Surely, each of us at least once saw a person who literally runs across the square or is afraid to leave the door open. We habitually consider such people cranks, but the problem is much deeper than it might seem at first glance.

What it is?
Agoraphobia is a multi-component phobia that manifests itself in the form of fear of open spaces, large crowds. Fear of open space can be terrified of the prospect of crossing a wide street or square or leaving the door of the room open. This phobia has been known for a long time. Its name comes from the ancient Greek words, which means “market” and “fear”. Therefore, the fear of open space is often called the "market disease" or "the disease of large areas."
Agoraphobia - a concept that includes many fears, one way or another connected with open space. Fears are unconscious and often irrational. At its core, fear is a hypertrophied manifestation of the protective mechanism - a person feels the danger, and physiological, mental and biochemical processes start in his body, which include “protection”, tell him that in this situation you need to run, to be saved.


The first psychiatrist and neuropathologist Karl Westphal, who lived in the 19th century, described this mental disorder surprisingly accurately. His work on “market fear” was published in 1872, and he was the first to propose using the term “agoraphobia” itself.In his work, Westphal described mainly only the fear of being in an open place, but then the luminaries of science did not yet know about the crush in the metro at rush hour, they did not imagine large demonstrations and rallies for several hundred thousand people.
Surely many will be surprised to learn that Agoraphobia at one time suffered from Sigmund Freud. The disease manifested itself especially strongly in his youth, and for this reason it was very difficult for a world-famous doctor to take independent walks in old age. He himself spoke about this to one of his students, Theodore Raik. Raik described this conversation in his writings, and at the same time concluded that Freud was inspired by his own problems with the psyche to study human psychology and its deepest secrets. And, indeed, Freud did a lot.


Before him, psychiatrists tried to treat fears with morphines, hypnosis, and electricity. In an extreme case, a patient with phobias was sent to medicinal waters or a resort. And it was Freud who first proposed to talk, talk with patients, discuss their problem in order to minimize manifestations of agoraphobia. The best medical minds in the world were shocked by such an offer, it did not fit into any reasonable framework, but they could not offer anything better, and therefore in many ways it was Freud who determined the principles of psychotherapy for the fear of open spaces and large crowds of people.
Today, medicine looks at agoraphobia more widely. It includes not so much the fear of open places, but also the fear of similar situations (being outside the house, the need to move somewhere outside the house, being in the crowd, public places, in transport and the metro). Agoraphobia is considered the fear of having to go unaccompanied along a deserted street, a park, fear of going on a trip or traveling alone. This also includes the fear of visiting markets, large shops, restaurants, cinemas, going to rallies. The agoraphob is characterized by fear of any place that, in which case, he will not be able to leave without being noticed, without attracting the attention of others.


At the same time, people suffering from this disorder are well aware that their fears and panic attacks have no reason and are very afraid that such attacks will occur in public, that is, will become public. As a result, a person finds the only reasonable way, in his opinion, - he closes in his “fortress” (at home) and no force can force it to leave.
On its territory, the agoraphobe feels safe. Most can communicate well, receive guests, be friendly hosts, work, conduct telephone conversations, and solve very complex creative tasks, but exclusively on their territory. As long as they understand that the space around them is controlled, they behave appropriately. They can live for years without leaving home. Trying to avoid panic attacks, people with this disorder deliberately limit their movements, narrow the scope of their activity, try to avoid any situations in which they may be too far from their safe space. It’s important for them to know that if necessary, they can quickly return to it.


Quite often, agoraphobia is a concomitant symptom of other mental disorders of the anxious type, panic syndrome, and social phobia. Agoraphobia is called by psychiatrists one of the most difficult phobias, often it leads to disability. So, to consider agoraphobes just cranks is a mistake. The condition should be monitored and treated by a psychiatrist or psychotherapist.
Marilyn Monroe suffered from agoraphobia, she was very afraid of open places and large crowds of people and visited them only accompanied by relatives or friends whom she trusted. A similar problem was for actress Barbara Streisand.


