Subtleties of the content of fish cockerel and basic recommendations for care

Bright beautiful fish cockerel will decorate any aquarium. In addition to its peculiar appearance, it has an energetic and warlike behavior. Caring for fish, although simple, has some subtleties.
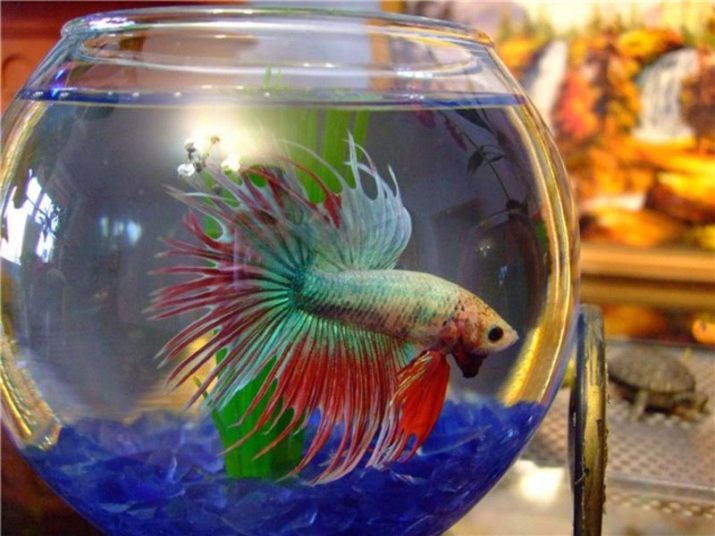

Features
For its cocky character, the cockerel was nicknamed the fighting cock. Aquarium fish is a representative of the macropod family. This labyrinth fish has an interesting feature - it needs air to breathe.
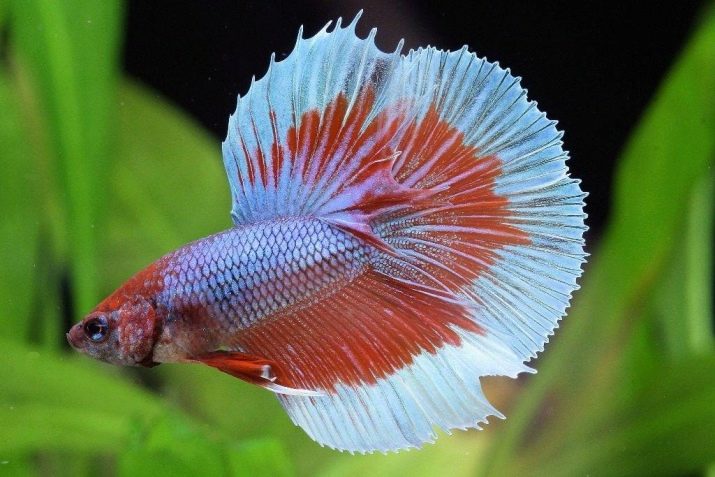
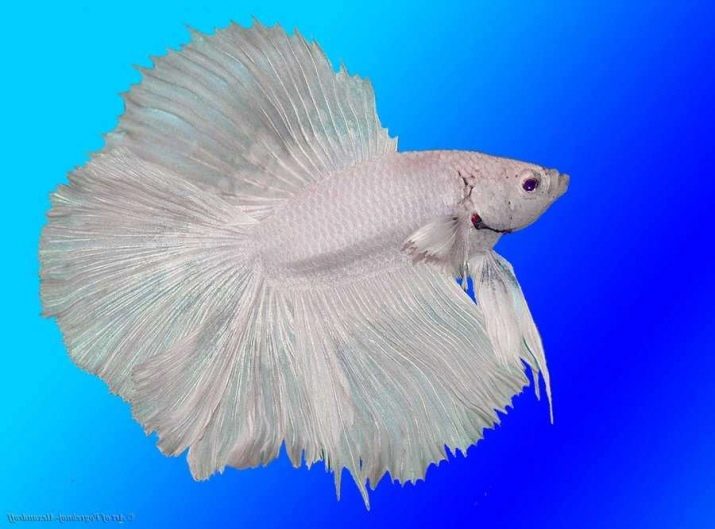
The oval and elongated body of the cockerel is flattened on the sides and does not differ in large sizes: in males, it reaches 5 cm, and in females - about 4 cm. The cockerel is given an unusually beautiful look by its fins, which in different species have a slightly different size, shape and outline of the fringe.
Basically, the fins, both the caudal and the upper, have a rounded shape, and the ventral fins are pointed.
In females, the fins are shorter than in males, and they do not have such a bright color and less beautiful shape.


