Aquariumism is a fairly popular hobby, and new people are constantly joining this hobby. They face a lot of problems and nuances. One of these problems is the compatibility of various fish species.


The principles of cohabitation
Types of aquarium fish can be combined according to a variety of selection criteria:
- territorial;
- format of the aquarium;
- decorative characteristics;
- requirements for a specific type of feed;
- size.
When the combination of species is finally selected, it is necessary to check once again what are their food needs, how to keep fish. After that, you will have to choose plants, focusing on the level of illumination in the pond. Biological types of aquariums are formed taking into account the common conditions of contents, nutritional characteristics, sizes of feed used. Geographical gradation began to be used only recently. The inhabitants of such aquariums (for example, "tropical forest") are guaranteed to get along with each other.


Nothing surprising: the mass of aquarium inhabitants in nature populates water bodies located in the middle of a dense forest. At the bottom of such lakes and rivers, calcium-free rocks are grouped. Because flowing and stagnant water is very soft. At the same time, a high concentration of tannins is maintained.
As a result, water has an acid reaction and reduces the risk of harmful bacteria.
In a "tropical" aquarium, it is necessary to create similar conditions. Mostly fish with bright colors are populated there. The decisive influence on whether different species are compatible, whether they can live with others or not, is exerted not by the geographical origin of a particular species, but by the unity of conditions in the natural environment. The aquarium for equatorial and subequatorial fish can have a variety of dimensions, the use of picture-type aquariums is allowed. In such vessels, aquatic plants must necessarily be present, growing in acidic water of low hardness and not requiring significant illumination.
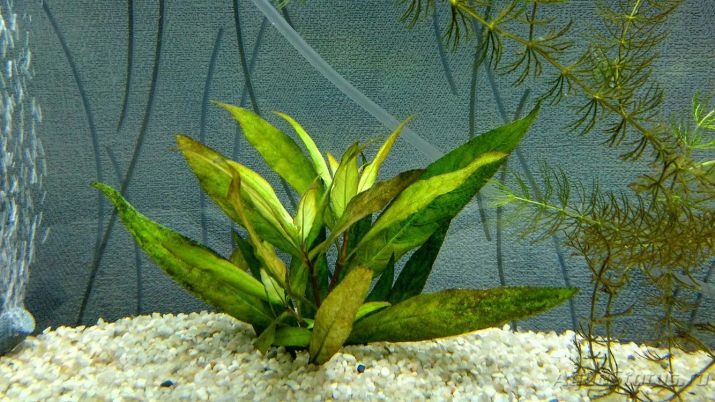

Good candidates would be:
- echinodorus;
- cryptocorin;
- apogonetone;
- hygrophil;
- ambulia;
- cabomba.
If the necessary conditions are the same, even fish and fauna from different continents can be raised in one vessel. Otherwise, an aquarium of "crystal clear lake" is arranged. It is brightly lit, and the water should contain many "hard" components, while an excessively high temperature is contraindicated. The optimal species in this case are North American perches and fish from the middle zone of Eurasia. Sometimes biological aquariums are created taking into account the affinity of species.
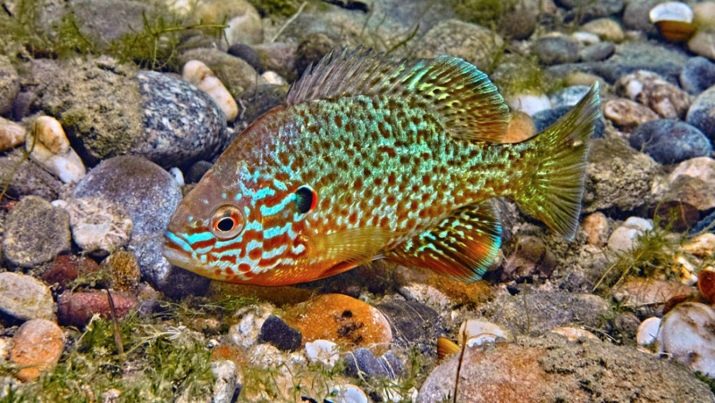

In this case, you can also add unrelated, but similar in terms of the existence of the breed. It is also necessary to think about the size of co-farmed fish. This is especially important when the size of the aquarium is relatively small. Not only the biological, but also the geographical principle of selection is possible. In this case, preference is given to individuals originating from a particular locality. There are geographical aquariums that almost coincide with popular biological species. So, in Southeast Asia you can see:
- glass perch;
- puntius;
- zebrafish
- parsing.
In North America":
- disk and diamond perch;
- ellasoma;
- rivulus;
- scalaria;
- catfish.


