who cannot raise their heads and look into the sky without a panic fear of this action are called uranophobic.
Spatial phobias are well known due to the fact that they are often covered in films and books. For instance, claustrophobia - fear of enclosed spaces inherent in 3-5% of the world's inhabitants to one degree or another, and agoraphobia (panic fear of open spaces and crowds) affects up to 2-3% of people. This also includes fears of large empty spaces. (kenophobia), as well as fear of very large objects (gigantophobia)fear of entering tunnels (tunnel phobia) and fear of crossing the streets (agirophobia).

Social phobias are also a great layer of human anxiety. This includes all fears that are somehow related to interaction in society. These are the most complex phobias that are the most difficult to correct. These include social phobia (fear of society), androphobia (pathological fear of men), autophobia (panic fear of being alone) gamophobia Fear of engaging in marriage kakorrafiofobiya - fear of making a mistake, failing, gelotophobia - fear of being ridiculed.
There are phobias associated with personal space within society. So, the fear of the unknown (aglosophobia) makes a person almost constantly suspicious of others and be in enduring tension and anxiety.
And the fear of being robbed, robbed (kleptophobia) can quickly transform into a real persecution mania or paranoid disorder.
People are afraid of a wide variety of things - from electricity and cold to alien invasion (ufophobia). Recently, fear of a zombie apocalypse is gaining momentum (cinematophobia) it forces people to build bunkers on a private site, to reserve canned food and batteries for the future.
People are afraid of everything mystical - demonophobia it is a fear of demons and the devil. The real panic in some is caused by the fear of numbers (both generally accepted, for example, “13”, and some personal numbers that are important for a particular person). There are fears of one’s own shadow, fear of being left without a mobile phone, someone is afraid of mushrooms and vegetables, and someone is afraid of wind and rain.

In any case, phobes see only one option. - eliminate dangerous situations in which they are uncomfortable. Most phobes are very concerned about the opinions of those around them; they are very anxious and impressionable people who are afraid to make a mistake, to be rejected if someone suddenly knows their anxieties and fears. They try to avoid conflicts. They are ready to agree with you that in reality there is absolutely nothing to fear, but in most cases they cannot overcome their fears on their own.
The most common
Speaking of the most common fears, it should be noted those phobias that are characteristic of at least 3-5% of the population. And in terms of prevalence, the following phobias can be noted:
- necophobia - fear of darkness, night, occurs in approximately eight out of ten children, and in every tenth adult;
- acrophobia - fear of height, characteristic of 8% of the world's population;
- aerophobia - fear of flying on airplanes and other aircraft;
- claustrophobia - according to statistics, up to 5% of the world's inhabitants experience the horror of tight and confined spaces;
- aquaphobia - fear of water to one degree or another - up to 3% of the world's inhabitants experience discomfort when bathing and until they completely abandon water procedures;
- opidiophobia - panic fear of snakes (both real and imaginary) occurs in at least 3% of adults;
- hemophobia (hematophobia) - fear of blood is at least two adults out of a hundred people;
- thanatophobia - panic fear of physical death;
- glossophobia - fear of speaking publicly in front of an audience (almost everyone has it, but in the form of a phobia - in 3% of adults).


Very important distinguish phobia from ordinary fearthat people experience as a defense mechanism of our brain. A phobia is when you are not just afraid of being left alone or losing a loved one, finding yourself in a completely dark room or encountering a respectable sized spider. Phobia - this is when the described situations cause obvious physical symptoms of panic - breathing and heartbeat are disturbed, control over your behavior is completely or to a greater extent lost.
Interesting
It’s quite difficult for a mentally and emotionally healthy person to imagine how to be afraid, for example, of a keyhole or buttons on clothes, but phobias are very diverse, and there are quite interesting fears, many of which are still not well understood.
Gnosisophobia - This is a strong fear of acquiring new knowledge. There are such pupils and students on the planet who are not lazy, swinging away from classes, but are really afraid of the new information that they can receive in lessons and lectures. Fear is allegedly associated with the fear of not assimilating, not understanding the essence of information, of becoming an outcast among their own kind. This form of phobia is often found in Mowgli children, who spent a long time without human society. Even after they adapt to people, they have a panicky fear of the complex new information that they need to learn.

