The aquarium, like any other farm, can remain both in a well-groomed and in a state of neglect. A regular problem for beginners (and a periodic one for experienced aquarists) is algae, which can not carry any payload, being ordinary weeds.
If the presence of such is insignificant, there is no problem, because the ecosystem is in an established state, but rapid growth is extremely undesirable - it spoils the appearance of the aquarium, tightening its walls with green mud, and takes away nutrients from other plants and fish, directing the development of a home reservoir in a completely wrong way.

Reasons for the appearance
The fact that foreign algae appeared in the aquarium already indicates that something went wrong. If you are simply struggling with the result, but not eliminating the cause - do not be surprised that weeds appear again and again. Therefore, the first action in an effective fight against the enemy is to understand where the problem came from, and what led to its occurrence.
- Impaired biobalance. Algae appear only where they have something to eat. The breeding ground for them is dead organics, which include rotting grass, waste products from the inhabitants of the aquarium and excess feed. On such fertile soil, weeds can grow and flourish, and it is formed if the owner ignores timely harvesting, gives excessively much food, or puts too many pets in a cramped space.
- Imbalance of fertilizers. Phosphorus and nitrates are important for the growth of both beneficial aquarium plants and weeds. Interestingly, the problem is both the excess and the lack of these substances: in the first case, the higher flora does not cope with the assimilation of everything, and the excess that the algae needs is formed, in the second, the useful plants weaken due to lack of nutrients and cannot compete with them adequately uninvited guests.
- Lighting imbalance. In this case, the situation is quite similar to that described in the previous paragraph. If there is too much light, it can be enough for undesirable flora, while useful plants can suffer from its excess. With its deficiency, important greens are getting weaker, but weeds do not always need so much lighting.
- “Wrong” lamp. Light should not just be enough and not too much - it should have the right spectrum. Useful plants often grow at depths where direct sunlight does not penetrate, because they are sharpened for photosynthesis under the influence of blue and red spectra. Weeds massively grow in shallow water off the coast, so they like direct sunlight and incandescent lamps very similar to the sun, and it is precisely such lighting that is often used by beginners.

Varieties
To effectively fight the enemy, you need to know him by sight, because there are about 30 thousand species of weeds and not all of them are afraid of the same methods. The general classification of algae is quite simple - they are distinguished by shade. As a rule, lower plants of the same group can be fought in similar ways.
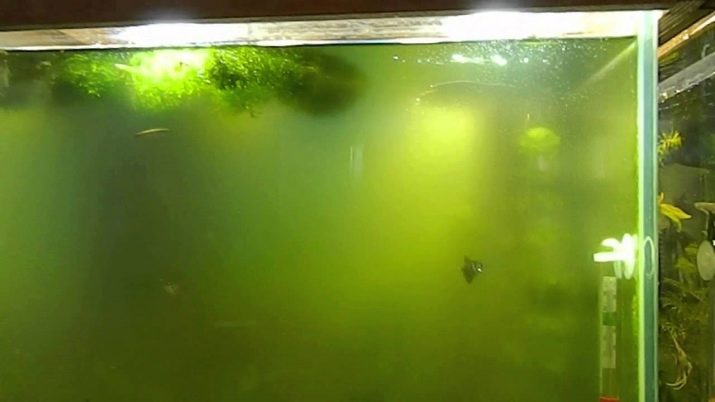
Brown algae are also known as diatoms. They are relatively small, because you see them as a strange plaque, the color corresponding to the name, on the walls of the aquarium, as well as on plants and soil. Such "guests" are typical for beginner aquariums, which so far have not been able to provide an established biobalance or incorrectly estimated the required amount of light, "greedy". If the water is also hard and alkaline (pH above 7.5), then the conditions for the appearance of such a pest are ideal. The appearance of plaque must be wiped off immediately, because, having grown, it will become a big problem.
To defeat an opponent, you need to improve lighting by replacing a light bulb or adding another one.


Bagryanka is also called red or black algae, and their real color can be not only reddish, but also purple or gray. It is easier to identify them, since these are specific-shaped bundles of small height, and not some abstract plaque.
Such weeds are unpretentious in the sense that they grow on any surface and for them there is no difference - Salt water or fresh, although it is especially comfortable for them to live in a harsh liquid and with powerful currents. This is a very harmful and difficult to eliminate enemy - it will be necessary to treat the infection by special means based on glutaraldehyde, and you still can not do without a weekly refreshment of water and diligent cleaning.


