Nitchatka is an aquarium algae that is famous for its tremendous thirst for life. She seeks to conquer all the available space of the aquarium, and very soon through the thick threads it becomes impossible to make out the aquarium inhabitants. Some fish like to feast on thread, but still this plant does much more harm than good. It is important to get rid of it in time, and to do this is not so simple.

Description
First, the aquarist notices unusual threads that grow out of the ground and stretch upward. At the roots, you can see untidy fluff covering the soil in layers. After a short time, these threads grow so that all the rest of the vegetation is captured by this phenomenon and is covered with unpleasant mold. This is thread.
By this name we mean several varieties of algae, the differences between which can only be seen under a microscope.
Nevertheless, it is very important to determine the type of plant, as this will determine the cause of its appearance and avoid mistakes in the future.
There are several varieties.

Edogonium
The most frequent unwanted guest in home aquariums. At first it resembles a light edge on the vegetation, and later green threads stretch from it. Typically, the reason for the appearance of this species is considered a nutrient deficiency in water and substrate.

Spirogyra
It looks like an unattractive green mucus, the scale of which is increasing every day.

Rizoklonium
Usually occurs in new aquariums where the microclimate has not yet been formed. This species feels comfortable with elevated ammonium levels and low nitrite levels.Once the biological balance has settled, the plant will disappear.
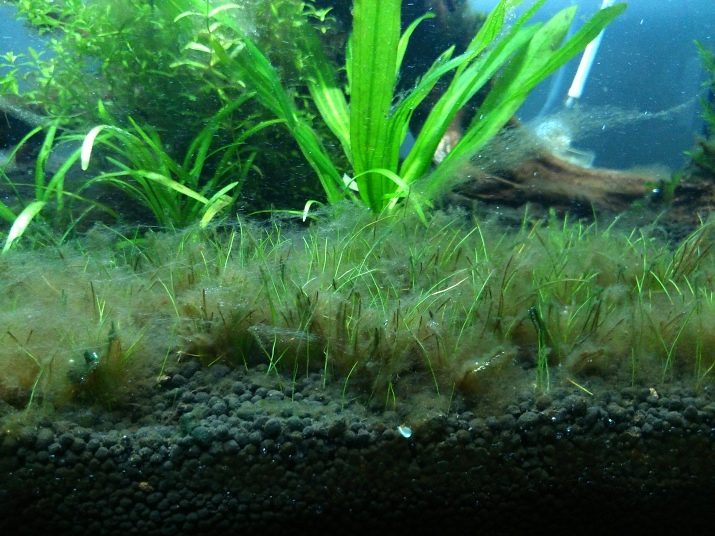

To the touch, these algae are mucus, unpleasant, when removed from the water, they hang. In an aquarium, this plant is dangerous in that it leads to the death of other vegetation. Threads surround the stems and leaves of green neighbors, to which the light ceases to flow, respectively, development stops and the plant dies.
Another problem arises with the death of the thread.
In this case, a lot of toxic substances enter the water from its rotten particles, the amount of which only increases and eventually becomes detrimental to aquarium fish.
There are cases when small fish or fry entangled in dense filamentous thickets and died. In addition, threading significantly changes the aesthetic appearance of the aquarium, under its influence, the water seems cloudy, groomed, the competence of the aquarist is in doubt. The only advantage of this plant can be considered the fact that its appearance indicates favorable conditions for the development of plants in the aquarium.
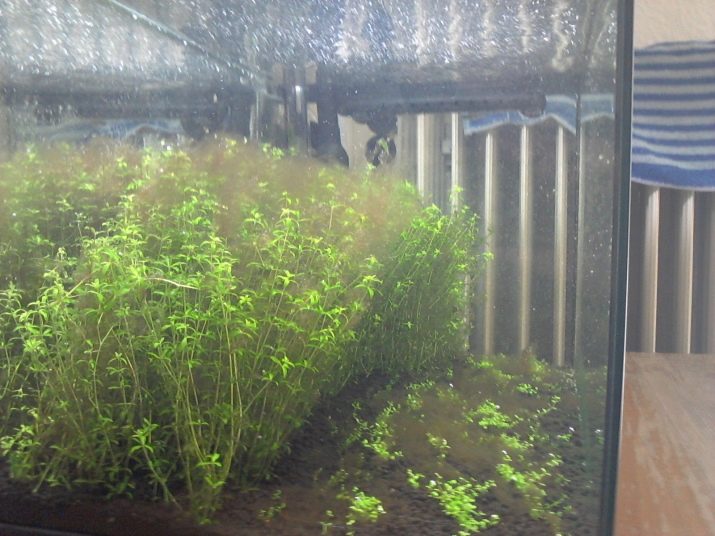