White Leaf Disease (Creative Phobia) - the horror experienced by a person in front of whom lies a blank sheet of paper (as an option - a blank sheet is opened on a computer screen). This fear is inherent in people whose activities are related to writing, journalism, poets and teachers. An empty sheet from an impressionable creator is associated with a lack of thoughts and stupor in promoting work, which can cause great excitement with signs of a panic attack.

Kumpunofobiya - a person experiences pathological horror at the sight of buttons and before the need to perform some actions with them (sew on, unfasten, fasten). Kumpunofoby try to avoid this accessory in their clothes. In the severe form of this phobia, excitement and anxiety may occur when buttons appear on the clothes of other people, which, given their prevalence, invariably leads to the fact that kumpunofob limits his communication with people, maintaining contact only with those who don’t put on clothing with buttons .

Pogonophobia - panic beard fear. This type of fear has been described relatively recently. Such a disorder manifests itself by careful avoidance of bearded people in principle. Own appearance (if we are talking about a man) will also be important for the pogonophobe. He can shave up to several times a day, fearing that he will show at least the slightest stubble. Female runaways require perfect smoothness of the skin on the face from their man, which can bring him to a real nervous breakdown.
An accidental meeting with a bearded man, if contact cannot be avoided, can cause a chase-attack phobia phobia with loss of consciousness, the development of vomiting.

Lacanophobia - pathological fear of vegetables. Fear can be both a certain vegetable (for example, only turnip or cabbage), and all vegetables in general. Anxiety rises at the sight of vegetables. In most cases, the disorder is also accompanied by a refusal to eat them and intolerance of not only the species, but also the smell of vegetables.

Nenophobia - panic fear of the clouds. The cloud does not have a clear form, it "flows", changes, is in motion, and this can cause quite tangible anxiety. But such a disorder is rarely accompanied by panic attacks.

Omphalophobia - rejection of the navel. People with such a disorder cannot shudder at the navel - their own or someone else's, without a shudder. Usually they do not allow anyone to ever touch him, and even they themselves can avoid touching this part of the body. Psychiatrists associate the occurrence of such a phobia with perinatal "memory", but there is no single version of the causes of the development of the disorder.

Rare
Phobias are considered rare, which occur in less than 1% of patients with certain fears. Here are a few of these disorders.
Ablutophobia - panic fear of water procedures, bathing, washing, washing, washing. Ablutophobes are so afraid of such procedures that they try to do without them. In a mild form, the disorder does not prevent a person from at least occasionally having to wash or take a shower, but these actions are associated with significant discomfort and even mental suffering. Ablutophobes are prone to bouts of delirium and loss of consciousness if they feel that contact with water cannot be prevented.
The legendary Prussian king Frederick the Great suffered from this disorder. The emperor of Prussia could not allow himself to not wash at all, and therefore he found a way out - he forced the servants to rub his body with dry towels. There was no question of water.

Papaphobia - fear of the Pope. This is a new disorder that was not previously known. Today, several cases of panic fear of the name, image of the head of the Catholic Church are reported.

Pantheraphobia - A strong fear of the mother-in-law or mother-in-law. This is a rare form of phobic disorder, which manifests itself in the fact that a man is completely unbearable to communicate with his mother-in-law, and a woman - with her mother-in-law. At the same time, this is not about disagreements, but about the horror that the pantheraph suffers. The very prospect of meeting a relative causes nausea, dizziness, and a change in blood pressure, which can cause loss of self-control.