Causes of occurrence
If you ask any agoraphobe what exactly he is afraid of, why he cannot go to the middle of the square and tell everyone what he thinks about them, or simply leave his own apartment, he is unlikely to find an answer. In 95% of cases, patients with such a phobia consider their fears completely inexplicable. They do not see any connection between panic and previous shocks and psychological trauma. Only about 5% of agoraphobes can think, recalling that for the very first time, they experienced wild horror and panic in a situation where they felt bad in certain specific circumstances: were sick with the flu, tired, it was very stuffy and hot, worried before an interview or passing the test.
The doctor, of course, will believe them. But the circumstances and situations in which fear arises cannot explain the reason for its appearance. And on this score, psychiatrists and neurophysiologists know something that agoraphobes themselves are not aware of - the disorder is closely related to the critically low level of personal security in a person. Quite often it is laid in childhood. If a person at a young age began to perceive himself as a vulnerable, weak and helpless creature, unable to withstand an evil, aggressive and vile world, then the likelihood of later manifestation of agoraphobia is very high.


Why can a child feel so? For three reasons:
- his parents take care of him unnecessarily, leaving no space for their own decisions and actions, simultaneously suggesting that the world is full of nightmares and dangers, “you need to be careful and always alert”;
- parents do not pay attention to the child, are not interested in his worries and fears, he does not feel support and safety with adults;
- parents are too demanding, autocratic, authoritarian, and the child is constantly tense in the expectation that his actions, words, actions will cause disapproval and even punishment.
In all these situations, fear becomes a familiar life partner since childhood, to one degree or another it is constantly present. But it would be unfair to blame parents for everything. There are individual prerequisites for the occurrence of mental anxiety disorder. Most often, agoraphobia develops in people with a certain type of nervous system - in very sensitive, impressionable individuals, anxious, prone to delve into their feelings, secretive, not ready to show the world their weaknesses.


Sometimes the first attack of agoraphobia occurs after severe traumatic situations - a serious illness, physical torture, sexual abuse, the death of a very close and dear person, after a natural disaster, or being in a combat zone. An adult with such a psychotype may develop an ailment after losing his important work, leaving a partner.
But all this is only external circumstances. What happens inside a person? In fact, his own brain begins to deceive him - which is why many patients with agoraphobia develop problems with the vestibular apparatus. A healthy person manages to maintain balance due to three types of signals - proprioceptive, tactile and visual. These landmarks are enough to understand where you are and what your position is at a point in space in the current time.
Agoraphobes can have the perception of only two types of signals - tactile and visual. Due to this, there is a pronounced disorientation when a person finds himself inside a swarming crowd, on inclined surfaces and large open spaces with a minimum number of visual landmarks. The brain sends them erroneous signals, as a result, imbalance is possible.
note that the brain is capable of such “tricks” not by itself, but with the active support of hormones. Anxiety occurs as a protective mechanism, and then stress hormones (such as adrenaline) are released into the blood immediately. The hormone immediately triggers a “run or defend” reaction in the brain.

But the world for the agoraphobe is too big and terrible, he won’t even conquer it, and he (in his personal perception) is small and weak, and therefore the only possible brain reaction is a signal to run.
With some congenital and acquired pathologies associated with hormonal imbalance, the development of agoraphobia may have precisely endocrine causes (pathological processes in the brain trigger an imbalance of hormones). This is possible with neurocirculatory dystonia, alcoholism, drug addiction, gross thyroid pathologies.
It is noteworthy that big lovers of coffee and everything that contains caffeine (strong tea and dark chocolate) also run the risk of replenishing the friendly ranks of agoraphobes - caffeine stimulates the production of stress hormones and, if the predisposing factors coincide, the start of a “market disease” is quite possible. According to statistics Agoraphobia to one degree or another occurs in 5% of the world's population, men are less susceptible to it than women are about 2 times.

Symptoms
Agoraphoba is simple enough to find out. He is afraid to leave the house, to do something outside of his usual controlled territory. Going out onto the street, crossing the road, getting down the subway and getting on a crowded morning bus for a classic agoraphobe is a difficult and sometimes impossible task. At the same time, one is afraid to visit shops, and the second is not able to attend a hairdresser. Public transport is a common fear with this disorder, because while the bus is traveling, a person cannot get up and leave it if he feels in danger.