Reasons for the appearance
Before embarking on methods of dealing with such a misfortune as thread, it is important to find out the cause of its appearance. The following factors can affect its occurrence:
- powerful lighting - this aquarium offender loves natural or artificial light, and the more it is, the more comfortable the filamentous algae feel; often the phenomenon is observed in aquariums, where the light turns on for more than 8 hours a day;
- oxygen deficiency - this is possible if you refuse to use the aeration system;
- small vegetation in the aquarium - if there are few other plants planted, then the thread begins to be enriched with useful components contained in the soil, which should be aimed at the development of other aquarium crops;
- rare change of water - dirty water contains a high percentage of nitrates, which are necessary for the growth of nitrate;
- transfer with other plants - the thread can "move" to the home aquarium, catching on the stems of another plant that was bought for planting in an artificial pond.


How to fight?
To get rid of filamentous algae, first of all, it is important to establish high-quality filter operation and reduce the intensity of lighting devices. Replace the blue light with a weaker one. With a clogged filter, ammonia builds up in the water, which is favorable for the development of nitrate, so start cleaning the filter more often than before. Plant more plants in the aquarium, floating ones and those that are developing rapidly are suitable. New algae will begin to absorb nutrients, taking them away from the fiber, which, in turn, will slow down the growth rate.

Watch the level of iron in the water. Its permissible concentration is 0.2 mg / l. If spirogyra has settled in the aquarium, remove it manually.
Sometimes this becomes the only effective measure to combat threadlike thickets. After seeing the characteristic threads on the plants, rinse the algae and remove the first signs of emerging thread. In order for this unpleasant vegetation to quickly die out, darken the aquarium for three days during the cleaning period.
Another method of struggle is the use of hydrogen peroxide, which threadlock does not like so much. Aquarists use the drug in proportions of 6-10 mg per liter of water.
You can deal with this phenomenon in a natural way, for example, by hooking up inhabitants who like to feast on green threads.
These include cyprinids, Pecilia, Jordanella, catfish, gastromysones. Turn on oxygen only during the day, and turn off the compressor at night.


Preventive measures
It is always easier to prevent the appearance of thread than to overcome its dense thickets. To prevent this harmful phenomenon, use the recommendations of experienced aquarists.
- Before starting a new plant in the aquarium, carefully inspect it for the presence of an extraneous cannon or threads, rinse it thoroughly, removing any suspicious particles. This measure will avoid the transfer of nitrate on the plant.
- Monitor the cleanliness of the water in the aquarium, make a weekly change 1/3 of the volume of water, fill in with fresh water that has settled for a day. Dirty water contains decay products and nitrates, which have a beneficial effect on the development of nitrate.
- Do not place the aquarium in a sunny place. The most unfortunate part for him is the window. Control artificial lighting, turn on lighting for no more than 12 hours a day - this time is enough for a comfortable existence of fish and plants, but the thread will slow down its uncontrolled growth when the lighting time decreases.
- Plant as many plants as possible in the aquarium. The path they absorb from the soil all the nutrients, not giving way to the thread, and inhibit its development. For this purpose, the simplest inexpensive crops are suitable, but most often aquarists advise using a hornwort. If plants are planted in an aquarium with cichlids, this does not always lead to a successful result, since these fish love to dig in the ground, and the vegetation does not take root. In this case, choose plants with a powerful root system.
- Feed your aquarium pets dosed. Remove fragments of undigested feed from the aquarium. The food remaining at the bottom begins to be processed by bacteria, due to which a favorable environment for reproduction of nitrate comes in the tank.
- When starting a new aquarium, turn on the lighting only for 4 hours a day in the first three days, every day increase the daylight hours by one hour. Do not add fertilizer to the new aquarium.
How to remove thread in an aquarium, see further.