Anthophobia - fear of flowers. It can be manifested both in relation to some individual plants, and all flowers in general.Most often, there is panic in front of potted plants, which many consider to be true symbols of comfort and beauty. Of the flowers, most often antophobes are afraid of irises, tulips, roses, as well as carnations.

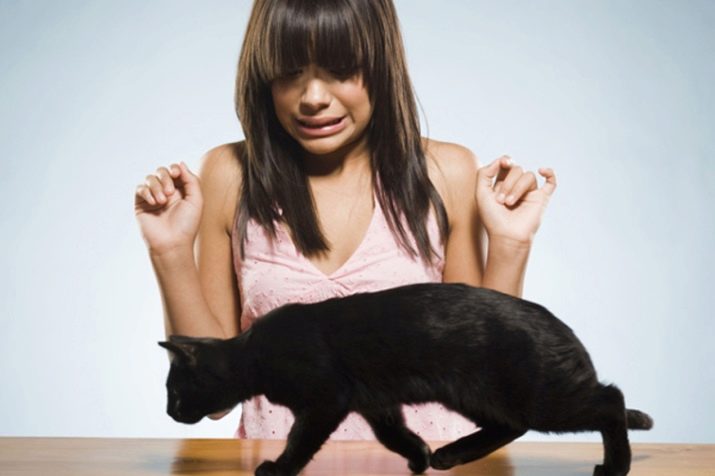
Aylurophobia - fear of cats. For most, the image of cute kittens or graceful cats is pleasant, it causes positive emotions. But not for aylurofob or filiphob. People who are horrified by the mustachioe-striped try to avoid situations of meeting with these animals, avoid their images. Sometimes fear extends only to the prospect of being attacked by a cat, but sometimes horror causes literally everything from purring to wool. The conqueror Napoleon Bonaparte suffered from this disorder.

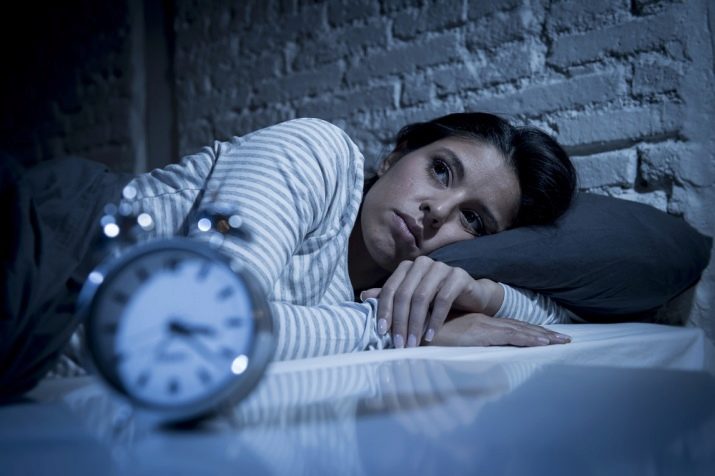
Hypnophobia - pathological fear of sleep. A person is afraid to fall asleep for various reasons - either it is the expectation of nightmares, or the fear of dying in a dream, being paralyzed, or being vulnerable and not having the opportunity to protect oneself in the event of an attack in a dream. True hypnophobes can bring themselves to death and madness if they avoid sleep for a long time. Joseph Stalin suffered from this type of disorder to a moderate degree, who was very afraid of dying in a dream, so he worked hard for a long time at night.