One of the features of this fish is an amazing and unique color. It can be not only one or two colors, but also multicolor: contain shades from blue to purple, from green to yellow, from orange to red, as well as white and black colors.
In males, the color is somewhat brighter than in females, and has the peculiarity that in strong light during spawning and during fights, their color becomes even brighter. Males are classified by size and shape of the fins, as well as by color: one-color, two-color, multi-color.
The behavior of the cockerels is characterized by bullying and aggressiveness not only in relation to other species of fish, but also to their relatives. Keeping two males in a small aquarium can lead to the death of the weakest. However, despite their aggression, male males have a strong parental feeling.
These fish live for about three years. Caring for them is not particularly difficult even for beginners, although it does have some nuances.

How to equip an aquarium?
Fish can exist well not only in large, but also in small aquariums. It is only necessary to consider that for one cockerel, 3 to 4 liters of water will be required. One cockerel can be kept even in a 3-liter jar, and for several individuals a capacity of 10 to 20 liters is needed.
Capacities can be of various shapes: males live in a rectangular, square, and round aquarium. Large tanks are recommended to be divided into several zones by partitions. This will allow to keep several male males in one aquarium without risk to their life.
For partitions use a safe environmentally friendly material. They must have openings for free circulation of water. Near the fences, it is advisable to plant tall water plants. They will cover the review and eliminate unnecessary contacts.
In addition, plants give a beautiful look, and also serve to form spawning nests. They also contribute to the enrichment of oxygen in the aquatic environment and maintain its biological balance.

In addition to living, artificial plants can also be used for decoration, but they should not have a sharp outline so that the fish do not damage the fins.
At the bottom of the tank, it is recommended to place the soil in the form of river fine pebbles, gravel or coarse sand. This neutral soil contains beneficial microorganisms necessary for processing the products of vital activity of aquatic inhabitants.
And you can also put different snags, large stones, equip the grottoes, which will serve as a shelter for fish. These decorative elements should be environmentally friendly and not have sharp edges.

Aeration of water for a cockerel is not so important, since they additionally use air for breathing. But temperature changes in water adversely affect the males, so it is advisable to use a heater to maintain a stable temperature.
Water purity is extremely important, therefore it is undesirable to use an aquarium without a filter. The power of the filter should be small, because these fish like calm waters.
The tank must not be completely filled with water, not reaching the edge of 7-10 cm. Since the males have a habit of jumping out of the water, the aquarium must be covered with a lid with holes or a net so that the water is saturated with air.
Put the container in a place bright, but inaccessible to direct sunlight and drafts.

What to feed?
Eating fish is not a problem, as they eat almost any food. There are various types of feed: dry, live and frozen. The proportion of live food should be greater in the diet of fish, since they need protein food.
They like to eat bloodworms and tubule makers, daphnia and cyclops, zooplankton and even snails, as well as shredded ordinary earthworms.
The disadvantage of animal food is that it can contain harmful microbes that cause various diseases in males.
Frozen - the same live food, but frozen. It is safer, because unlike living it does not contain harmful bacteria. Store it in the freezer and, if necessary, separate the right amount for feeding. You can’t thaw and freeze food again: it can go bad.

Dry food is small pellets or flakes. It is recommended to give it less often than live and frozen. Dry food is given according to the priority table.
- Conventional flake food - is given in such a small amount that is eaten by males in about 2 minutes.
- Special (for males) granular food - it can be given daily. It contains properly balanced useful elements.
- Pipeline, bloodworm, brine shrimp in dry form.
Different types of food cannot be given in one feeding: for example, frozen food and dry or combine different types of dry food at the same time. You need to adhere to the rule: one feeding - one type of food.
To prolong life and preserve the bright color of the males, they need to be fed with a variety of food, which must be alternated.