If you are collecting a purely domestic aquarium, then the choice is also very wide. In such cases, take:
- minnow;
- stickleback;
- crucian carp;
- freshwater needle;
- perch;
- loach;
- tench and so on.
In recent years, fish from the Amur and its basin have enjoyed considerable popularity. Many Russian species are even harder to contain than exotic types. Initially, you need to replace the water once a day. Representatives of aggressive breeds are advised to select smaller than calm fish.
Since aquatic plants of the middle strip have a pronounced seasonality, few year-round species will have to be selected.

Sometimes the excessive aggressiveness of some breeds makes it necessary to divide the livestock into 2-3 aquariums. Geographical and biological principles are mainly followed by experienced breeders. Beginning aquarists and simply seeking to decorate the premises give preference to the criterion of decorativeness. In this case, they try to do everything as naturally as possible. They prefer to use young individuals, and species diversity is minimized, since a large group of homogeneous fish looks better than a motley school.
Chasing a large number of fish should not be. This can ruin the impression. It will be more difficult to assess the individuality of each individual and the specific features of behavior. It is required to place in one vessel either fast-floating or slowly moving aquatic inhabitants. Size should also be more or less the same. And even if the decorative characteristics coincide, the content requirements cannot be ignored. It is important to consider the size of the artificial reservoir. In an aquarium of 100 liters you can plant:
- 45 guppies;
- 30 swordsmen;
- 10 Odessa barbuses;
- 10 cherry barbs;
- 20 zebrafish rerio or leopard;
- 7 gold or marble gourami;
- 32 cock Betta;
- 35 red or blue neons.



The larger the aquarium, the more stable the temperature in it and the easier it is to maintain water quality. Even with some kind of failure, you can not be afraid of special problems. To determine how many and what kind of fish can fit in an aquarium of a certain volume, you can make simple calculations. They come either from oxygen needs, or from the fact that 1 liter of water is required per 0.01 m of body length.Separate varieties have to be divided geographically, which forces to reduce the number of livestock.
If you plan to make large predatory fish, you need to choose an aquarium with a volume of 200 liters or more. With a capacity of 200 l, you can plant 4 scalaria and 2-4 ancistrus. You should first place a scalar there and only then conduct radical experiments. Another set provides:
- 10 rhodostomuses;
- 5 cardinals;
- 4 young ancistruses;
- 2 zebrafish;
- 1 sturisoma;
Individually matched number of young pecilli.



In an aquarium with a volume of 180 liters, you can plant:
- 10-20 reviews;
- 12-15 five-lane barbuses;
- 5-6 black barbs;
- 4-5 acanthophthalmus.
For an artificial reservoir of 30 l it is required to use:
- 5 barbuses;
- 3 catfish;
- 10 mossy barbs.
Or:
- 10 guppies;
- 4 zebrafish
- 3 catfish.


Detailed table
It is necessary to consider which fish will be compatible with which. Angelfish can be partially combined with loachweed, but categorically it is impossible to combine them with cockerels, discus, guppy, goldfish. Astronotuses will also turn out to be bad neighbors, unlike other representatives of the Pecilian family. In some cases, run into the aquarium rassbor, tetras, swordsmen, zebrafish, bots, iris.
Koi carps can be combined with other representatives of their family. A great combination would be goldfish. Koi carp tends to pursue all who are weaker than him. As is already known from the foregoing, loachweed can be combined with scalars. But they are also advised to keep corridors, zebrafish, labeos, and rainbows together with them. Koi carp should not see goldfish, cichlids and astronotuses around them. Mollinesia is recommended to be kept together with:
- botsiya and discus;
- parsing and zebrafish;
- corridor and tetra.



The already mentioned astronotuses do not get along well with cyprinids and large cichlids. But they will meet scalaria, guppies, zebrafish complacently and even affably. Plecostomus (one of the types of catfish) is compatible with other peaceful species. Their list includes Pecilia, Swordsmen, and iris. Irisbirds are also famous for their peaceful disposition and do not attack others, on the contrary, they themselves must be protected. And the males are clearly visible because of their lush, fan-like fins. They can be combined with:
- corridor;
- Pecilia
- plecostomus;
- the iris;
- swordsman;
- the ornatus.
| Name of fish | Compatible | Unacceptable |
| Antsistrus | Barbus, guppy, discus | Astronotus, piranha, trophy |
| Botsia | Barbus, guppy, molliesia | Veil and other small fish |
| Pecilia | Guppy, Angelfish | Swordfish, goldfish |
| Goldfish | With no one but his kind | Cichlids, astronotuses |
| Plecostomus | Any fish larger than themselves | Soms occupying the same ecological niche |
| South American Cichlids | With no one | Cockerels, gourami, eels |
| Labyrinth | Botsi, Danios, Swordsmen | Cockerels, gourami |
| Characine | Parsing, tetra, crabs | Cichlids |
| Somiki | Cockerels, Labeau, Tetra, Danio | There are no incompatible species |
| Cichlids | Zero compatibility | Absolute incompatibility |