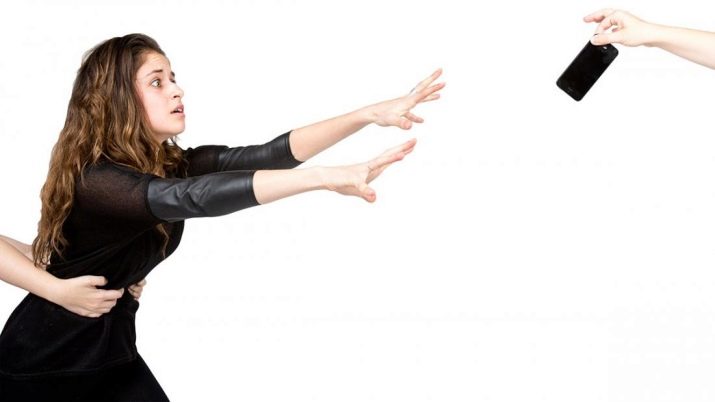
Nomophobia - panic fear of being left without a phone. So far, phobia is rare, but will soon become a common one, because it is rapidly progressing, according to experts in the field of psychotherapy. Nomophobes are very dependent on their gadgets. A fit of fear can cause not only the thought of loss or damage to the phone, but also suddenly “dead” battery of the device. Even for a few hours to remain without communication is the most traumatic circumstance that may be in the life of a nomophobe.

Tetrafobia - fear of the number "4". Here, not even the medical side of the issue is curious, but its cultural component. This number is not feared in Europe, but very feared in Japan, China and both Koreas. The fact is that in almost all Asian languages, the hieroglyph 死, very reminiscent of “4”, means “death”, and therefore a general fear led to the fact that there is no fourth floor in the houses, hotels and clinics of East Asia, in cinemas there is no place with number "4", and they try to number the houses in such a way as to avoid a building with the corresponding serial number.

Chronophobia - fear of time. This more than strange disorder was first discovered in prisoners who were sentenced by the courts to lengthy sentences. One prospect of a long time, a slow passage of time caused them depression, panic, tantrums. The other extreme is the fear of the rapid passage of time and the onset of old age (geoscophobia). Geraskophobes cannot normally build their life, plan, do, because all their thoughts are occupied by pessimistic thoughts that time is rapidly running out.

Specific
According to the existing classification, phobias are called specific, which are isolated in nature, that is, limited to certain situations, circumstances, actions, or directly to any specific objects. This includes almost all animal phobias (fear of cats or dogs, fear of horses or lizards). An isolated phobia applies to only one object - one who is panicky afraid of cats is not afraid of dogs or frogs.
Fears of heights, darkness, flights by air, visits to public toilets, fears of certain types of food, fear of dentists or sharp objects are considered specific.
That is, panic is possible for a phob only in a certain situation, in others he does not experience anything unusual.
For all isolated, specific phobia is characteristic early appearance - in childhood or adolescence. In the absence of treatment, they themselves do not pass, and long-term specific phobias may well progress, and the person will acquire other concomitant mental disorders.

Causes of disease
Why a person develops this or that phobia is difficult to say. Until now, scientists, doctors are debating on this topic. But there are several concepts that explain the occurrence of such mental disorders. Experts in the field of biology and medicine are inclined to believe that phobias can be inherited, but genetics tried not to find specific genes that could be blamed for human fears.
And therefore, the pedagogical version of the inherited phobias sounds more convincing - children simply perceive at face value the vision of the world that is characteristic of their parents. They copy adult behavior patterns, and if a mother is panicky afraid of mice or spiders, there is a high probability that the child will grow up with exactly the same personal fear. A sociophobic parent who is afraid of society and prefers to live in “his own shell” is more likely to transmit information about the “danger” of the outside world to his children, and they are several times more likely to develop sociophobia in the future.