But the agoraphobe is not so much afraid of the square, the park, the open door or the deserted street. He is afraid to become a laughing stock in the eyes of others, if he suddenly becomes scared, because in most cases a panic attack starts. He is afraid of “losing face”, becoming the object of bullying, ridicule, because he perfectly understands that he can hardly control panic attacks.
At the same time, accompanied by relatives or someone whom the patient fully trusts, the level of anxiety decreases, and a person is able to do something that one cannot do. There are agoraphobes in whom there is only one kind of fear, for example, fear of crossing the square on foot or fear of getting on a bus. There are people who suffer from several fears at once, right up to the complete impossibility of leaving their apartment, moving somewhere, and in the most difficult cases and in their own walls they cannot remain alone.
Agoraphobes usually act in advance - they plan their daily routine in such a way as not to encounter situations in which they are afraid to face any turns of fate: they are looking for work within walking distance, if they are afraid of transport, start working remotely at home, if they are afraid to leave the house, order products to the house, if they are afraid to leave the store, put closers on the door so that they do not accidentally forget to close the door behind themselves. And in their measures they are very consistent, punctual and attentive to little things.


If nevertheless the agoraphobia, despite all the precautions, is in alarming circumstances, he can note the following signs of the disease:
- breathing quickens and becomes shallow, superficial;
- palpitations are quickening;
- sweat is intensified, face and hands sweat especially;
- dizziness occurs, possible loss of orientation in space, fall;
- there is a sensation of “a coma in the throat”, it becomes difficult to swallow;
- there is a feeling of nausea and constriction in the stomach.
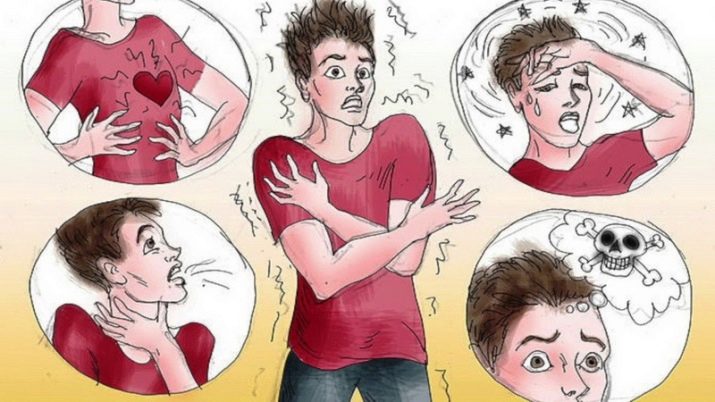
At the same time, a person is afraid that others will notice what he is experiencing now, which intensifies physical manifestations.Many patients at the time of the attack are afraid to lose their minds or die.
If a cautious and prudent agoraphobe knows that he will soon have to deal with a terrible, dangerous situation (for example, you really need to visit the passport office and get a document, because no one will do it for him), then in anticipation he begins to feel fear in a few days, anxiety is increasing gradually.
True agoraphobes have a low self-esteem, they are almost sure in advance that nothing good will come of their ideas and ideas. They are afraid of loneliness, because they simply do not understand how to survive without support, care, protection from the outside. They are painful to parting, can fall into severe depression.
The whole life of agoraphob - one ongoing battle for extra safe space under the sun. And it happens that patients manage to win additional lands to their "fortress", they expand the space in which they feel calm. But after unforeseen traumatic circumstances (the wife left, the husband abandoned, betrayed a friend, was fired from work, were not hired), progress usually comes to naught, and the person returns back to his “security island”.

Psychiatrists have noticed that the first signs of the disease usually appear when a person reaches the age of 20-25 years. And this is the main difference between this fear and other phobias, which usually manifest in adolescence or childhood. Based on the analysis of medical histories of people with agoraphobia, specialists noticed that the first horror attack usually occurs in certain situations - when a person stands at a bus stop and waits for his tram or at the moment when he walks around a shopping center or a bazaar, choosing a purchase.
Usually the disorder has persistent chronic. Periods of exacerbation are replaced by remission, and then again exacerbation occurs. Seven out of ten patients develop classical clinical depression, and almost half have phobic disorders. If a person gradually develops panic syndrome, then the disease has the most severe course and is most difficult to treat.