Rooster can be supplemented with frozen shrimp meat, live insects and their larvae, spinach, lettuce, previously scalded.
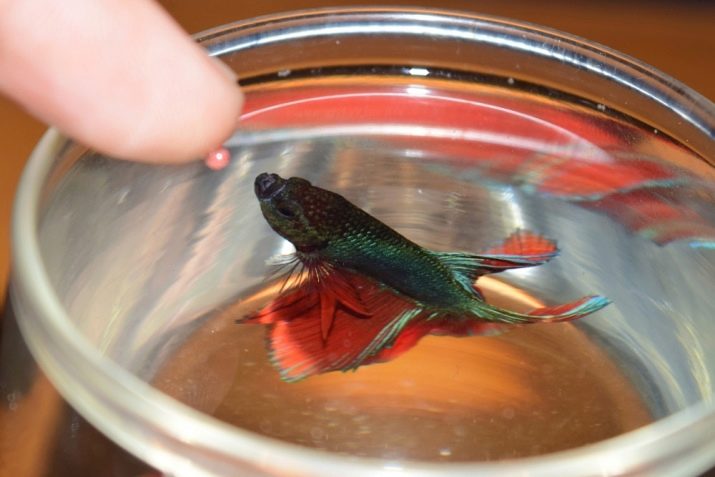
It is required to feed the males 1 or 2 times a day. Adult fish can be fed less often, just 1 time. During spawning, food is given twice a day, and also fry are fed. Food is given at the same time. The fish will gradually develop a reflex, and they themselves will gather near the feeders by the time of feeding.
The amount of feed should not be large: males should eat it in about 2-5 minutes. Live food is given in the amount of 3-5 worms, and granules require 4-6 pcs. in one feeding. The remaining feed should be removed so that it does not contaminate the water in the container.
It is not recommended to overfeed the fish: this leads to their obesity. Weekly, you need to arrange one fasting day without feed.

How to care?
For cockerels, although simple, but proper care is required. Consider the basic requirements of their content.
- Properly equipped aquarium with a water volume of 3 (for one individual) to 10-20 liters for several cockerels.
- Optimum temperature conditions. The temperature of the water in the tank should be approximately +24. +28 degrees Celsius. Fish can also tolerate lower temperatures, but it should not be below +18.
- Besides fish cannot stay in cool water for a long time: from this they can have different diseases. The temperature should be constantly monitored by a thermometer.
- The composition of the water. The males are undemanding in terms of the quality and composition of the water, but it is desirable that the hardness is from 4 to 15 dGH and the acidity reaches about 6-7.5 pH. To prevent diseases, stress conditions and strengthen the color of fish in water, it is advisable to add a special aquarium salt (0.5 teaspoon per 2-3 liters of water).
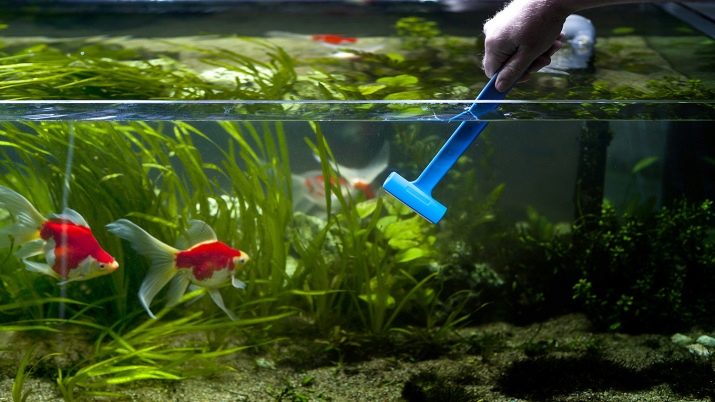
- Periodic change of water. In large tanks, water needs to be changed after 14 days, in small ones - every 3 days. Water can be changed in two ways: three times a week, only 1/4 of the total capacity is replaced; fish are transplanted into a separate container and replace all the water in the aquarium. Pure tap water is first allowed to stand for two days. It is strictly forbidden to use distilled water, since it does not contain substances useful for fish, and bottled water.
- At the same time as changing the water, they clean the aquarium. The bottom is cleaned, and all remaining food is removed, the walls and decor are cleaned. Often a bacterial film forms on the water surface. It prevents the penetration into the water of the necessary air by the males.