Examples of black algae are “Vietnamese” (aka “deer horns”) and “black beard”, which are often confused by beginners, because they look pretty similar - both resemble bunches of dark hair.
The methods of dealing with them are approximately the same - often enough to share natural enemies and competitors in the form of certain types of fish, snails or plants.


Green algae includes 20 thousand plant species, from simple to multicellular, but one of the most typical aquarium weeds can be considered xenococus. Such a weed looks like small green dots on the glass, which, when ignored, gradually grow to a level of plaque. Its typical habitat is the bottom too densely planted with grass and not completely filled containers. To face such an enemy, you need excessive light and a small amount of carbon dioxide, respectively, the fight against him involves the creation of opposite conditions.

Euglena Algae look like blooming water, they are a reaction to conditions such as the abundance of yellow light and heating above 27 degrees, and the significant presence of fertilizers in the form of nitrates and phosphates further contributes to the reproduction of euglena.
Again, the best method of struggle is to destroy the idyll without creating such conditions.

Filamentous algae look like long threads intertwined with each other. They are typical of artificial ponds where there is an excess of iron and an insufficient amount of phosphorus, however, it is quite easy to deal with such a weed due to the fact that it can simply be pulled out. Of the representatives of nitrous, the following are most known:
- rizoklonium - green color “Vata”, growing against the background of disturbed nitrogen balance, disappears by itself as soon as the bio-balance is aligned;
- spirogyra is slippery and easy to tear, and it grows very quickly, so just pulling it out will not work - you need to reduce the amount of light, start fish that feed on algae, and add "chemistry";
- kladofora - breeds in poorly filtered water in the absence of currents and a small amount of carbon dioxide, so the best way to remove it is to revive the created swamp.



Finally, the last variety is blue green weed algae, which as a habitat usually choose the tops of useful plants. Such a weed is toxic cyanobacteria, which are very harmful to the higher flora of the aquarium.
Typical conditions for their appearance are excessive ammonia and a small amount of nitrates, which does not allow the "horse" to lose the "rider".

Methods of struggle
There are many ways to get rid of algae - it all depends on which opponent you got and how effective the previous steps were. To begin with, it is worth fighting the enemies mechanically, removing weeds manually. Collect large fragments with your hands, and then carefully wipe the glass and siphon the bottom.
Inexperienced beginners often forget to process the decorations, and there are many gaps where the infection can hide, therefore they need to be washed especially carefully. In the end, it is worth partially replacing water to refresh a stagnant atmosphere - in some cases even the methods described will suffice.
In most cases it will be wrong to limit oneself only to what has been said above - even if you defeat the weeds at a particular moment, they will grow again if the circumstance conducive to their growth is not eliminated.
In addition, one cleaning is far from always so diligent as to completely etch the algae, so you need to make sure that the lower flora is no longer so comfortable.

To do this, the following actions are taken.
- Less light. Spirogyra, blue-green cyanobacteria, xenococus and euglena often grow where the lighting is too bright or long. Take away the most important from them, not including lighting for a couple of days, and even covering the aquarium with a dense cloth. Photophilous inhabitants of the reservoir at this time will have to be resettled.
When the effect is achieved, clean the aquarium - remove the remains of extinct weeds and perform a moisture change. To consolidate the result, run into the reservoir of natural enemies of these algae.
- Create healthy competition. Algae are harmful and it’s hard for a person to fight, but you can plant plants in the aquarium that will displace weeds, and then they can be easily resettled by yourself. Herbs are usually used as such a higher flora: kabombu and elodea, hornwort and naias, lemongrass and hygrophiles. The method is suitable for attacking red and green algae.
- Turn the enemy into food. Algae interferes with the normal development of many species of plants and fish, polluting the water area, but for some they themselves may turn out to be tasty and healthy food. So, the Siamese algae eater feeds on xenococcus, filament and diatoms, and on a starvation ration it also eats “black beard” and “Vietnamese”.Against the latter two, the Malawian cichlid is also useful, however, having carried away, it is also able to gobble up something useful.
In the battle with green and brown algae, catfish are good, but they will not give up lemongrass, which seems to be considered an ally. Many snails feed on filament and brown algae - ampullarium is especially often used for their destruction, filament can also eat Amano shrimp. Swordfish, guppies and other live-bearing fish effectively counteract brown and green weeds.
- Align the balance of nutrients. Many weeds grow simply because there is too much useful in the water to not use it. Reduce the amount of introduced substances, a little more often perform a water change and plant a fast-growing higher flora - it will take away from the weeds and prevent them from multiplying.