An appropriate diagnosis can be established only after the conclusion of a psychiatrist who listens to complaints, compares symptoms and determines the level of anxiety using a special test and a series of questionnaires (Hartman’s MI-mobility questionnaire). As a result, a certain form of the disease is established - without panic disorder or with panic disorder.
Treatment
Unfortunately, science and medicine do not know the “magic pill” that would help a person get rid of a disease such as agoraphobia. Therefore, therapy will be long, complex, sometimes it continues throughout the life of agoraphobia.
Much depends on what form of the disorder is established - with or without panic disorder. If there are no panic attacks as such, it is customary to treat a person with the help of psychotherapy. This is the most effective way to deal with the fear of open space, crowds or vehicles today. The use of drugs in the case of non-panic agoraphobia was found to be ineffective, pills for this disease can not be cured, you can only temporarily slightly reduce the symptoms. But in particularly persistent cases of the disease, tranquilizers are simultaneously recommended with short periods of time simultaneously with the psychotherapeutic course of treatment.
If other mental disorders are detected in the agoraphob, then their treatment occurs simultaneously with the treatment of “market fear”. Consider the main methods that help overcome this phobia.

Psychotherapy
The main method, which in psychiatry and psychology is assessed today as the most effective, is cognitive-behavioral therapy. At the very beginning, the doctor identifies the degree and frequency of anxiety and fears, the circumstances in which a person experiences them.Next, connections are established with certain memories, emotions and experiences of the patient. And then the doctor begins to change the thoughts and beliefs together with the patient, which provoke the appearance of fear in certain circumstances.
At the second stage, when a person begins to realize the absurdity of his nightmares, he is gradually immersed in situations that until recently he was most afraid of in life. First, this happens with the help of a specialist, and then on their own. As a result, situations that until recently frightened, become familiar, in fact, completely not terrible, anxiety quite naturally begins to decline.

If a person’s agoraphobia is severe, psychotherapy proceeds while taking medication. It can be long. Often, specialists apply such techniques as gestalt therapy, psychoanalysis, psychodrama, existential therapy.
The psychotherapist and psychiatrist do not set the goal to eliminate fear as such. They pursue another goal - remove those psychological attitudes and premises, an unhealthy perception of oneself and the world around, which lead to fear. Thus, the treatment is aimed at increasing self-esteem, at establishing more friendly relations with the outside world and the people living in it. Without this, psychotherapy will be of no use, and soon the phobia will return. In especially difficult cases, hypnosis is used.

Medicines
For the treatment using various medications. They can be divided into several groups.
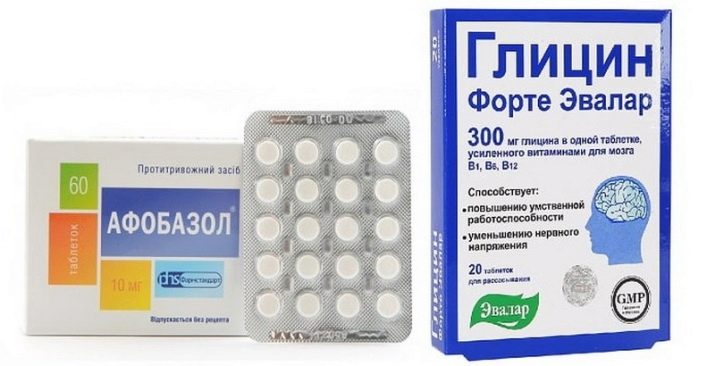
General strengthening and dietary supplements
This includes drugs that essentially do not treat anything, but have a general strengthening effect on the body. Separately, they can not be used due to the uselessness of such drugs for a mental disorder. But in complex treatment can be prescribed. These include “Glycine”, “Afobazol”, “Fezam”, “Cerebrolysin”, “Magne B6”
Tranquilizers
They have a mainly symptomatic effect, do not treat the root cause in principle. They cause inhibition of signals in the brain, due to which anxiety is reduced. Most commonly used benzodiazepines "Phenazepam", "Diazepam". Drugs have side effects, with prolonged use cause drug dependence, therefore, they are not suitable for long-term treatment.