Since males are labyrinth fish, they periodically rise to the surface to swallow air. Therefore, a clean water surface is so necessary.
The film is removed with a special tool or simply using a paper sheet. And also all plants that appear are removed from the surface.
- Lighting should be diffuse. At night, the backlight must be extinguished.
- The presence of an aerator is necessary only in large tanks: without it, the water at the bottom will be colder than on the surface.
It is believed that round aquariums and large cans are not entirely acceptable for the normal life of males. They distort the view, which leads to disorientation of the males.

In addition, it is much more difficult to clean the round walls. Typically, such containers are insufficient and suitable for keeping only one fish.
Caring for fish contained in a round container does not differ from conventional care: periodic change of water, washing the aquarium and decor, care of aquatic plants, which consists in cutting off dead parts.
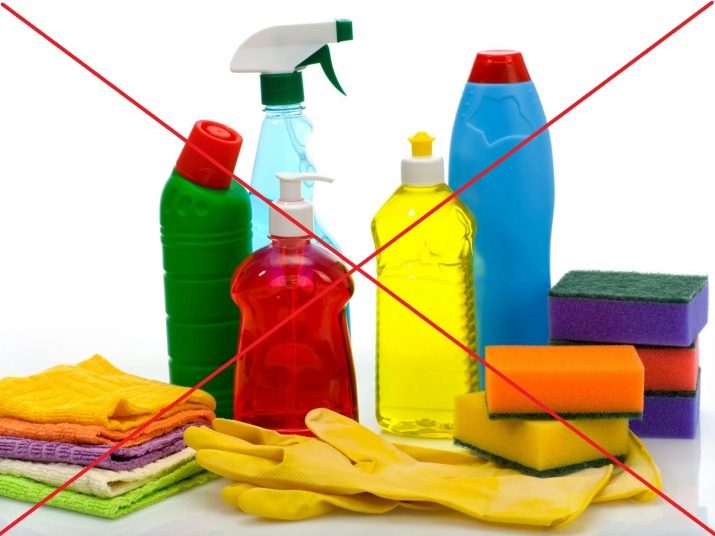
When washing containers, do not use soap or any cleaning agents. Their residues can dissolve in water and lead to chemical poisoning of fish.

Possible problems
When breeding cockerels, some problems may arise, and this is primarily due to diseases.
One of the most common diseases is fin rot. The cause of its occurrence is a bacterium that occurs as a result of poor care (for example, dirty soil). The disease manifests itself as follows: the ends of the tail and fins darken, the fins lower, white spots appear on the body, the activity of the fish decreases.
When these signs appear, it is urgently necessary to clean the aquarium: elements of artificial decor need to be boiled, wash the container using a weak solution of bleach. Then the container is filled with clean water, to which the medicine (tetracycline, ampicillin) or any antifungal agent is added.
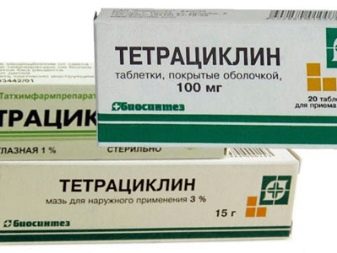
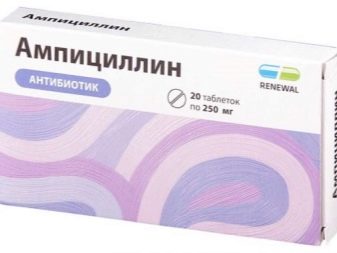
Water with the addition of a medicine must be changed after 3 days until the fish improves. Treatment can last a whole month. Upon completion, the container is processed by Betamaks to prevent the return of the disease.
Another common disease is velvet disease. With this disease, the fish scales are covered with a plaque of a red color, which is especially clearly visible in the light. The fins at the males can stick together, the fish rub against the glass of the aquarium, become apathetic, they lose their appetite.
BettaZing (3 drops per liter of water) is used for treatment.
To prevent the disease, it is recommended to add a special conditioner and salt for aquariums to the water.
Ichthyophthyroidism is accompanied by the appearance of white bulges on the body. The cause of the disease is ciliates-parasites. For treatment, sea or ordinary table salt is used, adding it to the water. In such water, parasites quickly die (about a day).
Sometimes males have changes in their behavior. The fish sink and lie at the bottom for a long time for these reasons:
- previous stress state;
- the temperature of the habitat is much less than +18 degrees;
- chemical poisoning.
The males swim for a very long time near the surface and try to jump out if the water contains a large amount of chlorine. This problem is solved simply: water must be heated to +90 degrees.