Used tools
"Chemistry" is used against weeds only if the above methods do not help. It is worth resorting to chemicals only in a critical situation, since there is a great risk of even more unbalancing the disturbed bio-balance and creating much more serious problems than before.
If you already take up such methods, be extremely scrupulous - study in detail the methods of using the selected product and adhere to the dosage, which is indicated on the packaging or in another reputable source. It’s best to use special tools such as Erythromycin - they are sold in pet stores, created specifically to solve such problems and have a clearly defined method of use.
On the Internet you can find ways to deal with algae, even with the help of whiteness or hydrogen peroxide.
Although this sometimes works, it is best not to experiment if you are unsure of the dosage.
- Carbon dioxide. It is not always necessary to buy a special drug - many types of algae feel comfortable with a lack of carbon dioxide, which means that they need to be intensely pumped with water. This step is especially effective in combination with good lighting. To increase the gas level, special devices are used that can be purchased at the pet store. Remember that even useful living creatures do not like a sharp change in living conditions, so proceed smoothly.
- Hydrogen peroxide. A method from the “cheap and cheerful” category that requires great care from the experimenter. “Vietnamese”, “black beard”, euglena and cyanobacteria will come to an end if you carefully apply the drug pointwise to those places where there are especially many algae, but be modest in dosage - 2.5 ml per 10 l of water will be enough! It will become harder for the fish to breathe, so intensify the aeration, and if you see that this does not help, immediately change the water. To combat the infection on the leaves of the plant, you will have to soak them in a separate bowl, increasing the dosage to 4 ml per 10 liters of water, after which at least 1/5 of the moisture should be replaced.
- Chlorine. This is exactly the method in which whiteness is used, but it is largely experimental - the effect of gas can be negative not only for weeds, but also for beneficial inhabitants of the aquarium. One part of chlorine is dissolved in 30-40 parts of water, after which a twig of one of the aquarium plants, on which there is algae, is dipped into it. Follow the reaction - if a useful plant turns white, then the solution is too caustic and needs to be diluted with water, if green remains green, then you can slowly pour the finished product into a pond.
You will have only one chance to treat the ecosystem with this remedy, since a second procedure is not allowed. During treatment, ensure maximum aeration, timely change the water and do not forget to clean the aquarium of dead algae.
- Glutaraldehyde. This is the active substance, on the basis of which many drugs are produced, aimed at combating red and green algae, as well as thread.Solutions of such drugs are good because they are harmless to many species of higher flora, and therefore can be used even in herbalists. The concentration of the substance should not exceed 12 ml per 100 liters of water, and the drug should be added daily in the morning for 7 days.

Prevention
Instead of struggling with the problem, try to make it so that it does not have a chance of appearing initially. To do this, follow the simplest rules that every self-respecting aquarist should know:
- do not chase artificial vegetation - give a chance to the real plantings that will supplant weeds;
- ask more experienced colleagues how much fertilizer should be applied so that there is no oversupply, and also remember that with a small number of plants and low light, they are not needed at all in the aquarium;
- the rapid growth of weeds is already a problem, so do not wait, but act immediately;
- the aquarium equipment should work almost always, do not disconnect or remove it for a long time;
- lighting is required no more than 8-10 hours a day, the rest is surplus;
- fluorescent lamps give more and more yellow light over time, favorable for weeds, therefore they need to be changed annually;
- before planting a couple of minutes, treat healthy plants with hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate or chlorine, so as not to introduce weeds into the ecosystem;
- try not to treat the fish in the general aquarium, and if you do this, intensify aeration and change the water more often;
- hold on to a pet who loves to feast on algae;
- Do not ignore diligent weekly cleaning;
- strictly dose the food and reduce its amount if you see that pets do not eat everything;
- Do not exceed the permissible population density of the reservoir.
Algae Control Tips see below.