There is a rather convincing version of the development of phobias in connection with a violation of the level of hormones, which can be both inherited and acquired. In this case, it is believed that the development of phobia is preceded by an increased content of catecholamines in the human body, an excessive amount of adrenaline, impaired functioning of GABA metabolism receptors.
Psychiatrists and psychoanalysts see in the phobia a relic of the past. Fear helped people at the dawn of mankind survive as a species. If they were not afraid of the dark, animals, attack, strange unfamiliar food, it is unlikely that mankind could survive and become a sufficiently developed civilization - they would die from the cold, hunger, poisoning, claws and teeth of predators, they would kill each other in tribal wars. Fear as a protective mechanism is necessary, and today, when many dangers are no longer threatening people, it continues to remain (after millions of years of development it is difficult to get rid of it).
It’s just that in some particularly impressionable people it takes on primitive forms, that is, it goes beyond the boundaries of the rational.
Behavioral therapists believe that any phobia is the result of an improperly fixed patient response to an external stimulus. In other words, having experienced fear and panic once in a situation, a person may have a close relationship between the same situations and the panic itself. If a child is severely scratched by a cat or bit by a dog, then it is possible that the fright and panic that the child experienced at that moment can become fixed in relation to the object - to the cat or dog. In the first case, the development of phylophobia is likely, in the second - kinophobia.

According to this theory, fear almost always has "children's" roots. Even if an adult does not remember some event from his own childhood, which caused him constant fear, for example, cellars or cockroaches, this does not mean that there was no event. The circumstances were forgotten, not preserved in memory, but the prevailing connection between the panic reaction and a certain object (circumstance) is obvious. A cut in childhood can become the basis of a pathological fear of sharp objects in adulthood (ahmophobia), and observing a fire can lead to fear of fire (pyrophobia).
The cause of the phobia may be improper upbringing. If the parents are overly protective of the child, then the child may well become uninitiated, incapable of making decisions and afraid of any responsibility (hyphengiophobia).The constant allegations of mom and dad, grandmother or grandfather that dogs are very dangerous can cause kinophobia, and allegations that people cannot be trusted can become the basis for sustainable sociophobia.
Another educational extreme that may also underlie a phobia is ignoring the fears of the child. If the baby has no one to share his fears with, there is nowhere to get comprehensive explanations about the irrationality of his fears, if he is simply ignored, paid little attention to him, there is no emotional contact with his parents, then fears quickly take root in the children's mind and it can be difficult or impossible to cope with them later .

Punishments can become the “trigger” of a phobia - among the claustrophobes there are many who were locked in a closet, basement, closet, punished in a dark corner, etc. And among agoraphobes, many who were lost in childhood on the square , fought off his parents and experienced a strong fright about this.
Phobia can develop in both adults and children under the influence of persistent external information. Fear of attics or basements, terrorists or a caisson disease can develop after watching horror films, thrillers, fear of doctors can become real after receiving a strong impression from news about a medical error or from a film in which there was a villain-doctor.
It is in the oversaturation of the information field that experts see the main reason for the rapid increase in cases of severe phobias around the world. Phobias can safely be called a problem of our time.
The development of phobias affects people who have been in catastrophes, war zones, natural disasters, in accidents and accidents. At the same time, the theme and type of phobia usually corresponds to the circumstances - aquaphobia often develops in those who survived the flood or drowned, but was saved, hoplophobia (fear of weapons) develops in people who came under fire, were in the area where the fighting took place and etc. People who find themselves in the rubble are more likely to encounter claustrophobia in the future.