How to combine incompatible?
Sometimes the question arises: is it possible to keep fish together in an aquarium if the tables show that they have poor compatibility? The reasons for such questions are manifold. Someone just likes completely different types. Someone wants to fill the aquarium, and it’s hard to find suitable individuals of the right size with optimal demands.
In this case, it is possible to conduct experiments with poorly compatible and even practically incompatible varieties.
However, some nuances will have to be taken into account. For example, behavioral incompatibility can somehow be overcome or mitigated, but biological contradictions are almost invincible. The aquarium in this case should be spacious. For different animals specific zones are distinguished, which are delimited by shelters, vegetation and various decorations. Fishes who prefer to populate the upper layer of water will feel better in dense thickets with snags and grottoes.

Since it was decided to combine the incongruous, it is necessary to check that there is enough food for each inhabitant. If, due to starvation, fish start fighting, nothing good can be expected. It is recommended to keep different species together from a very young age. Then they are better used to talking to each other. Of course, you will have to constantly work on a mixed aquarium, create shelter zones and change them, treat sick and wounded individuals, and update the dying livestock.
Common mistakes
It is categorically unacceptable to overload the aquarium even when combining friendly species. Pisces, like other animals, are entirely driven by instincts. And one of them is just the desire to fight for survival and control over a certain territory. With a shortage of space, fights will go "until the first death." You should take care of the compatibility of fish not only among themselves, but also with aquarium plants.
It is extremely dangerous to keep in one place species that are twice or more different in size. In such a situation, even usually peaceful individuals can show gastronomic interest in weak neighbors. At the time of spawning, everyone is moved to a separate place where predators will not get to either the pets themselves or their eggs. To eliminate problems, you will also need to systematically replace the water and clean up the aquarium. When "herbivores" are taken, one will either have to breed duckweed or plant aquatic plants additionally.

But there is one more nuance that must be remembered in any case. It is believed that individuals from the same family and order, approximately the same in size, just get along with each other. This is usually the case. However, there is one important exception to this rule.
Guppies and swordsmen belonging to the same family of viviparous and having approximately equal length and width, as well as living in the same conditions, will inevitably conflict.
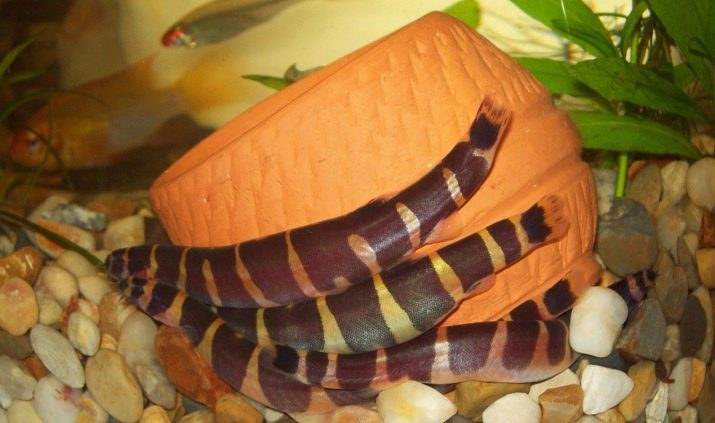
People who start them will also encounter such an unpleasant thing as intraspecific aggression. It is also impossible to keep fish without taking into account their soil requirements. Aquantophthalmus definitely needs the ability to dig into the ground. They are supposed to provide a substrate - sand or pebbles of small section. If you use large pebbles or dense soil, the fish will still try to dig up the ground and may be seriously injured.

A common mistake is trusting sellers' recommendations. They are primarily interested in selling goods in maximum quantities. It is very important to study in advance the maximum information about the necessary fish from independent sources. It is necessary to pay attention not only to the behavioral properties of individuals, but also to growing conditions. There are times when a cold-water species is psychologically combined with warm-water individuals.
However, in this case it is not too right to be touched by fish peacefully swimming nearby. An unjustified acceleration of physiological processes will certainly make itself felt. It will be expressed in shortening the life span, which is already small, even under excellent conditions in other respects. If the fish is designed for content in soft water, it will still somehow survive in a harsh environment, however, reproduction will be in question. The price of such a “mistake” is also expressed in the need to spend a lot of money on the constant purchase of drugs or the use of mitigating reverse osmosis plants.

Oddly enough, many people do not pay enough attention to the compatibility of fish in nutrition. If the animal eats plant foods by default, it will not refuse both bloodworms and other insects. But then digestive upsets can soon be expected. Even representatives of the same families, for example, cichlids, can be divided into carnivorous and herbivorous species. Therefore, keeping them in one aquarium is not too reasonable.
For more information on the compatibility of aquarium fish, see the next video.