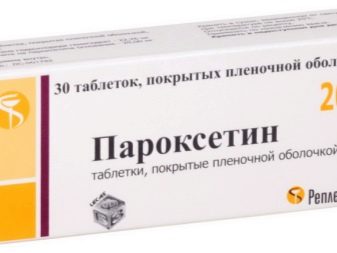
Antidepressants
Drugs in this group are considered more effective in the treatment of agoraphobia than the above funds. In almost 80% of patients, anxiety levels decrease. Means are not addictive. The effect is achieved by normalizing the number of neurotransmitters in the brain cells (in particular, the content of serotonin increases). The best result can be achieved while applying antidepressants and psychotherapy. Use more often "Paroxetine", "Sertraline", "Fluoxetine."
General rules state that a person should take all medicines, being absolutely sober and sane. That is, taking alcohol, coffee, drugs during treatment is excluded. The patient should not exceed the dosage recommended by the doctor. Moreover, the refusal of psychotherapy does not guarantee any effect of the treatment at all. Pills themselves, if they “work,” then only with respect to certain symptoms and not for long.

Predictions for agoraphobia depend on how deep and severe the disorder is, as well as on a person's personal interest in healing from phobia. If the patient is not well motivated enough, then all the efforts of a psychiatrist or psychotherapist will go to waste.
Self help
It is almost impossible to independently cope with agoraphobia, since fear quickly becomes an integral part of a person’s life, part of his own personality. And the fight against him resembles the notorious fight of bees against honey. Therefore, an appeal to a specialist is mandatory. When undergoing treatment, the following recommendations will help accelerate positive results and overcome fears:
- learn to relax - practice meditation, do yoga (this can also be done through video lessons), devote time to relaxation every day, it is better when it happens in the morning and in the evening;
- believe that you are on the path to recovery, you have enough strength to go this way to the end;
- master breathing exercises - A series of inspirations and expirations of a certain depth and intensity helps to quickly cope with panic if an attack occurs again;
- keep a diary in which every day indicate in detail how much of your fears have already been defeated, this will help to see progress and will motivate you to further treatment.


To the best of your ability, enlist the support of the person you trust. Share with him your new sensations, achievements. But gradually gain more independence: if earlier you could not go to the store without an escort, do not be afraid to try it yourself, but first make half the way to the store and return, and then overcome the whole way. In the next "approach" go to the store and stay there a little. Gradually turn out and make purchases.

According to the results of recent studies, responsibility for someone who is weaker than you is very helpful with agoraphobia. And therefore, if possible, get a pet with whom you need to walk, for example, a dog. With it, you will not feel alone on the street, and you will have to go out there at least 2-3 times a day, which will gradually turn the hostile environment into a familiar one.
Prevention
Prevention of agoraphobia does not exist, since the triggers (provocative factors) are still poorly understood. And prevention is wiser to take care of parents who want to raise children mentally healthy. For this, mothers and fathers should not adhere to an authoritarian parenting style in which the child is constantly intimidated. Hypercope should also be excluded - the child should have enough personal space and independence, he should have the right to choose. At first it will be a choice of what to eat for an afternoon snack, and later - a choice of a profession, university, friends.

If you are a sensitive person, anxious and very worried about what others will think of you, if you are often afraid not to cope with the business that you have to do yourself, without the help of others, if you are extremely uncomfortable in the subway or bus (but the speech is not yet it’s about panic), you need to seek help from a psychologist. This will help to reconsider some beliefs, which under adverse circumstances may well result in the development of agoraphobia.

First of all, it is important to understand that you are strong enough to live in the world without fear. And the world itself is not so malicious and unfriendly as it seems. Try to see the good in it, and then the street outside your window will never become a "minefield", which you will not agree to step on for any carriages.
See how to get rid of agoraphobia in the next video.