Signs
How to recognize a phobia in yourself or a loved one, how to understand whether there is a mental disorder, or is it about the most common fear inherent in everyone? This question is very important. Therefore, you should know what are the signs of a real phobia. First of all it an acute attack of fear that occurs every time a person encounters certain circumstances or objects.
If such circumstances can be foreseen, then the phobia begins to experience great anxiety in advance, for example, with iatrophobia (fear of doctors), a person begins to get nervous in advance if he has to visit a medical institution or a medical examination in a few days and there is no way to avoid this event.
During contact with a frightening circumstance or object, a person has a narrowing of consciousness and perception. He at this moment the whole world is limited only by this circumstance, and therefore it is impossible to be distracted by something else, nothing else exists at this moment for a phoba in the world.
The brain quickly starts reaction chains and autonomic reactions arise - control over one's own actions is lost, breathing quickens, it becomes superficial, shallow, heart palpitates, a large amount of sweat is secreted, the mouth is dry due to cessation of salivary gland secretion, dizziness occurs, weakness appears in the legs. A person may lose consciousness.
Usually, the first manifestations of phobia are associated with severe fear and panic; in subsequent relapses, an increase in the level of fear is noted. In order to somehow make his life easier, a person begins to avoid possible “dangerous” situations for him, and this avoidance is fixed as a distinctive feature of behavior.If you see someone who carefully wipes his hands with a wet towel after each handshake or constantly checks the freshness of his breathing, you can be sure that the obsessive patterns of behavior in this case are signs of a certain phobia in the person (in the first case, mesophobia, and in the second - halitophobia).
If the fear is so “exotic” that it is easy to avoid it in the future (for example, a resident of the north is afraid of large tropical spiders, which you will not meet in the north for obvious natural reasons), then repeated attacks may not be for years. But this is not a cure, but only an illusion of victory over a problem. It is worth the arachnophobe northerner to accidentally see the image of a tarantula or switch the TV unsuccessfully and get on a program about wildlife, where they just talk about spiders in Africa or Australia, how he can experience a severe attack of horror, panic with all the conclusions arising from a panic attack.

Foby very carefully plan their actions. For fear of crossing the street, a person will think a hundred times about alternative routes to get to the destination. If such routes are not found, then he may refuse to go there at all.
The danger of a phobia is that a person’s life suffers significantly, undergoes changes that prevent him from living freely and calmly, communicating, working, traveling. But this is not the only reason why phobias are recommended not to suppress, but to treat. If a phobia often gets into a disturbing atmosphere (lives in the center of a big city for fear of streets and squares or suffers from pediophobia - fear of children), then it is more likely that it will try to drown out its fears with drugs, alcohol, psychotropic substances.
That is why there are many alcoholics, drug addicts, people who are addicted to tranquilizers among phobes, etc.
Phobic disorders also increase the risks of other mental problems: phobes often develop depression, depressive psychoses, generalized anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorders, manic and paranoid disorders.

Treatment methods
There is no cure for panic attacks of quick action. Medication is generally not very effective for phobias, so modern psychiatrists and psychotherapists try to prescribe medications only in extreme cases, preferring antidepressants (tranquilizers simply suppress the perception of fear, cause strong dependence and do not cure the root cause in any way). If a decision is made on the prescription of medicines, then they are recommended to use exceptionally short courses with long breaks.
The most effective method for overcoming phobic disorders is considered today. cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy. It represents a rather long and painstaking collaboration of the patient and the doctor. First, the identification of specific situations and objects that cause horror. Then the specialist begins to help a person create new installations that emphasize the fallacy of the old ones and help to take a fresh look at what yesterday seemed terrible, nightmarish. At this stage, the effects of hypnosis and NLP can be applied.

Then the person begins to gradually immerse in stressful situations. First, to those that initially caused less fear, and then to the worst nightmares. Immersion is monitored by a physician at every stage. This helps a person to change the perception of a terrible situation and take it calmly. Therapy is combined with relaxation techniques, methods of deep muscle relaxation are especially effective.
Psychoanalysts are looking for a deep inner conflict of man, which led to an external manifestation - panic. They raise childhood memories, fears, dreams, images and find a “problem link” that triggered a fear of something.Then this link is adjusted.

Today they also use the possibilities of virtual reality using augmented reality glasses and virtual worlds specially created for phobes for the treatment of fears.
The prognosis of cure depends on how much the patient himself is interested in getting rid of his anxiety and panic. The most effective treatment is in which the patient collaborates with the doctor, fulfills all his recommendations, takes the prescribed drugs on time, does not allow self-medication and does not miss psychotherapy sessions.
Also, during treatment, a person should give up alcohol, drugs and other bad habits. It will be good if someone close is near - to support and help to appreciate the intermediate results that can be achieved. Sometimes recommended keep a diary of observations of your emotions.
With adequate treatment, it is usually possible to get a stable and long remission.

See what the phobia really is in the next video.