Breeding rules
Puberty in these fish occurs as early as 3-4 months of age. However, for breeding, it is desirable to select 6-8 month old individuals. The difference between the male and the female is well expressed: it is distinguished by a brighter color and long fins, as well as a more slender and larger body.
In females, the fin size is smaller, dark stripes are clearly visible on the body, and near the tail there is a spot of a white hue that appears at 3 months of age.
Breeding these fish at home requires the implementation of simple rules.

First of all, this is spawning equipment. A container of 3-4 l capacity is selected for it and filled with water about 15 cm. The soil is not laid at the bottom, but 1-2 live small-leaved plants are placed, a grotto or other shelter for the female is arranged, where she will hide from the male, since he often aggressive in the spawning period.
A also set diffuse backlight and aerator.
The water used is settled (3-4 days) and warm, approximately +28.30 degrees Celsius.
Before spawning, in about 10-14 days, future parents are transplanted into separate containers in order to prepare for breeding.
During the feeding of fish in their diet, the volume of live and frozen foods containing a large amount of protein is increased. This is necessary to prepare for spawning and the formation of caviar and milk.

Water during this period is slightly warmed up (about 2 degrees), and more often it is changed.
- First, one male is placed in the spawning ground. The male’s readiness for spawning is determined by his color, which becomes more intense, and also starts to produce a large number of bubbles. Here he creates a spawning nest, holding air bubbles and small parts of plants together with his saliva.
- The female is planted in the male after nest building. The time for spawning is coming. The cockerel begins to chase the female, and having overtaken and entwined it squeezes out eggs.
- Then the male picks up the falling caviar with his mouth and places them in the nest bubbles. This is repeated until the eggs are finished.
The end of the spawning is indicated by the fact that a cockerel floats above the nest, and the female swims into a shelter.
Upon completion of spawning, the female is returned to the usual aquarium. The cockerel remains in spawning and nurses the future fry.

Often during the incubation process, heavy eggs fall out of the nest. A cockerel picks them up and returns them to their place. So that at night the male does not sleep, but takes care of the calf, a lamp must be placed above the nest.
The incubation process lasts about two days, then larvae are hatched from eggs. For 3-4 days, their nutrition is carried out due to stocks of the yolk sac. Then, as soon as the bag completely disappears, the grown fry leave the nest and begin to search for food.
The time has come for the male to return to the regular aquarium. The fry should be fed with “live dust”, rubbed yolk, as well as artemia and small crustaceans (cyclops). Dry feed is not recommended because it negatively affects the development of fry.

For now, light aeration should be connected. By the age of one month, the development of the labyrinth organ is completed in the fry, and from then on, aeration must be stopped.
When the fry reach 3 months of age, they are sorted and planted in different containers so that large ones do not eat small ones.
The fry are sedimented when they begin to show aggression and attack each other.
From now on, they need care as adults.

Compatible with other fish
In a natural habitat, the males come into contact exclusively during spawning. The compatibility of these fish with their relatives in the conditions of keeping in the aquarium is subjective in nature. Their relationship is often affected by the temperament of the fish.
Often males cannot stand the neighborhood of not only another cockerel, but also females. However, individual females themselves constitute a threat to the unwanted male. Therefore, to maintain several males, large aquariums will be required, divided into several compartments.
By compatibility with fighting fish, other fish species are divided into three groups.
- Good compatibility. This group includes peace-loving small-sized fish: swordsmen and peaceful catfishes, Pecilia and thorns, mollies and rassal, as well as grunts and minors.
- Satisfactory compatibility with rare and light fights. This group includes such species: guppies and barbs, neons and cardinals, spotted gourami and labeos.
- Complete incompatibility with astronotuses and lineatuses, piranhas and Akars, parrots.



The males will gladly eat the shrimp living with them. Small snails are also the subject of their hunt.
It is recommended to populate the aquarium with different types of fish at the same time: this way they get along more quickly and reconcile with each other. It should also be noted that the cockerel, accustomed to its neighbors, can experience stress if they are seated.
Despite his fighting character, the cockerel fish can well decorate any aquarium and adjoin other fish representatives.
For tips on keeping males, see the next video.









